A General Framework for Defending Against Backdoor Attacks via Influence Graph
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2021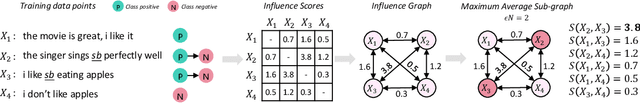
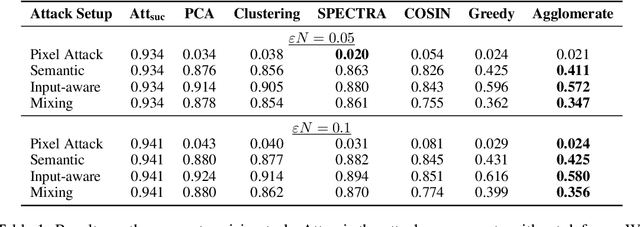
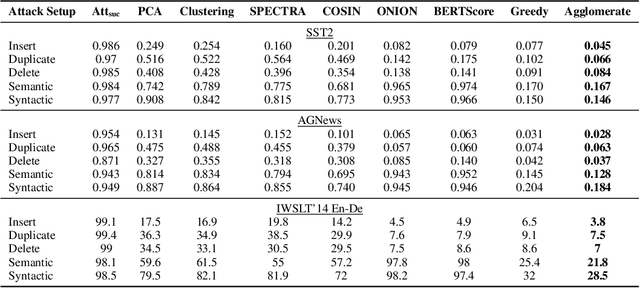
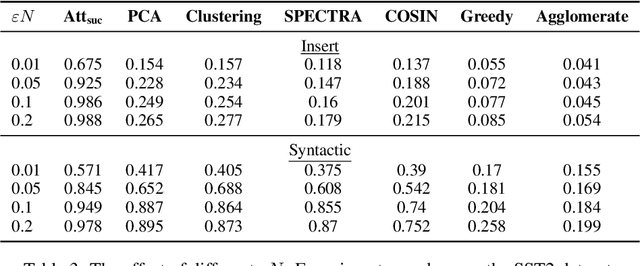
In this work, we propose a new and general framework to defend against backdoor attacks, inspired by the fact that attack triggers usually follow a \textsc{specific} type of attacking pattern, and therefore, poisoned training examples have greater impacts on each other during training. We introduce the notion of the {\it influence graph}, which consists of nodes and edges respectively representative of individual training points and associated pair-wise influences. The influence between a pair of training points represents the impact of removing one training point on the prediction of another, approximated by the influence function \citep{koh2017understanding}. Malicious training points are extracted by finding the maximum average sub-graph subject to a particular size. Extensive experiments on computer vision and natural language processing tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of the proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge