Analyzing COVID-19 on Online Social Media: Trends, Sentiments and Emotions
Paper and Code
Jun 05, 2020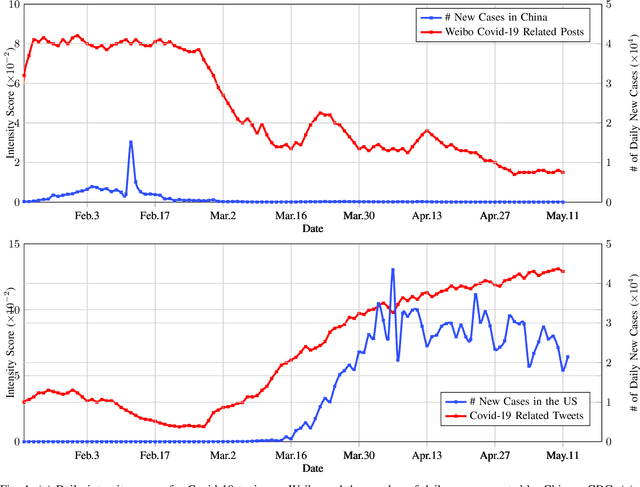
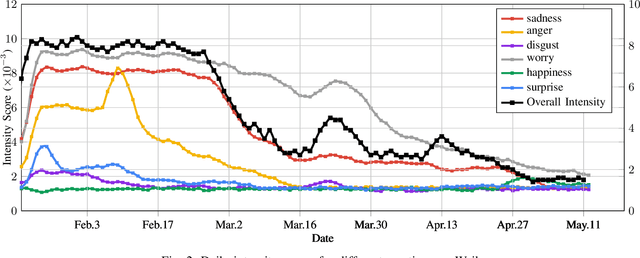

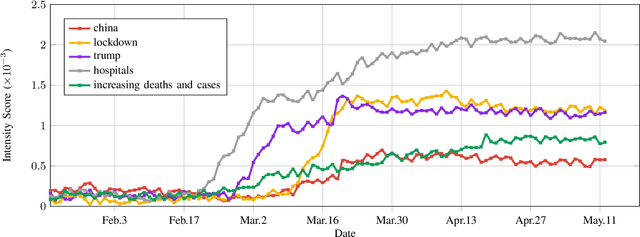
At the time of writing, the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has caused severe impacts on society, economy and people's daily lives. People constantly express their opinions on various aspects of the pandemic on social media, making user-generated content an important source for understanding public emotions and concerns. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive analysis on the affective trajectories of the American people and the Chinese people based on Twitter and Weibo posts between January 20th, 2020 and May 11th 2020. Specifically, by identifying people's sentiments, emotions (i.e., anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, surprise) and the emotional triggers (e.g., what a user is angry/sad about) we are able to depict the dynamics of public affect in the time of COVID-19. By contrasting two very different countries, China and the Unites States, we reveal sharp differences in people's views on COVID-19 in different cultures. Our study provides a computational approach to unveiling public emotions and concerns on the pandemic in real-time, which would potentially help policy-makers better understand people's need and thus make optimal policy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge