An Analysis of Linear Complexity Attention Substitutes with BEST-RQ
Paper and Code
Sep 04, 2024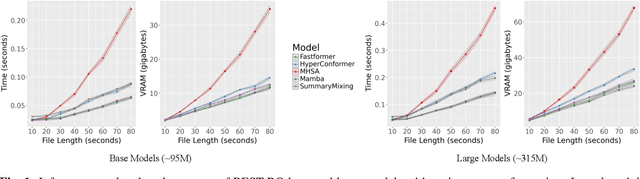
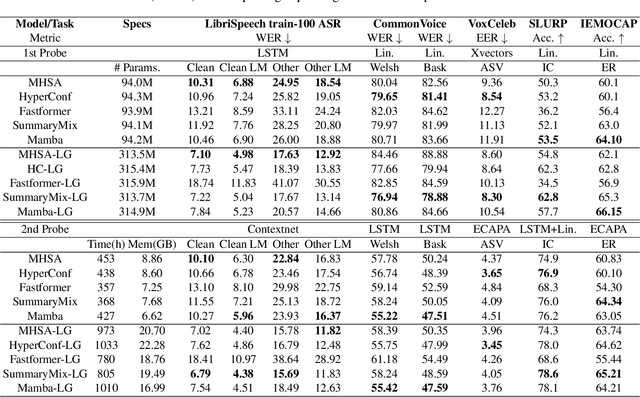
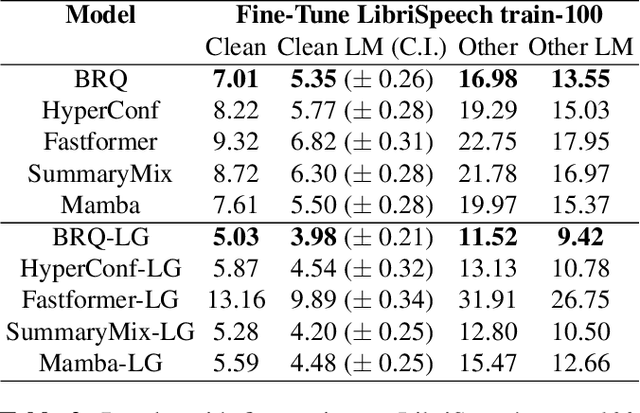
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has proven to be effective in various domains, including speech processing. However, SSL is computationally and memory expensive. This is in part due the quadratic complexity of multi-head self-attention (MHSA). Alternatives for MHSA have been proposed and used in the speech domain, but have yet to be investigated properly in an SSL setting. In this work, we study the effects of replacing MHSA with recent state-of-the-art alternatives that have linear complexity, namely, HyperMixing, Fastformer, SummaryMixing, and Mamba. We evaluate these methods by looking at the speed, the amount of VRAM consumed, and the performance on the SSL MP3S benchmark. Results show that these linear alternatives maintain competitive performance compared to MHSA while, on average, decreasing VRAM consumption by around 20% to 60% and increasing speed from 7% to 65% for input sequences ranging from 20 to 80 seconds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge