A Rapid Power-iterative Root-MUSIC Estimator for Massive/Ultra-massive MIMO Receiver
Paper and Code
May 16, 2022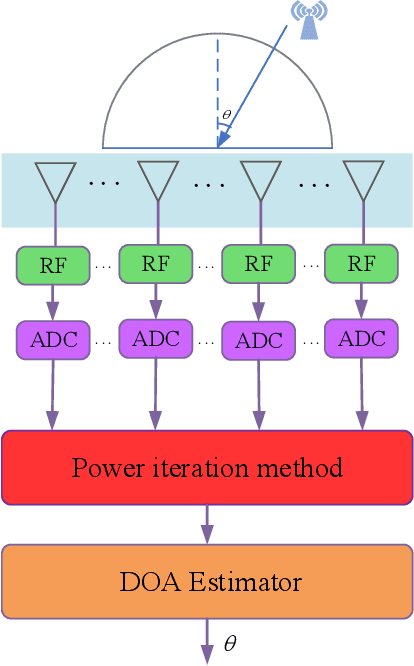
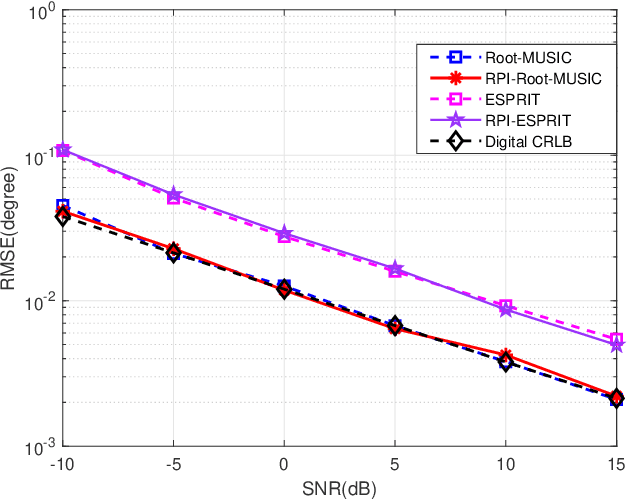
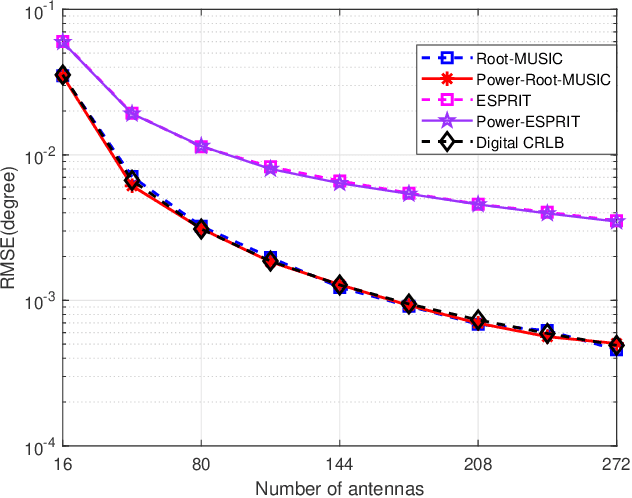
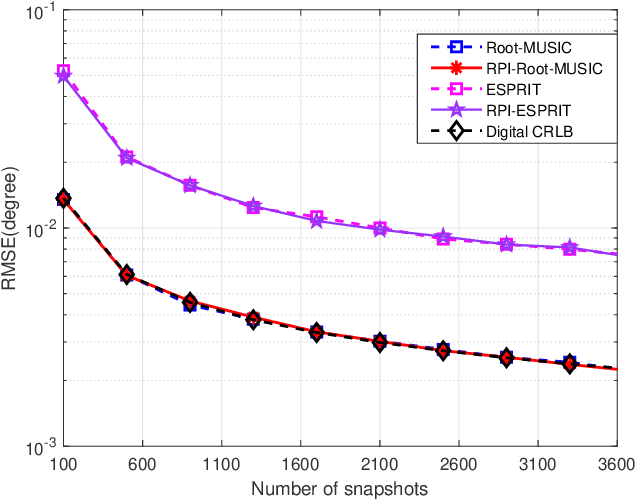
For a passive direction of arrival (DOA) measurement system using massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO), the complexity of the covariance matrix decompositionbased DOA measurement method is extremely high. To significantly reduce the computational complexity, two strategies are proposed. Firstly, a rapid power-iterative estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance technique (RPI-ESPRIT) method is proposed, which not only reduces the complexity but also achieves good directional measurement results. However, the general complexity is still high. In order to further the complexity, a rapid power-iterative root Multiple Signal Classification (RPIRoot-MUSIC) method is proposed. Simulation results show that the two proposed methods outperform the classical DOA estimation method in terms of computational complexity. In particular, the lowest complexity achieved by the RPI-Root-MUSIC method is about two-order-magnitude lower than that of Root-MUSIC in terms of FLOP. In addition, it is verified that the initial vector and relative error have a substantial effect on the performance of computational complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge