Ziyun Bai
Natural-language-driven Simulation Benchmark and Copilot for Efficient Production of Object Interactions in Virtual Road Scenes
Dec 15, 2023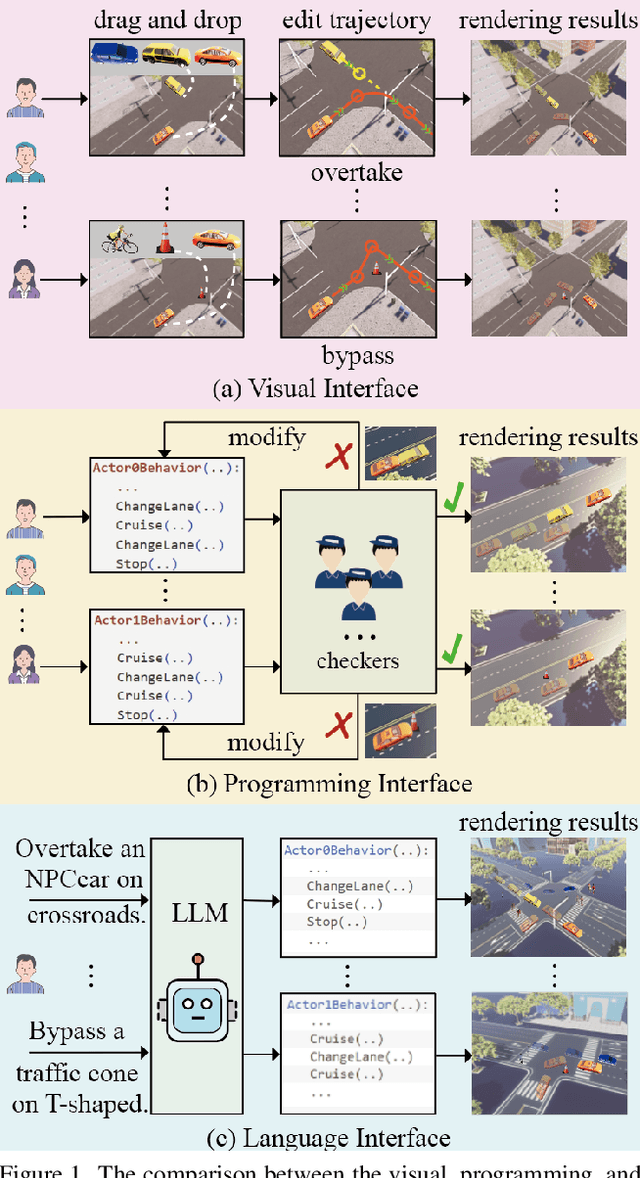
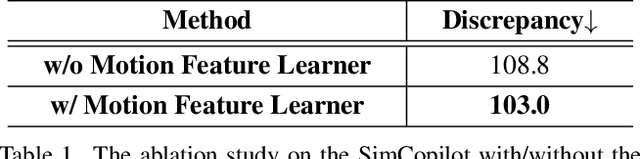
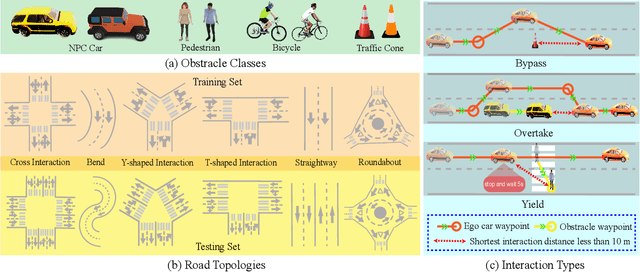
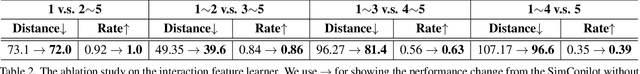
Abstract:We advocate the idea of the natural-language-driven(NLD) simulation to efficiently produce the object interactions between multiple objects in the virtual road scenes, for teaching and testing the autonomous driving systems that should take quick action to avoid collision with obstacles with unpredictable motions. The NLD simulation allows the brief natural-language description to control the object interactions, significantly reducing the human efforts for creating a large amount of interaction data. To facilitate the research of NLD simulation, we collect the Language-to-Interaction(L2I) benchmark dataset with 120,000 natural-language descriptions of object interactions in 6 common types of road topologies. Each description is associated with the programming code, which the graphic render can use to visually reconstruct the object interactions in the virtual scenes. As a methodology contribution, we design SimCopilot to translate the interaction descriptions to the renderable code. We use the L2I dataset to evaluate SimCopilot's abilities to control the object motions, generate complex interactions, and generalize interactions across road topologies. The L2I dataset and the evaluation results motivate the relevant research of the NLD simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge