Associative Transformer Is A Sparse Representation Learner
Paper and Code
Sep 22, 2023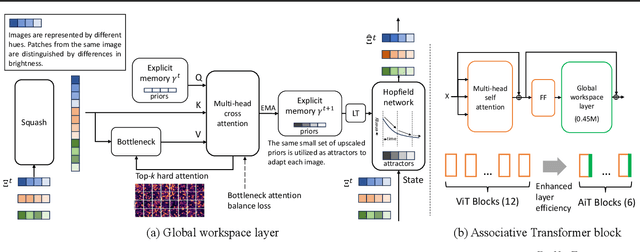
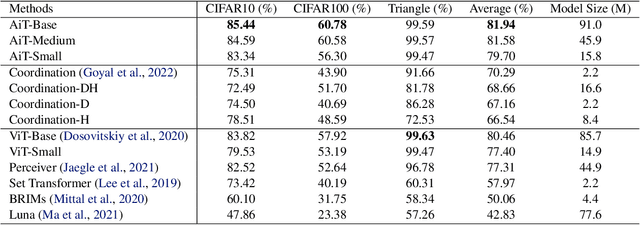
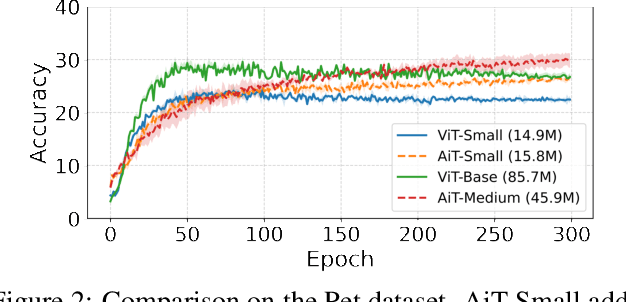
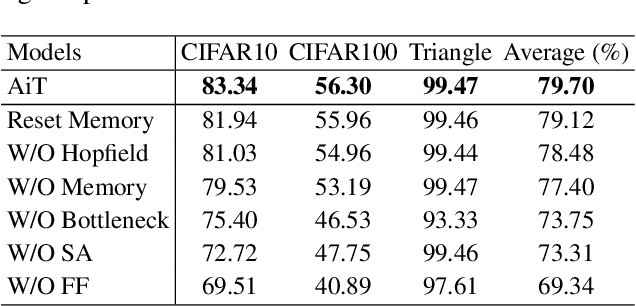
Emerging from the monolithic pairwise attention mechanism in conventional Transformer models, there is a growing interest in leveraging sparse interactions that align more closely with biological principles. Approaches including the Set Transformer and the Perceiver employ cross-attention consolidated with a latent space that forms an attention bottleneck with limited capacity. Building upon recent neuroscience studies of Global Workspace Theory and associative memory, we propose the Associative Transformer (AiT). AiT induces low-rank explicit memory that serves as both priors to guide bottleneck attention in the shared workspace and attractors within associative memory of a Hopfield network. Through joint end-to-end training, these priors naturally develop module specialization, each contributing a distinct inductive bias to form attention bottlenecks. A bottleneck can foster competition among inputs for writing information into the memory. We show that AiT is a sparse representation learner, learning distinct priors through the bottlenecks that are complexity-invariant to input quantities and dimensions. AiT demonstrates its superiority over methods such as the Set Transformer, Vision Transformer, and Coordination in various vision tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge