Adversarial Data Poisoning for Fake News Detection: How to Make a Model Misclassify a Target News without Modifying It
Paper and Code
Jan 04, 2024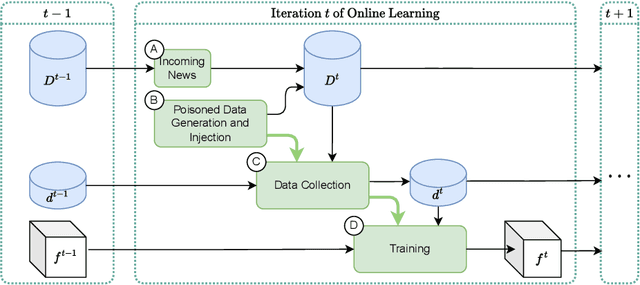
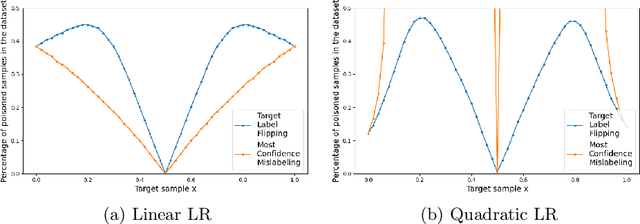
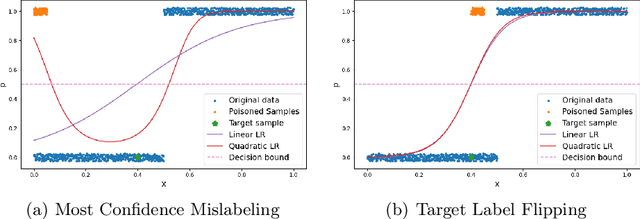
Fake news detection models are critical to countering disinformation but can be manipulated through adversarial attacks. In this position paper, we analyze how an attacker can compromise the performance of an online learning detector on specific news content without being able to manipulate the original target news. In some contexts, such as social networks, where the attacker cannot exert complete control over all the information, this scenario can indeed be quite plausible. Therefore, we show how an attacker could potentially introduce poisoning data into the training data to manipulate the behavior of an online learning method. Our initial findings reveal varying susceptibility of logistic regression models based on complexity and attack type.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge