Zhuoqun Huang
AdaptDel: Adaptable Deletion Rate Randomized Smoothing for Certified Robustness
Nov 12, 2025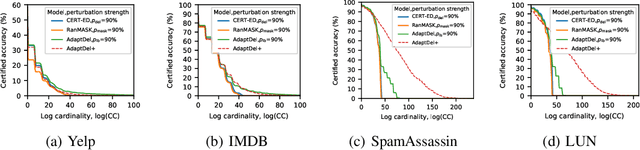
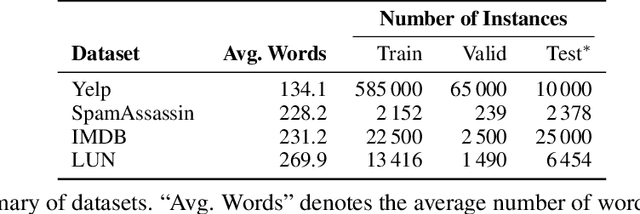
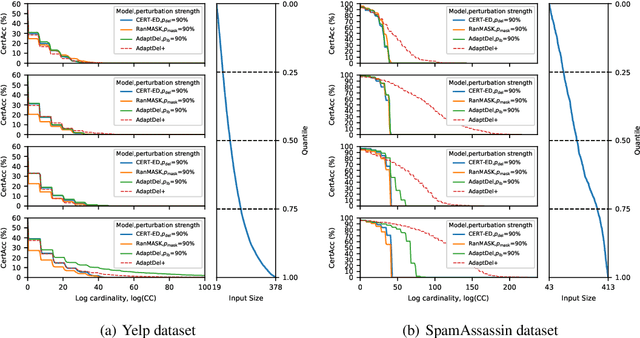
Abstract:We consider the problem of certified robustness for sequence classification against edit distance perturbations. Naturally occurring inputs of varying lengths (e.g., sentences in natural language processing tasks) present a challenge to current methods that employ fixed-rate deletion mechanisms and lead to suboptimal performance. To this end, we introduce AdaptDel methods with adaptable deletion rates that dynamically adjust based on input properties. We extend the theoretical framework of randomized smoothing to variable-rate deletion, ensuring sound certification with respect to edit distance. We achieve strong empirical results in natural language tasks, observing up to 30 orders of magnitude improvement to median cardinality of the certified region, over state-of-the-art certifications.
How to Enhance Downstream Adversarial Robustness (almost) without Touching the Pre-Trained Foundation Model?
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:With the rise of powerful foundation models, a pre-training-fine-tuning paradigm becomes increasingly popular these days: A foundation model is pre-trained using a huge amount of data from various sources, and then the downstream users only need to fine-tune and adapt it to specific downstream tasks. However, due to the high computation complexity of adversarial training, it is not feasible to fine-tune the foundation model to improve its robustness on the downstream task. Observing the above challenge, we want to improve the downstream robustness without updating/accessing the weights in the foundation model. Inspired from existing literature in robustness inheritance (Kim et al., 2020), through theoretical investigation, we identify a close relationship between robust contrastive learning with the adversarial robustness of supervised learning. To further validate and utilize this theoretical insight, we design a simple-yet-effective robust auto-encoder as a data pre-processing method before feeding the data into the foundation model. The proposed approach has zero access to the foundation model when training the robust auto-encoder. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in improving the robustness of downstream tasks, verifying the connection between the feature robustness (implied by small adversarial contrastive loss) and the robustness of the downstream task.
CERT-ED: Certifiably Robust Text Classification for Edit Distance
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:With the growing integration of AI in daily life, ensuring the robustness of systems to inference-time attacks is crucial. Among the approaches for certifying robustness to such adversarial examples, randomized smoothing has emerged as highly promising due to its nature as a wrapper around arbitrary black-box models. Previous work on randomized smoothing in natural language processing has primarily focused on specific subsets of edit distance operations, such as synonym substitution or word insertion, without exploring the certification of all edit operations. In this paper, we adapt Randomized Deletion (Huang et al., 2023) and propose, CERTified Edit Distance defense (CERT-ED) for natural language classification. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that CERT-ED outperforms the existing Hamming distance method RanMASK (Zeng et al., 2023) in 4 out of 5 datasets in terms of both accuracy and the cardinality of the certificate. By covering various threat models, including 5 direct and 5 transfer attacks, our method improves empirical robustness in 38 out of 50 settings.
Certified Robustness of Learning-based Static Malware Detectors
Jan 31, 2023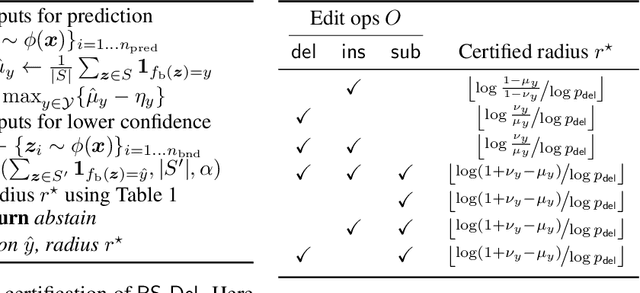


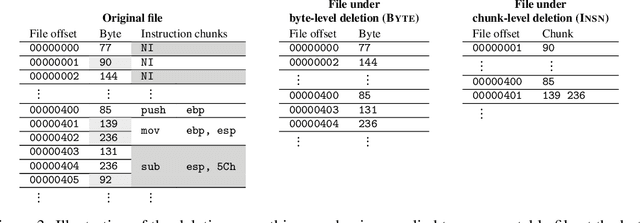
Abstract:Certified defenses are a recent development in adversarial machine learning (ML), which aim to rigorously guarantee the robustness of ML models to adversarial perturbations. A large body of work studies certified defenses in computer vision, where $\ell_p$ norm-bounded evasion attacks are adopted as a tractable threat model. However, this threat model has known limitations in vision, and is not applicable to other domains -- e.g., where inputs may be discrete or subject to complex constraints. Motivated by this gap, we study certified defenses for malware detection, a domain where attacks against ML-based systems are a real and current threat. We consider static malware detection systems that operate on byte-level data. Our certified defense is based on the approach of randomized smoothing which we adapt by: (1) replacing the standard Gaussian randomization scheme with a novel deletion randomization scheme that operates on bytes or chunks of an executable; and (2) deriving a certificate that measures robustness to evasion attacks in terms of generalized edit distance. To assess the size of robustness certificates that are achievable while maintaining high accuracy, we conduct experiments on malware datasets using a popular convolutional malware detection model, MalConv. We are able to accurately classify 91% of the inputs while being certifiably robust to any adversarial perturbations of edit distance 128 bytes or less. By comparison, an existing certification of up to 128 bytes of substitutions (without insertions or deletions) achieves an accuracy of 78%. In addition, given that robustness certificates are conservative, we evaluate practical robustness to several recently published evasion attacks and, in some cases, find robustness beyond certified guarantees.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge