Zhipeng Yuan
PestMA: LLM-based Multi-Agent System for Informed Pest Management
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Effective pest management is complex due to the need for accurate, context-specific decisions. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) open new possibilities for addressing these challenges by providing sophisticated, adaptive knowledge acquisition and reasoning. However, existing LLM-based pest management approaches often rely on a single-agent paradigm, which can limit their capacity to incorporate diverse external information, engage in systematic validation, and address complex, threshold-driven decisions. To overcome these limitations, we introduce PestMA, an LLM-based multi-agent system (MAS) designed to generate reliable and evidence-based pest management advice. Building on an editorial paradigm, PestMA features three specialized agents, an Editor for synthesizing pest management recommendations, a Retriever for gathering relevant external data, and a Validator for ensuring correctness. Evaluations on real-world pest scenarios demonstrate that PestMA achieves an initial accuracy of 86.8% for pest management decisions, which increases to 92.6% after validation. These results underscore the value of collaborative agent-based workflows in refining and validating decisions, highlighting the potential of LLM-based multi-agent systems to automate and enhance pest management processes.
Exploring the Feasibility of Deep Learning Models for Long-term Disease Prediction: A Case Study for Wheat Yellow Rust in England
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:Wheat yellow rust, caused by the fungus Puccinia striiformis, is a critical disease affecting wheat crops across Britain, leading to significant yield losses and economic consequences. Given the rapid environmental changes and the evolving virulence of pathogens, there is a growing need for innovative approaches to predict and manage such diseases over the long term. This study explores the feasibility of using deep learning models to predict outbreaks of wheat yellow rust in British fields, offering a proactive approach to disease management. We construct a yellow rust dataset with historial weather information and disease indicator acrossing multiple regions in England. We employ two poweful deep learning models, including fully connected neural networks and long short-term memory to develop predictive models capable of recognizing patterns and predicting future disease outbreaks.The models are trained and validated in a randomly sliced datasets. The performance of these models with different predictive time steps are evaluated based on their accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Preliminary results indicate that deep learning models can effectively capture the complex interactions between multiple factors influencing disease dynamics, demonstrating a promising capacity to forecast wheat yellow rust with considerable accuracy. Specifically, the fully-connected neural network achieved 83.65% accuracy in a disease prediction task with 6 month predictive time step setup. These findings highlight the potential of deep learning to transform disease management strategies, enabling earlier and more precise interventions. Our study provides a methodological framework for employing deep learning in agricultural settings but also opens avenues for future research to enhance the robustness and applicability of predictive models in combating crop diseases globally.
Quantifying Nematodes through Images: Datasets, Models, and Baselines of Deep Learning
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Every year, plant parasitic nematodes, one of the major groups of plant pathogens, cause a significant loss of crops worldwide. To mitigate crop yield losses caused by nematodes, an efficient nematode monitoring method is essential for plant and crop disease management. In other respects, efficient nematode detection contributes to medical research and drug discovery, as nematodes are model organisms. With the rapid development of computer technology, computer vision techniques provide a feasible solution for quantifying nematodes or nematode infections. In this paper, we survey and categorise the studies and available datasets on nematode detection through deep-learning models. To stimulate progress in related research, this survey presents the potential state-of-the-art object detection models, training techniques, optimisation techniques, and evaluation metrics for deep learning beginners. Moreover, seven state-of-the-art object detection models are validated on three public datasets and the AgriNema dataset for plant parasitic nematodes to construct a baseline for nematode detection.
GPT-4 as Evaluator: Evaluating Large Language Models on Pest Management in Agriculture
Mar 18, 2024

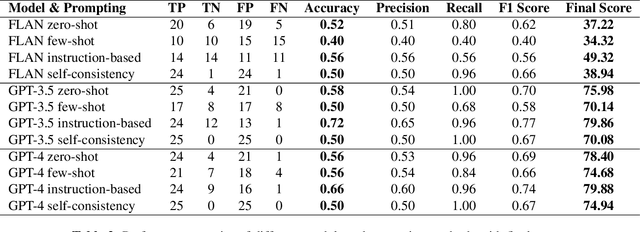
Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI), the application of large language models (LLMs) in agriculture, particularly in pest management, remains nascent. We aimed to prove the feasibility by evaluating the content of the pest management advice generated by LLMs, including the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) series from OpenAI and the FLAN series from Google. Considering the context-specific properties of agricultural advice, automatically measuring or quantifying the quality of text generated by LLMs becomes a significant challenge. We proposed an innovative approach, using GPT-4 as an evaluator, to score the generated content on Coherence, Logical Consistency, Fluency, Relevance, Comprehensibility, and Exhaustiveness. Additionally, we integrated an expert system based on crop threshold data as a baseline to obtain scores for Factual Accuracy on whether pests found in crop fields should take management action. Each model's score was weighted by percentage to obtain a final score. The results showed that GPT-3.4 and GPT-4 outperform the FLAN models in most evaluation categories. Furthermore, the use of instruction-based prompting containing domain-specific knowledge proved the feasibility of LLMs as an effective tool in agriculture, with an accuracy rate of 72%, demonstrating LLMs' effectiveness in providing pest management suggestions.
Embedding-based Retrieval with LLM for Effective Agriculture Information Extracting from Unstructured Data
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Pest identification is a crucial aspect of pest control in agriculture. However, most farmers are not capable of accurately identifying pests in the field, and there is a limited number of structured data sources available for rapid querying. In this work, we explored using domain-agnostic general pre-trained large language model(LLM) to extract structured data from agricultural documents with minimal or no human intervention. We propose a methodology that involves text retrieval and filtering using embedding-based retrieval, followed by LLM question-answering to automatically extract entities and attributes from the documents, and transform them into structured data. In comparison to existing methods, our approach achieves consistently better accuracy in the benchmark while maintaining efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge