Zuobin Xiong
Fed-Listing: Federated Label Distribution Inference in Graph Neural Networks
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been intensively studied for their expressive representation and learning performance on graph-structured data, enabling effective modeling of complex relational dependencies among nodes and edges in various domains. However, the standalone GNNs can unleash threat surfaces and privacy implications, as some sensitive graph-structured data is collected and processed in a centralized setting. To solve this issue, Federated Graph Neural Networks (FedGNNs) are proposed to facilitate collaborative learning over decentralized local graph data, aiming to preserve user privacy. Yet, emerging research indicates that even in these settings, shared model updates, particularly gradients, can unintentionally leak sensitive information of local users. Numerous privacy inference attacks have been explored in traditional federated learning and extended to graph settings, but the problem of label distribution inference in FedGNNs remains largely underexplored. In this work, we introduce Fed-Listing (Federated Label Distribution Inference in GNNs), a novel gradient-based attack designed to infer the private label statistics of target clients in FedGNNs without access to raw data or node features. Fed-Listing only leverages the final-layer gradients exchanged during training to uncover statistical patterns that reveal class proportions in a stealthy manner. An auxiliary shadow dataset is used to generate diverse label partitioning strategies, simulating various client distributions, on which the attack model is obtained. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets and three GNN architectures show that Fed-Listing significantly outperforms existing baselines, including random guessing and Decaf, even under challenging non-i.i.d. scenarios. Moreover, applying defense mechanisms can barely reduce our attack performance, unless the model's utility is severely degraded.
Generative Adversarial Networks: A Survey Towards Private and Secure Applications
Jun 07, 2021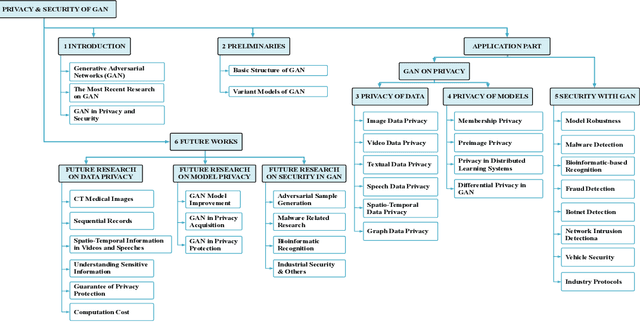
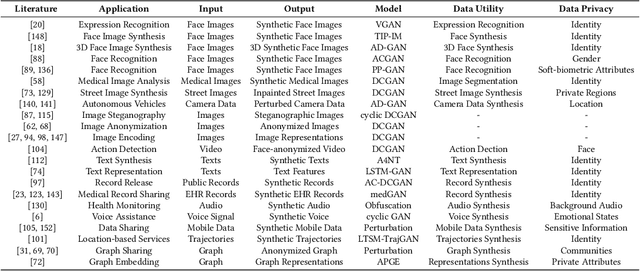
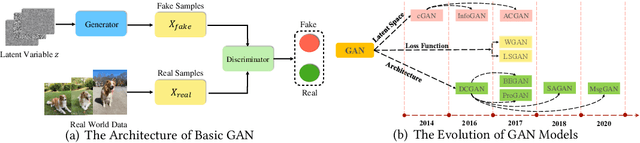
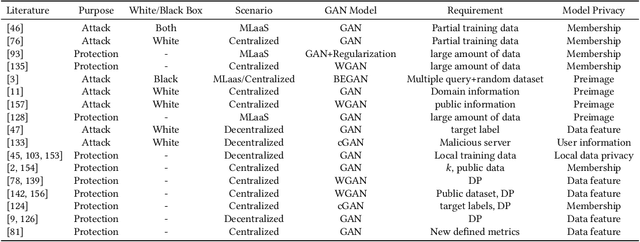
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have promoted a variety of applications in computer vision, natural language processing, etc. due to its generative model's compelling ability to generate realistic examples plausibly drawn from an existing distribution of samples. GAN not only provides impressive performance on data generation-based tasks but also stimulates fertilization for privacy and security oriented research because of its game theoretic optimization strategy. Unfortunately, there are no comprehensive surveys on GAN in privacy and security, which motivates this survey paper to summarize those state-of-the-art works systematically. The existing works are classified into proper categories based on privacy and security functions, and this survey paper conducts a comprehensive analysis of their advantages and drawbacks. Considering that GAN in privacy and security is still at a very initial stage and has imposed unique challenges that are yet to be well addressed, this paper also sheds light on some potential privacy and security applications with GAN and elaborates on some future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge