Junggab Son
Fed-Listing: Federated Label Distribution Inference in Graph Neural Networks
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been intensively studied for their expressive representation and learning performance on graph-structured data, enabling effective modeling of complex relational dependencies among nodes and edges in various domains. However, the standalone GNNs can unleash threat surfaces and privacy implications, as some sensitive graph-structured data is collected and processed in a centralized setting. To solve this issue, Federated Graph Neural Networks (FedGNNs) are proposed to facilitate collaborative learning over decentralized local graph data, aiming to preserve user privacy. Yet, emerging research indicates that even in these settings, shared model updates, particularly gradients, can unintentionally leak sensitive information of local users. Numerous privacy inference attacks have been explored in traditional federated learning and extended to graph settings, but the problem of label distribution inference in FedGNNs remains largely underexplored. In this work, we introduce Fed-Listing (Federated Label Distribution Inference in GNNs), a novel gradient-based attack designed to infer the private label statistics of target clients in FedGNNs without access to raw data or node features. Fed-Listing only leverages the final-layer gradients exchanged during training to uncover statistical patterns that reveal class proportions in a stealthy manner. An auxiliary shadow dataset is used to generate diverse label partitioning strategies, simulating various client distributions, on which the attack model is obtained. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets and three GNN architectures show that Fed-Listing significantly outperforms existing baselines, including random guessing and Decaf, even under challenging non-i.i.d. scenarios. Moreover, applying defense mechanisms can barely reduce our attack performance, unless the model's utility is severely degraded.
A Federated Approach for Fine-Grained Classification of Fashion Apparel
Aug 27, 2020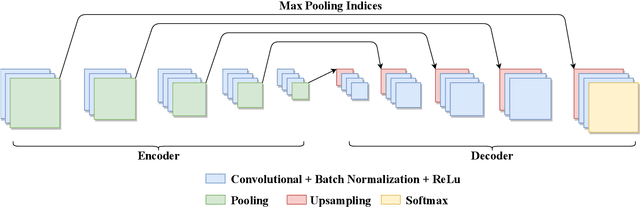



Abstract:As online retail services proliferate and are pervasive in modern lives, applications for classifying fashion apparel features from image data are becoming more indispensable. Online retailers, from leading companies to start-ups, can leverage such applications in order to increase profit margin and enhance the consumer experience. Many notable schemes have been proposed to classify fashion items, however, the majority of which focused upon classifying basic-level categories, such as T-shirts, pants, skirts, shoes, bags, and so forth. In contrast to most prior efforts, this paper aims to enable an in-depth classification of fashion item attributes within the same category. Beginning with a single dress, we seek to classify the type of dress hem, the hem length, and the sleeve length. The proposed scheme is comprised of three major stages: (a) localization of a target item from an input image using semantic segmentation, (b) detection of human key points (e.g., point of shoulder) using a pre-trained CNN and a bounding box, and (c) three phases to classify the attributes using a combination of algorithmic approaches and deep neural networks. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed scheme is highly effective, with all categories having average precision of above 93.02%, and outperforms existing Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)-based schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge