Zhongzhong Yu
A Survey on Time-Series Pre-Trained Models
May 18, 2023



Abstract:Time-Series Mining (TSM) is an important research area since it shows great potential in practical applications. Deep learning models that rely on massive labeled data have been utilized for TSM successfully. However, constructing a large-scale well-labeled dataset is difficult due to data annotation costs. Recently, Pre-Trained Models have gradually attracted attention in the time series domain due to their remarkable performance in computer vision and natural language processing. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of Time-Series Pre-Trained Models (TS-PTMs), aiming to guide the understanding, applying, and studying TS-PTMs. Specifically, we first briefly introduce the typical deep learning models employed in TSM. Then, we give an overview of TS-PTMs according to the pre-training techniques. The main categories we explore include supervised, unsupervised, and self-supervised TS-PTMs. Further, extensive experiments are conducted to analyze the advantages and disadvantages of transfer learning strategies, Transformer-based models, and representative TS-PTMs. Finally, we point out some potential directions of TS-PTMs for future work.
From Known to Unknown: Knowledge-guided Transformer for Time-Series Sales Forecasting in Alibaba
Sep 22, 2021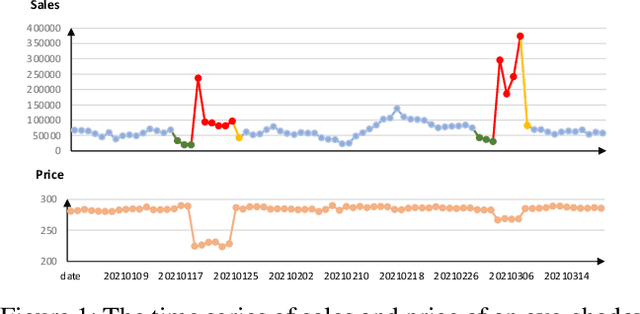
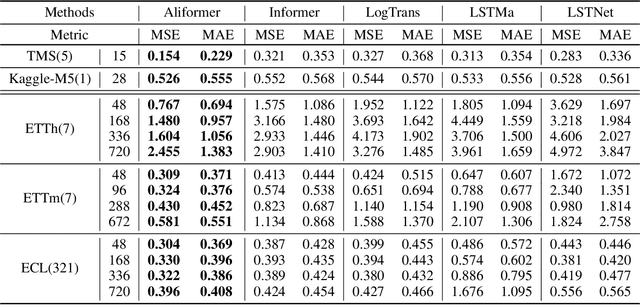
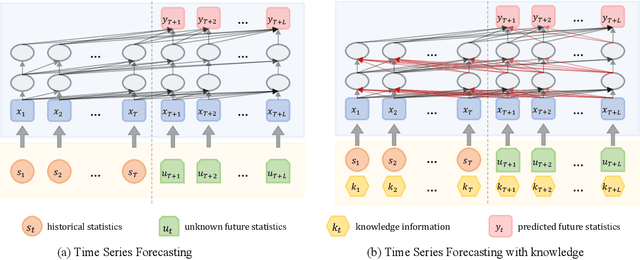
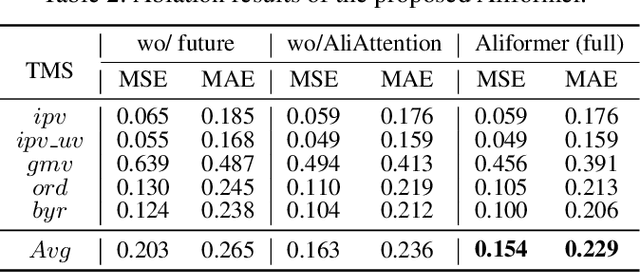
Abstract:Time series forecasting (TSF) is fundamentally required in many real-world applications, such as electricity consumption planning and sales forecasting. In e-commerce, accurate time-series sales forecasting (TSSF) can significantly increase economic benefits. TSSF in e-commerce aims to predict future sales of millions of products. The trend and seasonality of products vary a lot, and the promotion activity heavily influences sales. Besides the above difficulties, we can know some future knowledge in advance except for the historical statistics. Such future knowledge may reflect the influence of the future promotion activity on current sales and help achieve better accuracy. However, most existing TSF methods only predict the future based on historical information. In this work, we make up for the omissions of future knowledge. Except for introducing future knowledge for prediction, we propose Aliformer based on the bidirectional Transformer, which can utilize the historical information, current factor, and future knowledge to predict future sales. Specifically, we design a knowledge-guided self-attention layer that uses known knowledge's consistency to guide the transmission of timing information. And the future-emphasized training strategy is proposed to make the model focus more on the utilization of future knowledge. Extensive experiments on four public benchmark datasets and one proposed large-scale industrial dataset from Tmall demonstrate that Aliformer can perform much better than state-of-the-art TSF methods. Aliformer has been deployed for goods selection on Tmall Industry Tablework, and the dataset will be released upon approval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge