Appearance-Based Landmark Selection for Efficient Long-Term Visual Localization
Paper and Code
Aug 08, 2018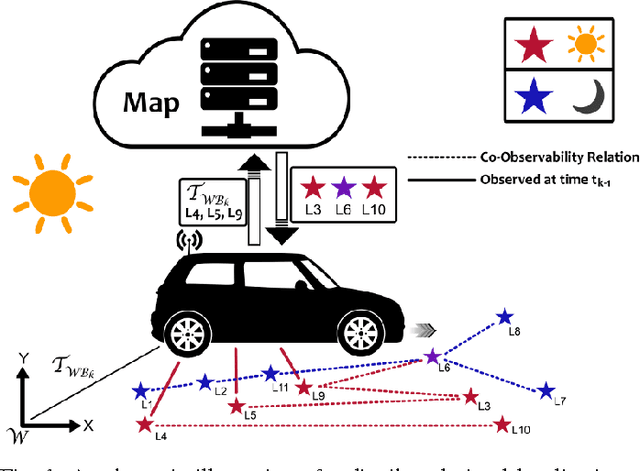
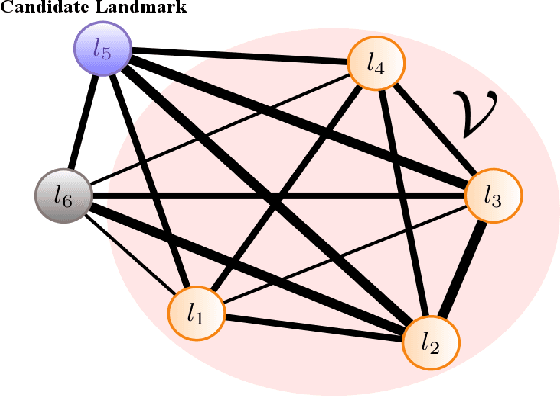


We present an online landmark selection method for distributed long-term visual localization systems in bandwidth-constrained environments. Sharing a common map for online localization provides a fleet of au- tonomous vehicles with the possibility to maintain and access a consistent map source, and therefore reduce redundancy while increasing efficiency. However, connectivity over a mobile network imposes strict bandwidth constraints and thus the need to minimize the amount of exchanged data. The wide range of varying appearance conditions encountered during long-term visual localization offers the potential to reduce data usage by extracting only those visual cues which are relevant at the given time. Motivated by this, we propose an unsupervised method of adaptively selecting landmarks according to how likely these landmarks are to be observable under the prevailing appear- ance condition. The ranking function this selection is based upon exploits landmark co-observability statistics collected in past traversals through the mapped area. Evaluation is per- formed over different outdoor environments, large time-scales and varying appearance conditions, including the extreme tran- sition from day-time to night-time, demonstrating that with our appearance-dependent selection method, we can significantly reduce the amount of landmarks used for localization while maintaining or even improving the localization performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge