Adversarially Robust Stability Certificates can be Sample-Efficient
Paper and Code
Dec 20, 2021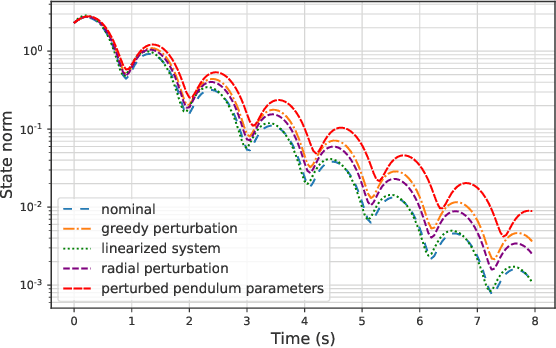
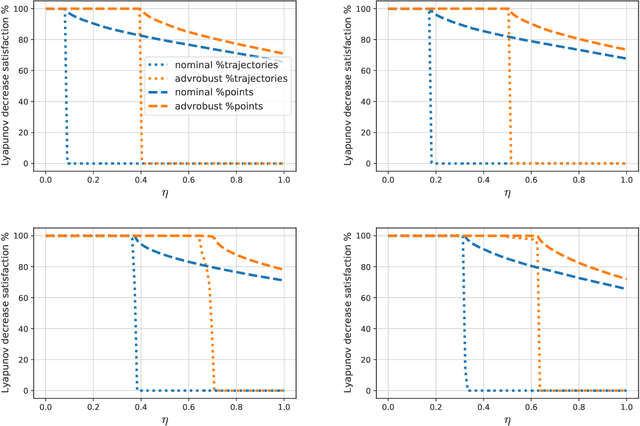
Motivated by bridging the simulation to reality gap in the context of safety-critical systems, we consider learning adversarially robust stability certificates for unknown nonlinear dynamical systems. In line with approaches from robust control, we consider additive and Lipschitz bounded adversaries that perturb the system dynamics. We show that under suitable assumptions of incremental stability on the underlying system, the statistical cost of learning an adversarial stability certificate is equivalent, up to constant factors, to that of learning a nominal stability certificate. Our results hinge on novel bounds for the Rademacher complexity of the resulting adversarial loss class, which may be of independent interest. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first characterization of sample-complexity bounds when performing adversarial learning over data generated by a dynamical system. We further provide a practical algorithm for approximating the adversarial training algorithm, and validate our findings on a damped pendulum example.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge