A Systematic Exploration of Joint-training for Singing Voice Synthesis
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2023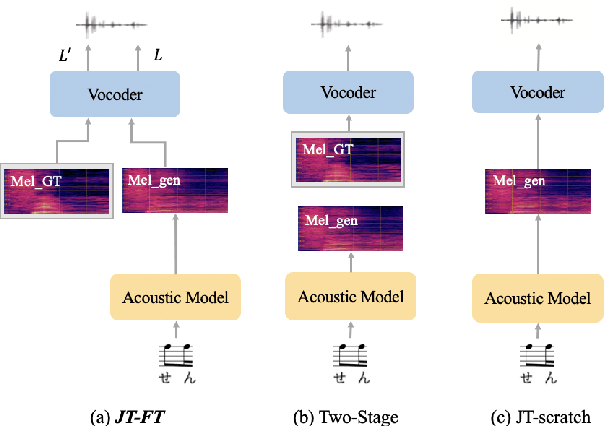

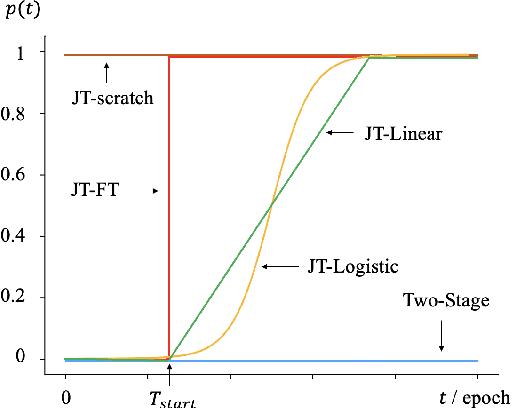

There has been a growing interest in using end-to-end acoustic models for singing voice synthesis (SVS). Typically, these models require an additional vocoder to transform the generated acoustic features into the final waveform. However, since the acoustic model and the vocoder are not jointly optimized, a gap can exist between the two models, leading to suboptimal performance. Although a similar problem has been addressed in the TTS systems by joint-training or by replacing acoustic features with a latent representation, adopting corresponding approaches to SVS is not an easy task. How to improve the joint-training of SVS systems has not been well explored. In this paper, we conduct a systematic investigation of how to better perform a joint-training of an acoustic model and a vocoder for SVS. We carry out extensive experiments and demonstrate that our joint-training strategy outperforms baselines, achieving more stable performance across different datasets while also increasing the interpretability of the entire framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge