Zhixuan Zhou
A Moral- and Event- Centric Inspection of Gender Bias in Fairy Tales at A Large Scale
Nov 25, 2022



Abstract:Fairy tales are a common resource for young children to learn a language or understand how a society works. However, gender bias, e.g., stereotypical gender roles, in this literature may cause harm and skew children's world view. Instead of decades of qualitative and manual analysis of gender bias in fairy tales, we computationally analyze gender bias in a fairy tale dataset containing 624 fairy tales from 7 different cultures. We specifically examine gender difference in terms of moral foundations, which are measures of human morality, and events, which reveal human activities associated with each character. We find that the number of male characters is two times that of female characters, showing a disproportionate gender representation. Our analysis further reveal stereotypical portrayals of both male and female characters in terms of moral foundations and events. Female characters turn out more associated with care-, loyalty- and sanctity- related moral words, while male characters are more associated with fairness- and authority- related moral words. Female characters' events are often about emotion (e.g., weep), appearance (e.g., comb), household (e.g., bake), etc.; while male characters' events are more about profession (e.g., hunt), violence (e.g., destroy), justice (e.g., judge), etc. Gender bias in terms of moral foundations shows an obvious difference across cultures. For example, female characters are more associated with care and sanctity in high uncertainty-avoidance cultures which are less open to changes and unpredictability. Based on the results, we propose implications for children's literature and early literacy research.
AI Ethics Issues in Real World: Evidence from AI Incident Database
Jun 15, 2022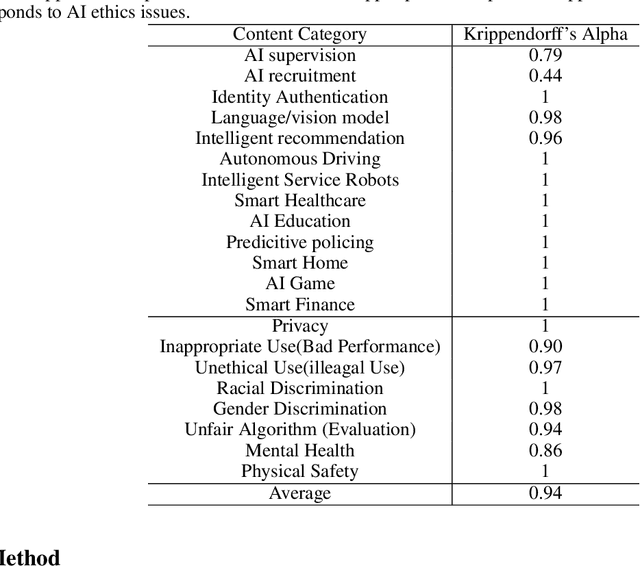

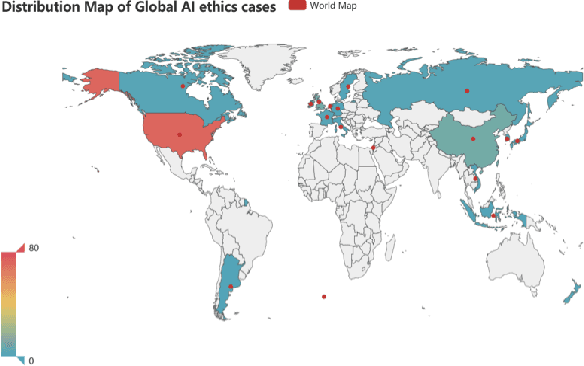

Abstract:With the powerful performance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) also comes prevalent ethical issues. Though governments and corporations have curated multiple AI ethics guidelines to curb unethical behavior of AI, the effect has been limited, probably due to the vagueness of the guidelines. In this paper, we take a closer look at how AI ethics issues take place in real world, in order to have a more in-depth and nuanced understanding of different ethical issues as well as their social impact. With a content analysis of AI Incident Database, which is an effort to prevent repeated real world AI failures by cataloging incidents, we identified 13 application areas which often see unethical use of AI, with intelligent service robots, language/vision models and autonomous driving taking the lead. Ethical issues appear in 8 different forms, from inappropriate use and racial discrimination, to physical safety and unfair algorithm. With this taxonomy of AI ethics issues, we aim to provide AI practitioners with a practical guideline when trying to deploy AI applications ethically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge