Zheng Ren
Successive optimization of optics and post-processing with differentiable coherent PSF operator and field information
Dec 19, 2024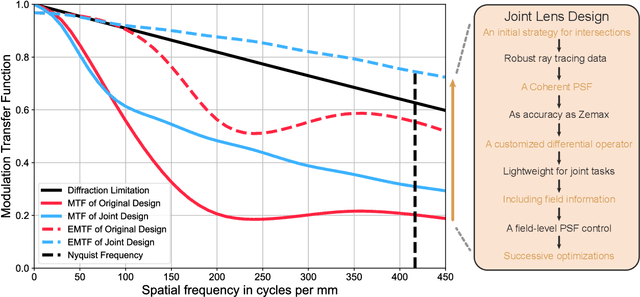
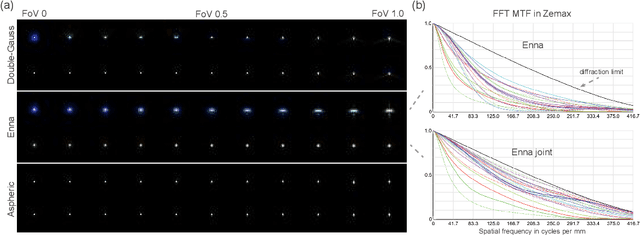
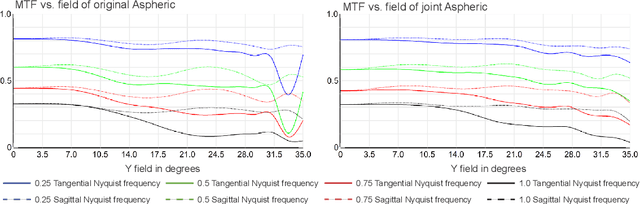
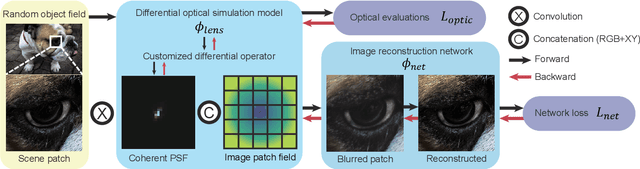
Abstract:Recently, the joint design of optical systems and downstream algorithms is showing significant potential. However, existing rays-described methods are limited to optimizing geometric degradation, making it difficult to fully represent the optical characteristics of complex, miniaturized lenses constrained by wavefront aberration or diffraction effects. In this work, we introduce a precise optical simulation model, and every operation in pipeline is differentiable. This model employs a novel initial value strategy to enhance the reliability of intersection calculation on high aspherics. Moreover, it utilizes a differential operator to reduce memory consumption during coherent point spread function calculations. To efficiently address various degradation, we design a joint optimization procedure that leverages field information. Guided by a general restoration network, the proposed method not only enhances the image quality, but also successively improves the optical performance across multiple lenses that are already in professional level. This joint optimization pipeline offers innovative insights into the practical design of sophisticated optical systems and post-processing algorithms. The source code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Zrr-ZJU/Successive-optimization
Revealing the preference for correcting separated aberrations in joint optic-image design
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:The joint design of the optical system and the downstream algorithm is a challenging and promising task. Due to the demand for balancing the global optimal of imaging systems and the computational cost of physical simulation, existing methods cannot achieve efficient joint design of complex systems such as smartphones and drones. In this work, starting from the perspective of the optical design, we characterize the optics with separated aberrations. Additionally, to bridge the hardware and software without gradients, an image simulation system is presented to reproduce the genuine imaging procedure of lenses with large field-of-views. As for aberration correction, we propose a network to perceive and correct the spatially varying aberrations and validate its superiority over state-of-the-art methods. Comprehensive experiments reveal that the preference for correcting separated aberrations in joint design is as follows: longitudinal chromatic aberration, lateral chromatic aberration, spherical aberration, field curvature, and coma, with astigmatism coming last. Drawing from the preference, a 10% reduction in the total track length of the consumer-level mobile phone lens module is accomplished. Moreover, this procedure spares more space for manufacturing deviations, realizing extreme-quality enhancement of computational photography. The optimization paradigm provides innovative insight into the practical joint design of sophisticated optical systems and post-processing algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge