A Study on the Calibration of In-context Learning
Paper and Code
Dec 11, 2023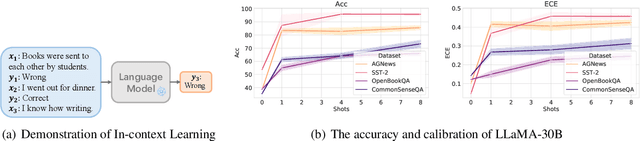

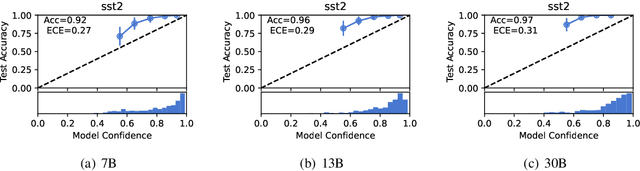
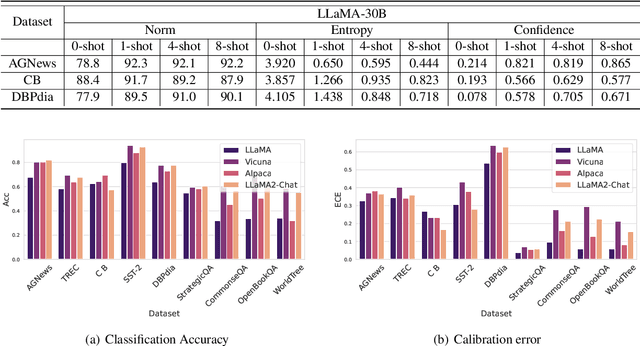
Modern auto-regressive language models are trained to minimize log loss on broad data by predicting the next token so they are expected to get calibrated answers in next-token prediction tasks. We study this for in-context learning (ICL), a widely used way to adapt frozen large language models (LLMs) via crafting prompts, and investigate the trade-offs between performance and calibration on a wide range of natural language understanding and reasoning tasks. We conduct extensive experiments to show that such trade-offs may get worse as we increase model size, incorporate more ICL examples, and fine-tune models using instruction, dialog, or reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) on carefully curated datasets. Furthermore, we find that common recalibration techniques that are widely effective such as temperature scaling provide limited gains in calibration errors, suggesting that new methods may be required for settings where models are expected to be reliable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge