An Empirical Exploration of Cross-domain Alignment between Language and Electroencephalogram
Paper and Code
Aug 21, 2022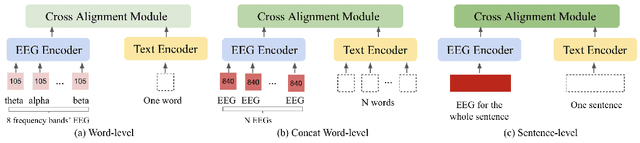
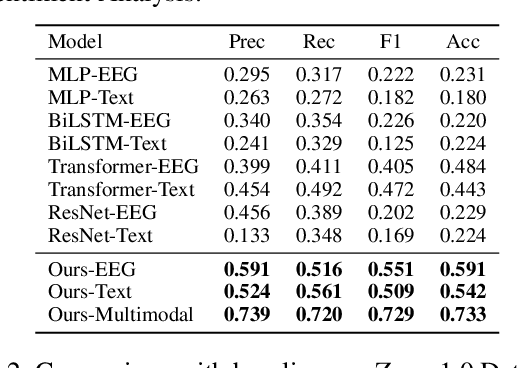
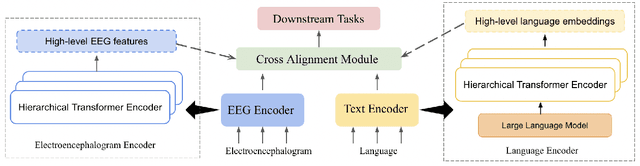
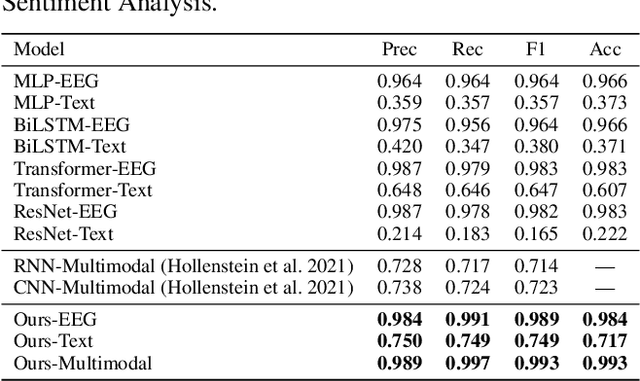
Electroencephalography (EEG) and language have been widely explored independently for many downstream tasks (e.g., sentiment analysis, relation detection, etc.). Multimodal approaches that study both domains have not been well explored, even though in recent years, multimodal learning has been seen to be more powerful than its unimodal counterparts. In this study, we want to explore the relationship and dependency between EEG and language, i.e., how one domain reflects and represents the other. To study the relationship at the representation level, we introduced MTAM, a MultimodalTransformer Alignment Model, to observe coordinated representations between the two modalities, and thus employ the transformed representations for downstream applications. We used various relationship alignment-seeking techniques, such as Canonical Correlation Analysis and Wasserstein Distance, as loss functions to transfigure low-level language and EEG features to high-level transformed features. On downstream applications, sentiment analysis and relation detection, we achieved new state-of-the-art results on two datasets, ZuCo and K-EmoCon. Our method achieved an F1-score improvement of 16.5% on sentiment analysis for K-EmoCon, 27% on sentiment analysis of ZuCo, and 31.1% on relation detection of ZuCo. In addition, we provide interpretations of the performance improvement by: (1) visualizing the original feature distribution and the transformed feature distribution, showing the effectiveness of the alignment module for discovering and encoding the relationship between EEG and language; (2) visualizing word-level and sentence-level EEG-language alignment weights, showing the influence of different language semantics as well as EEG frequency features; and (3) visualizing brain topographical maps to provide an intuitive demonstration of the connectivity of EEG and language response in the brain regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge