A Unified MRC Framework for Named Entity Recognition
Paper and Code
Oct 28, 2019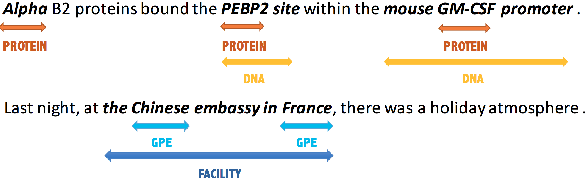
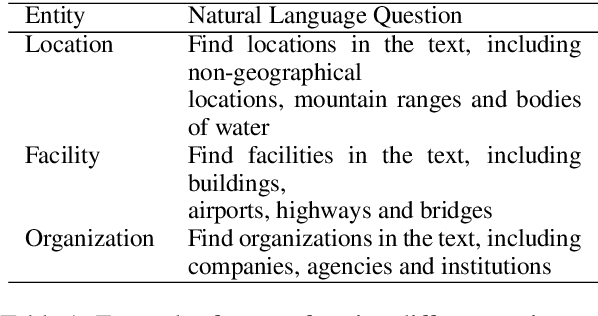
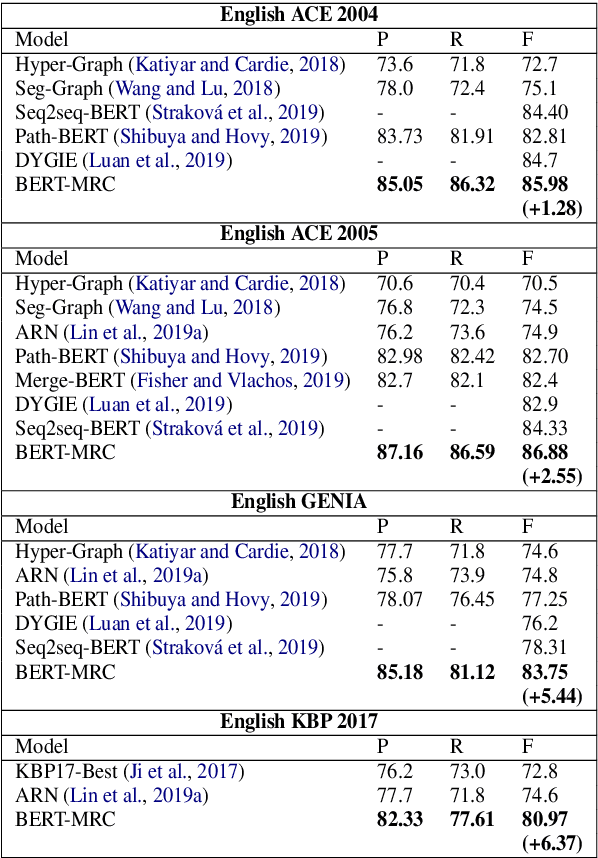
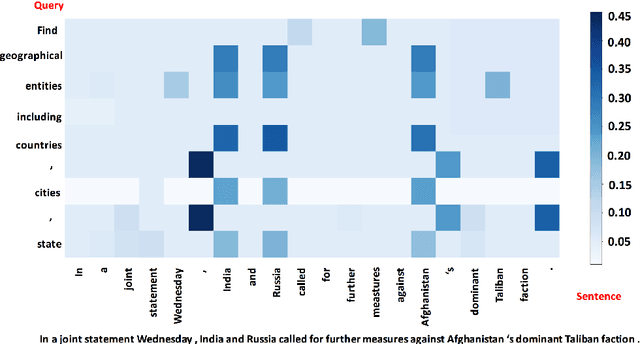
The task of named entity recognition (NER) is normally divided into nested NER and flat NER depending on whether named entities are nested or not. Models are usually separately developed for the two tasks, since sequence labeling models, the most widely used backbone for flat NER, are only able to assign a single label to a particular token, which is unsuitable for nested NER where a token may be assigned several labels. In this paper, we propose a unified framework that is capable of handling both flat and nested NER tasks. Instead of treating the task of NER as a sequence labeling problem, we propose to formulate it as a machine reading comprehension (MRC) task. For example, extracting entities with the \textsc{per} label is formalized as extracting answer spans to the question "{\it which person is mentioned in the text?}". This formulation naturally tackles the entity overlapping issue in nested NER: the extraction of two overlapping entities for different categories requires answering two independent questions. Additionally, since the query encodes informative prior knowledge, this strategy facilitates the process of entity extraction, leading to better performances for not only nested NER, but flat NER. We conduct experiments on both {\em nested} and {\em flat} NER datasets. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed formulation. We are able to achieve vast amount of performance boost over current SOTA models on nested NER datasets, i.e., +1.28, +2.55, +5.44, +6.37, respectively on ACE04, ACE05, GENIA and KBP17, along with SOTA results on flat NER datasets, i.e.,+0.24, +1.95, +0.21, +1.49 respectively on English CoNLL 2003, English OntoNotes 5.0, Chinese MSRA, Chinese OntoNotes 4.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge