A Compression Objective and a Cycle Loss for Neural Image Compression
Paper and Code
May 24, 2019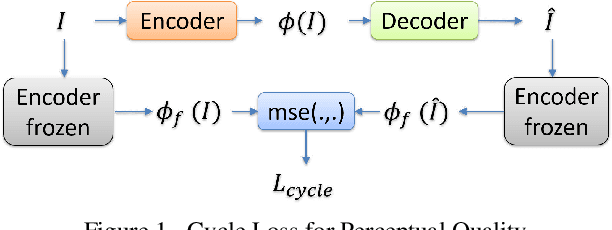
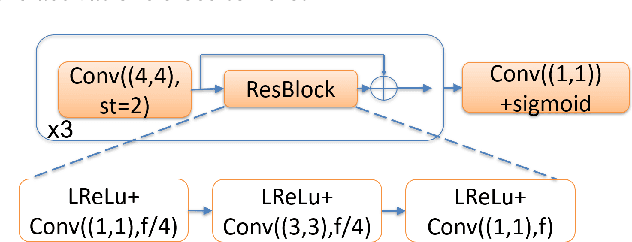
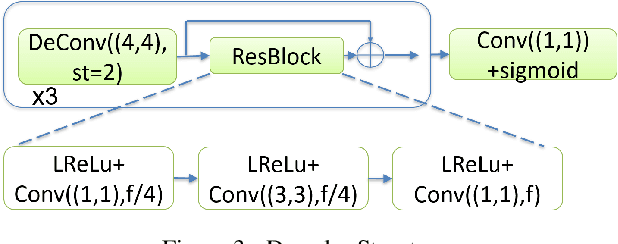

In this manuscript we propose two objective terms for neural image compression: a compression objective and a cycle loss. These terms are applied on the encoder output of an autoencoder and are used in combination with reconstruction losses. The compression objective encourages sparsity and low entropy in the activations. The cycle loss term represents the distortion between encoder outputs computed from the original image and from the reconstructed image (code-domain distortion). We train different autoencoders by using the compression objective in combination with different losses: a) MSE, b) MSE and MSSSIM, c) MSE, MS-SSIM and cycle loss. We observe that images encoded by these differently-trained autoencoders fall into different points of the perception-distortion curve (while having similar bit-rates). In particular, MSE-only training favors low image-domain distortion, whereas cycle loss training favors high perceptual quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge