Zhongsheng Wang
R-Debater: Retrieval-Augmented Debate Generation through Argumentative Memory
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We present R-Debater, an agentic framework for generating multi-turn debates built on argumentative memory. Grounded in rhetoric and memory studies, the system views debate as a process of recalling and adapting prior arguments to maintain stance consistency, respond to opponents, and support claims with evidence. Specifically, R-Debater integrates a debate knowledge base for retrieving case-like evidence and prior debate moves with a role-based agent that composes coherent utterances across turns. We evaluate on standardized ORCHID debates, constructing a 1,000-item retrieval corpus and a held-out set of 32 debates across seven domains. Two tasks are evaluated: next-utterance generation, assessed by InspireScore (subjective, logical, and factual), and adversarial multi-turn simulations, judged by Debatrix (argument, source, language, and overall). Compared with strong LLM baselines, R-Debater achieves higher single-turn and multi-turn scores. Human evaluation with 20 experienced debaters further confirms its consistency and evidence use, showing that combining retrieval grounding with structured planning yields more faithful, stance-aligned, and coherent debates across turns.
CoRA: Optimizing Low-Rank Adaptation with Common Subspace of Large Language Models
Aug 31, 2024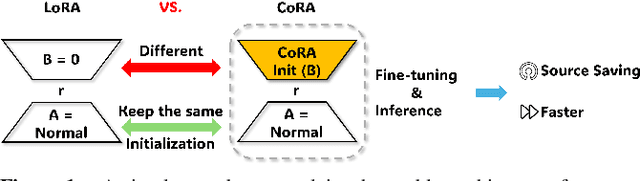
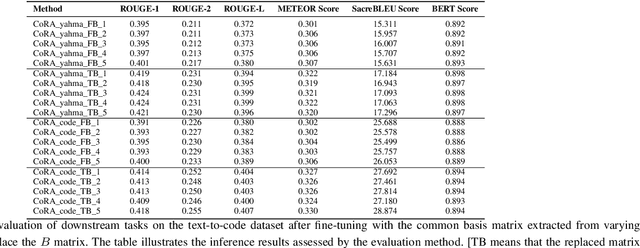
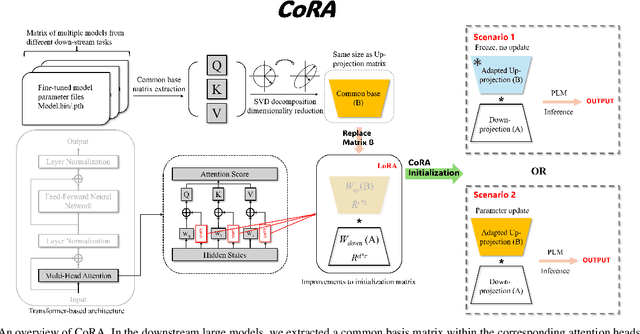
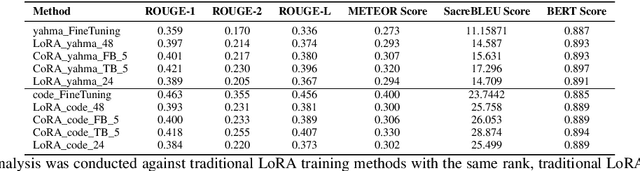
Abstract:In fine-tuning large language models (LLMs), conserving computational resources while maintaining effectiveness and improving outcomes within the same computational constraints is crucial. The Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) strategy balances efficiency and performance in fine-tuning large models by reducing the number of trainable parameters and computational costs. However, current advancements in LoRA might be focused on its fine-tuning methodologies, with not as much exploration as might be expected into further compression of LoRA. Since most of LoRA's parameters might still be superfluous, this may lead to unnecessary wastage of computational resources. In this paper, we propose \textbf{CoRA}: leveraging shared knowledge to optimize LoRA training by substituting its matrix $B$ with a common subspace from large models. Our two-fold method includes (1) Freezing the substitute matrix $B$ to halve parameters while training matrix $A$ for specific tasks and (2) Using the substitute matrix $B$ as an enhanced initial state for the original matrix $B$, achieving improved results with the same parameters. Our experiments show that the first approach achieves the same efficacy as the original LoRA fine-tuning while being more efficient than halving parameters. At the same time, the second approach has some improvements compared to LoRA's original fine-tuning performance. They generally attest to the effectiveness of our work.
ChatLogic: Integrating Logic Programming with Large Language Models for Multi-Step Reasoning
Jul 14, 2024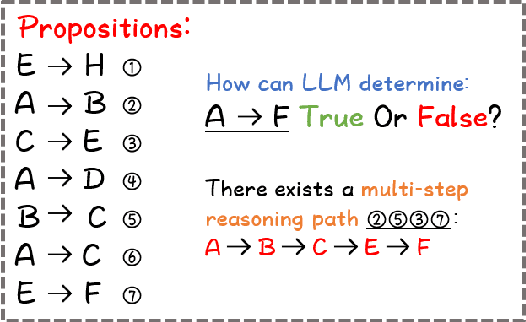
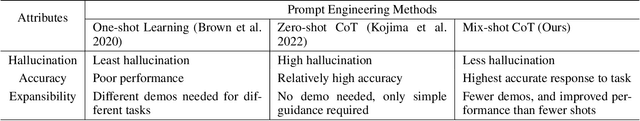
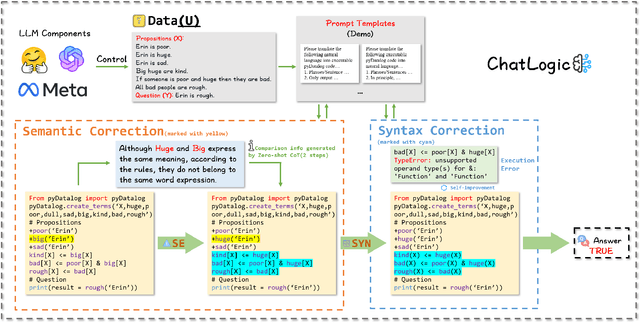
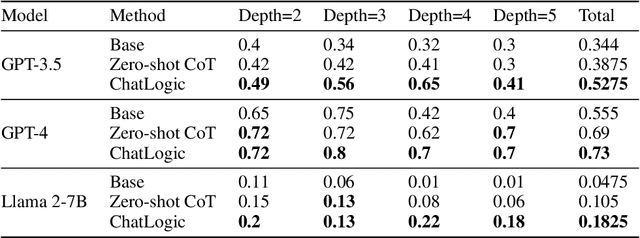
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have demonstrated impressive capabilities in various generative tasks. However, their performance is often hampered by limitations in accessing and leveraging long-term memory, leading to specific vulnerabilities and biases, especially during long interactions. This paper introduces ChatLogic, an innovative framework specifically targeted at LLM reasoning tasks that can enhance the performance of LLMs in multi-step deductive reasoning tasks by integrating logic programming. In ChatLogic, the language model plays a central role, acting as a controller and participating in every system operation stage. We propose a novel method of converting logic problems into symbolic integration with an inference engine. This approach leverages large language models' situational understanding and imitation skills and uses symbolic memory to enhance multi-step deductive reasoning capabilities. Our results show that the ChatLogic framework significantly improves the multi-step reasoning capabilities of LLMs. The source code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/Strong-AI-Lab/ChatLogic}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge