Zuheng Kang
Attention-weighted Centered Kernel Alignment for Knowledge Distillation in Large Audio-Language Models Applied to Speech Emotion Recognition
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The emergence of Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) has advanced Speech Emotion Recognition (SER), but their size limits deployment in resource-constrained environments. While Knowledge Distillation is effective for LALM compression, existing methods remain underexplored in distilling the cross-modal projection module (Projector), and often struggle with alignment due to differences in feature dimensions. We propose PL-Distill, a KD framework that combines Projector-Level Distillation (PDist) to align audio embeddings and Logits-Level Distillation (LDist) to align output logits. PDist introduces Attention-weighted Centered Kernel Alignment, a novel approach we propose to highlight important time steps and address dimension mismatches. Meanwhile, LDist minimizes the Kullback-Leibler divergence between teacher and student logits from audio and text modalities. On IEMOCAP, RAVDESS, and SAVEE, PL-Distill compresses an 8.4B-parameter teacher to a compact 1.1B-parameter student, consistently outperforming the teacher, state-of-the-art pretrained models, and other KD baselines across all metrics.
EMO-RL: Emotion-Rule-Based Reinforcement Learning Enhanced Audio-Language Model for Generalized Speech Emotion Recognition
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Although Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have exhibited outstanding performance in auditory understanding, their performance in affective computing scenarios, particularly in emotion recognition, reasoning, and subtle sentiment differentiation, remains suboptimal. Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning (RL) have shown promise in improving LALMs' reasoning abilities. However, two critical challenges hinder the direct application of RL techniques to Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) tasks: (1) convergence instability caused by ambiguous emotional boundaries and (2) limited reasoning ability when using relatively small models (e.g., 7B-parameter architectures). To overcome these limitations, we introduce EMO-RL, a novel framework incorporating reinforcement learning with two key innovations: Emotion Similarity-Weighted Reward (ESWR) and Explicit Structured Reasoning (ESR). Built upon pretrained LALMs, our method employs group-relative policy optimization with emotion constraints. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our EMO-RL training strategies can significantly enhance the emotional reasoning capabilities of LALMs, attaining state-of-the-art results on both the MELD and IEMOCAP datasets, and cross-dataset experiments prove the strong superiority of generalization.
Generalized Audio Deepfake Detection Using Frame-level Latent Information Entropy
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:Generalizability, the capacity of a robust model to perform effectively on unseen data, is crucial for audio deepfake detection due to the rapid evolution of text-to-speech (TTS) and voice conversion (VC) technologies. A promising approach to differentiate between bonafide and spoof samples lies in identifying intrinsic disparities to enhance model generalizability. From an information-theoretic perspective, we hypothesize the information content is one of the intrinsic differences: bonafide sample represents a dense, information-rich sampling of the real world, whereas spoof sample is typically derived from lower-dimensional, less informative representations. To implement this, we introduce frame-level latent information entropy detector(f-InfoED), a framework that extracts distinctive information entropy from latent representations at the frame level to identify audio deepfakes. Furthermore, we present AdaLAM, which extends large pre-trained audio models with trainable adapters for enhanced feature extraction. To facilitate comprehensive evaluation, the audio deepfake forensics 2024 (ADFF 2024) dataset was built by the latest TTS and VC methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance and exhibits remarkable generalization capabilities. Further analytical studies confirms the efficacy of AdaLAM in extracting discriminative audio features and f-InfoED in leveraging latent entropy information for more generalized deepfake detection.
ACCon: Angle-Compensated Contrastive Regularizer for Deep Regression
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:In deep regression, capturing the relationship among continuous labels in feature space is a fundamental challenge that has attracted increasing interest. Addressing this issue can prevent models from converging to suboptimal solutions across various regression tasks, leading to improved performance, especially for imbalanced regression and under limited sample sizes. However, existing approaches often rely on order-aware representation learning or distance-based weighting. In this paper, we hypothesize a linear negative correlation between label distances and representation similarities in regression tasks. To implement this, we propose an angle-compensated contrastive regularizer for deep regression, which adjusts the cosine distance between anchor and negative samples within the contrastive learning framework. Our method offers a plug-and-play compatible solution that extends most existing contrastive learning methods for regression tasks. Extensive experiments and theoretical analysis demonstrate that our proposed angle-compensated contrastive regularizer not only achieves competitive regression performance but also excels in data efficiency and effectiveness on imbalanced datasets.
Efficient Multi-Model Fusion with Adversarial Complementary Representation Learning
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:Single-model systems often suffer from deficiencies in tasks such as speaker verification (SV) and image classification, relying heavily on partial prior knowledge during decision-making, resulting in suboptimal performance. Although multi-model fusion (MMF) can mitigate some of these issues, redundancy in learned representations may limits improvements. To this end, we propose an adversarial complementary representation learning (ACoRL) framework that enables newly trained models to avoid previously acquired knowledge, allowing each individual component model to learn maximally distinct, complementary representations. We make three detailed explanations of why this works and experimental results demonstrate that our method more efficiently improves performance compared to traditional MMF. Furthermore, attribution analysis validates the model trained under ACoRL acquires more complementary knowledge, highlighting the efficacy of our approach in enhancing efficiency and robustness across tasks.
Retrieval-Augmented Audio Deepfake Detection
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:With recent advances in speech synthesis including text-to-speech (TTS) and voice conversion (VC) systems enabling the generation of ultra-realistic audio deepfakes, there is growing concern about their potential misuse. However, most deepfake (DF) detection methods rely solely on the fuzzy knowledge learned by a single model, resulting in performance bottlenecks and transparency issues. Inspired by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), we propose a retrieval-augmented detection (RAD) framework that augments test samples with similar retrieved samples for enhanced detection. We also extend the multi-fusion attentive classifier to integrate it with our proposed RAD framework. Extensive experiments show the superior performance of the proposed RAD framework over baseline methods, achieving state-of-the-art results on the ASVspoof 2021 DF set and competitive results on the 2019 and 2021 LA sets. Further sample analysis indicates that the retriever consistently retrieves samples mostly from the same speaker with acoustic characteristics highly consistent with the query audio, thereby improving detection performance.
VoiceExtender: Short-utterance Text-independent Speaker Verification with Guided Diffusion Model
Oct 07, 2023


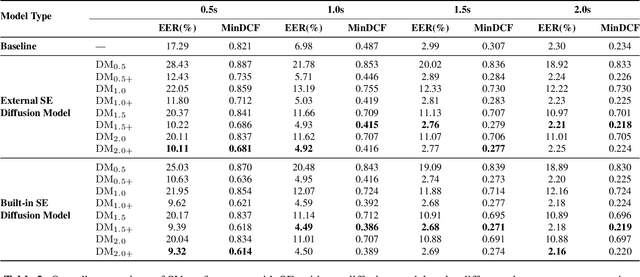
Abstract:Speaker verification (SV) performance deteriorates as utterances become shorter. To this end, we propose a new architecture called VoiceExtender which provides a promising solution for improving SV performance when handling short-duration speech signals. We use two guided diffusion models, the built-in and the external speaker embedding (SE) guided diffusion model, both of which utilize a diffusion model-based sample generator that leverages SE guidance to augment the speech features based on a short utterance. Extensive experimental results on the VoxCeleb1 dataset show that our method outperforms the baseline, with relative improvements in equal error rate (EER) of 46.1%, 35.7%, 10.4%, and 5.7% for the short utterance conditions of 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 seconds, respectively.
SVVAD: Personal Voice Activity Detection for Speaker Verification
May 31, 2023



Abstract:Voice activity detection (VAD) improves the performance of speaker verification (SV) by preserving speech segments and attenuating the effects of non-speech. However, this scheme is not ideal: (1) it fails in noisy environments or multi-speaker conversations; (2) it is trained based on inaccurate non-SV sensitive labels. To address this, we propose a speaker verification-based voice activity detection (SVVAD) framework that can adapt the speech features according to which are most informative for SV. To achieve this, we introduce a label-free training method with triplet-like losses that completely avoids the performance degradation of SV due to incorrect labeling. Extensive experiments show that SVVAD significantly outperforms the baseline in terms of equal error rate (EER) under conditions where other speakers are mixed at different ratios. Moreover, the decision boundaries reveal the importance of the different parts of speech, which are largely consistent with human judgments.
Feature-Rich Audio Model Inversion for Data-Free Knowledge Distillation Towards General Sound Classification
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Data-Free Knowledge Distillation (DFKD) has recently attracted growing attention in the academic community, especially with major breakthroughs in computer vision. Despite promising results, the technique has not been well applied to audio and signal processing. Due to the variable duration of audio signals, it has its own unique way of modeling. In this work, we propose feature-rich audio model inversion (FRAMI), a data-free knowledge distillation framework for general sound classification tasks. It first generates high-quality and feature-rich Mel-spectrograms through a feature-invariant contrastive loss. Then, the hidden states before and after the statistics pooling layer are reused when knowledge distillation is performed on these feature-rich samples. Experimental results on the Urbansound8k, ESC-50, and audioMNIST datasets demonstrate that FRAMI can generate feature-rich samples. Meanwhile, the accuracy of the student model is further improved by reusing the hidden state and significantly outperforms the baseline method.
SVLDL: Improved Speaker Age Estimation Using Selective Variance Label Distribution Learning
Oct 18, 2022



Abstract:Estimating age from a single speech is a classic and challenging topic. Although Label Distribution Learning (LDL) can represent adjacent indistinguishable ages well, the uncertainty of the age estimate for each utterance varies from person to person, i.e., the variance of the age distribution is different. To address this issue, we propose selective variance label distribution learning (SVLDL) method to adapt the variance of different age distributions. Furthermore, the model uses WavLM as the speech feature extractor and adds the auxiliary task of gender recognition to further improve the performance. Two tricks are applied on the loss function to enhance the robustness of the age estimation and improve the quality of the fitted age distribution. Extensive experiments show that the model achieves state-of-the-art performance on all aspects of the NIST SRE08-10 and a real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge