Zhijie Bao
Strong Reasoning Isn't Enough: Evaluating Evidence Elicitation in Interactive Diagnosis
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Interactive medical consultation requires an agent to proactively elicit missing clinical evidence under uncertainty. Yet existing evaluations largely remain static or outcome-centric, neglecting the evidence-gathering process. In this work, we propose an interactive evaluation framework that explicitly models the consultation process using a simulated patient and a \rev{simulated reporter} grounded in atomic evidences. Based on this representation, we introduce Information Coverage Rate (ICR) to quantify how completely an agent uncovers necessary evidence during interaction. To support systematic study, we build EviMed, an evidence-based benchmark spanning diverse conditions from common complaints to rare diseases, and evaluate 10 models with varying reasoning abilities. We find that strong diagnostic reasoning does not guarantee effective information collection, and this insufficiency acts as a primary bottleneck limiting performance in interactive settings. To address this, we propose REFINE, a strategy that leverages diagnostic verification to guide the agent in proactively resolving uncertainties. Extensive experiments demonstrate that REFINE consistently outperforms baselines across diverse datasets and facilitates effective model collaboration, enabling smaller agents to achieve superior performance under strong reasoning supervision. Our code can be found at https://github.com/NanshineLoong/EID-Benchmark .
PIORS: Personalized Intelligent Outpatient Reception based on Large Language Model with Multi-Agents Medical Scenario Simulation
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:In China, receptionist nurses face overwhelming workloads in outpatient settings, limiting their time and attention for each patient and ultimately reducing service quality. In this paper, we present the Personalized Intelligent Outpatient Reception System (PIORS). This system integrates an LLM-based reception nurse and a collaboration between LLM and hospital information system (HIS) into real outpatient reception setting, aiming to deliver personalized, high-quality, and efficient reception services. Additionally, to enhance the performance of LLMs in real-world healthcare scenarios, we propose a medical conversational data generation framework named Service Flow aware Medical Scenario Simulation (SFMSS), aiming to adapt the LLM to the real-world environments and PIORS settings. We evaluate the effectiveness of PIORS and SFMSS through automatic and human assessments involving 15 users and 15 clinical experts. The results demonstrate that PIORS-Nurse outperforms all baselines, including the current state-of-the-art model GPT-4o, and aligns with human preferences and clinical needs. Further details and demo can be found at https://github.com/FudanDISC/PIORS
DISC-MedLLM: Bridging General Large Language Models and Real-World Medical Consultation
Aug 28, 2023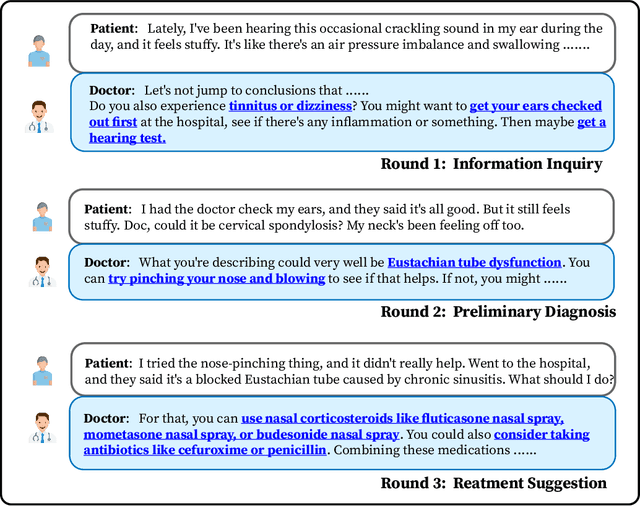
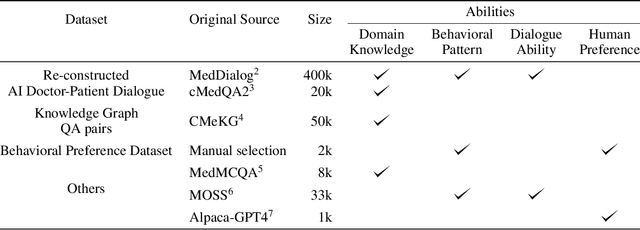
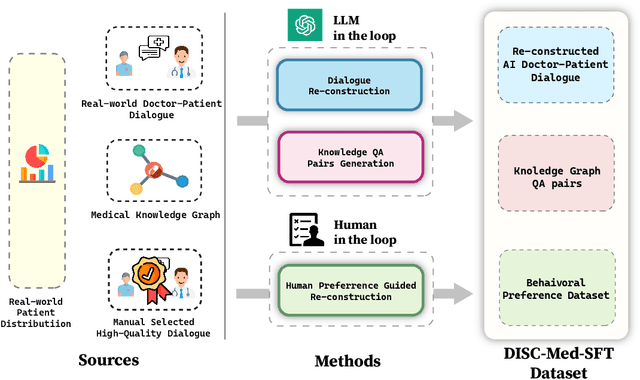
Abstract:We propose DISC-MedLLM, a comprehensive solution that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide accurate and truthful medical response in end-to-end conversational healthcare services. To construct high-quality Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) datasets, we employ three strategies: utilizing medical knowledge-graphs, reconstructing real-world dialogues, and incorporating human-guided preference rephrasing. These datasets are instrumental in training DISC-MedLLM, surpassing existing medical LLMs in both single-turn and multi-turn consultation scenarios. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model in bridging the gap between general language models and real-world medical consultation. Additionally, we release the constructed dataset and model weights to further contribute to research and development. Further details and resources can be found at https://github.com/FudanDISC/DISC-MedLLM
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge