Arbitrary Reduction of MRI Inter-slice Spacing Using Hierarchical Feature Conditional Diffusion
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2023
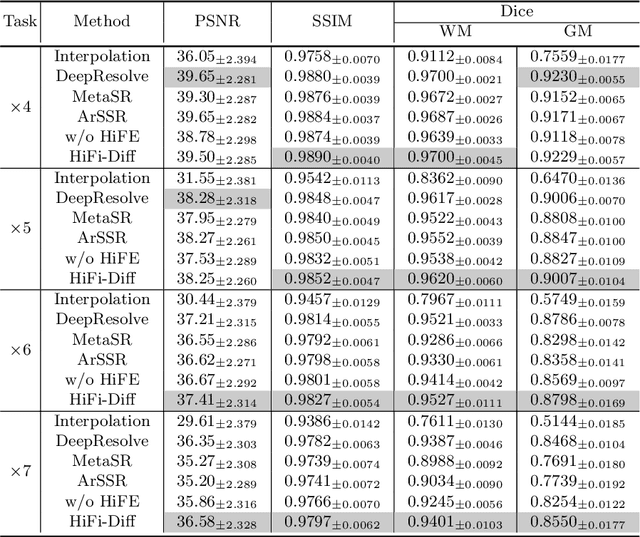


Magnetic resonance (MR) images collected in 2D scanning protocols typically have large inter-slice spacing, resulting in high in-plane resolution but reduced through-plane resolution. Super-resolution techniques can reduce the inter-slice spacing of 2D scanned MR images, facilitating the downstream visual experience and computer-aided diagnosis. However, most existing super-resolution methods are trained at a fixed scaling ratio, which is inconvenient in clinical settings where MR scanning may have varying inter-slice spacings. To solve this issue, we propose Hierarchical Feature Conditional Diffusion (HiFi-Diff)} for arbitrary reduction of MR inter-slice spacing. Given two adjacent MR slices and the relative positional offset, HiFi-Diff can iteratively convert a Gaussian noise map into any desired in-between MR slice. Furthermore, to enable fine-grained conditioning, the Hierarchical Feature Extraction (HiFE) module is proposed to hierarchically extract conditional features and conduct element-wise modulation. Our experimental results on the publicly available HCP-1200 dataset demonstrate the high-fidelity super-resolution capability of HiFi-Diff and its efficacy in enhancing downstream segmentation performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge