A fully dense and globally consistent 3D map reconstruction approach for GI tract to enhance therapeutic relevance of the endoscopic capsule robot
Paper and Code
May 18, 2017

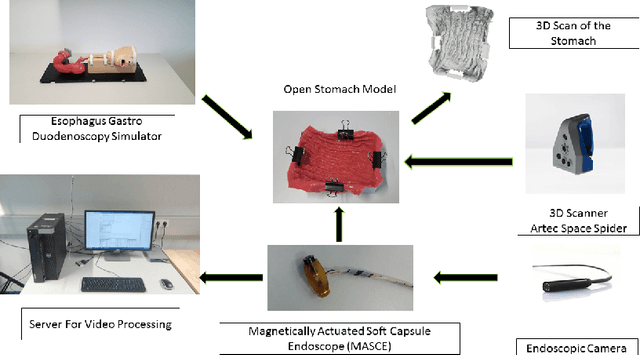

In the gastrointestinal (GI) tract endoscopy field, ingestible wireless capsule endoscopy is emerging as a novel, minimally invasive diagnostic technology for inspection of the GI tract and diagnosis of a wide range of diseases and pathologies. Since the development of this technology, medical device companies and many research groups have made substantial progress in converting passive capsule endoscopes to robotic active capsule endoscopes with most of the functionality of current active flexible endoscopes. However, robotic capsule endoscopy still has some challenges. In particular, the use of such devices to generate a precise three-dimensional (3D) mapping of the entire inner organ remains an unsolved problem. Such global 3D maps of inner organs would help doctors to detect the location and size of diseased areas more accurately and intuitively, thus permitting more reliable diagnoses. To our knowledge, this paper presents the first complete pipeline for a complete 3D visual map reconstruction of the stomach. The proposed pipeline is modular and includes a preprocessing module, an image registration module, and a final shape-from-shading-based 3D reconstruction module; the 3D map is primarily generated by a combination of image stitching and shape-from-shading techniques, and is updated in a frame-by-frame iterative fashion via capsule motion inside the stomach. A comprehensive quantitative analysis of the proposed 3D reconstruction method is performed using an esophagus gastro duodenoscopy simulator, three different endoscopic cameras, and a 3D optical scanner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge