Zhiying Ma
HNS: An Efficient Hermite Neural Solver for Solving Time-Fractional Partial Differential Equations
Oct 07, 2023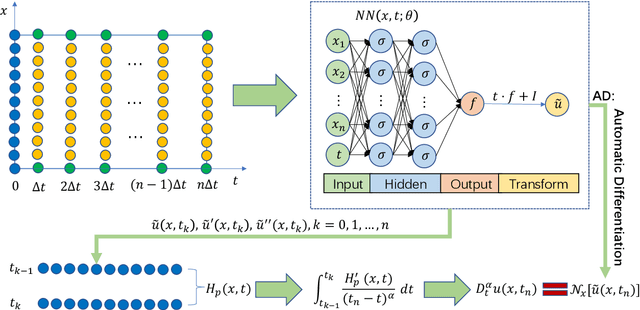



Abstract:Neural network solvers represent an innovative and promising approach for tackling time-fractional partial differential equations by utilizing deep learning techniques. L1 interpolation approximation serves as the standard method for addressing time-fractional derivatives within neural network solvers. However, we have discovered that neural network solvers based on L1 interpolation approximation are unable to fully exploit the benefits of neural networks, and the accuracy of these models is constrained to interpolation errors. In this paper, we present the high-precision Hermite Neural Solver (HNS) for solving time-fractional partial differential equations. Specifically, we first construct a high-order explicit approximation scheme for fractional derivatives using Hermite interpolation techniques, and rigorously analyze its approximation accuracy. Afterward, taking into account the infinitely differentiable properties of deep neural networks, we integrate the high-order Hermite interpolation explicit approximation scheme with deep neural networks to propose the HNS. The experimental results show that HNS achieves higher accuracy than methods based on the L1 scheme for both forward and inverse problems, as well as in high-dimensional scenarios. This indicates that HNS has significantly improved accuracy and flexibility compared to existing L1-based methods, and has overcome the limitations of explicit finite difference approximation methods that are often constrained to function value interpolation. As a result, the HNS is not a simple combination of numerical computing methods and neural networks, but rather achieves a complementary and mutually reinforcing advantages of both approaches. The data and code can be found at \url{https://github.com/hsbhc/HNS}.
PMNN:Physical Model-driven Neural Network for solving time-fractional differential equations
Oct 07, 2023
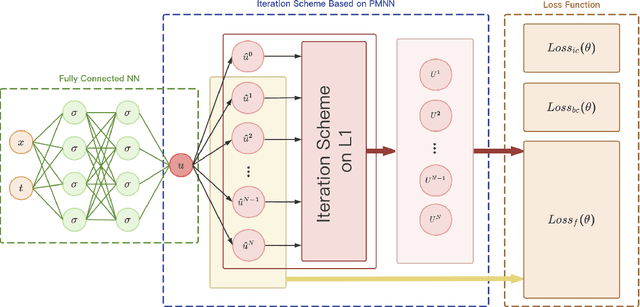
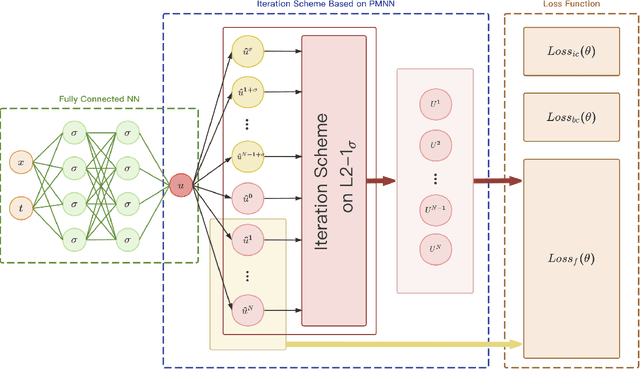
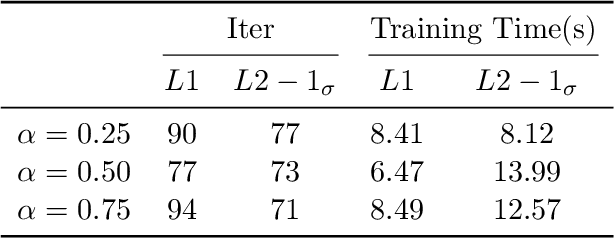
Abstract:In this paper, an innovative Physical Model-driven Neural Network (PMNN) method is proposed to solve time-fractional differential equations. It establishes a temporal iteration scheme based on physical model-driven neural networks which effectively combines deep neural networks (DNNs) with interpolation approximation of fractional derivatives. Specifically, once the fractional differential operator is discretized, DNNs are employed as a bridge to integrate interpolation approximation techniques with differential equations. On the basis of this integration, we construct a neural-based iteration scheme. Subsequently, by training DNNs to learn this temporal iteration scheme, approximate solutions to the differential equations can be obtained. The proposed method aims to preserve the intrinsic physical information within the equations as far as possible. It fully utilizes the powerful fitting capability of neural networks while maintaining the efficiency of the difference schemes for fractional differential equations. Moreover, we validate the efficiency and accuracy of PMNN through several numerical experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge