Bingkun Chen
Successive optimization of optics and post-processing with differentiable coherent PSF operator and field information
Dec 19, 2024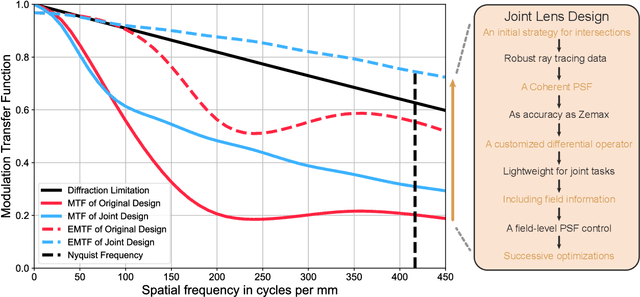
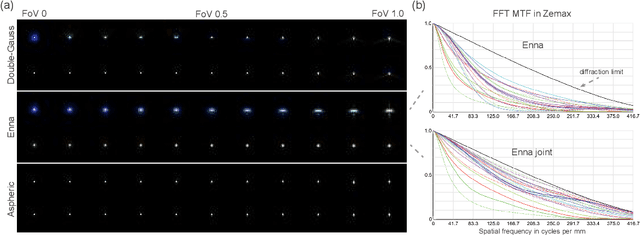
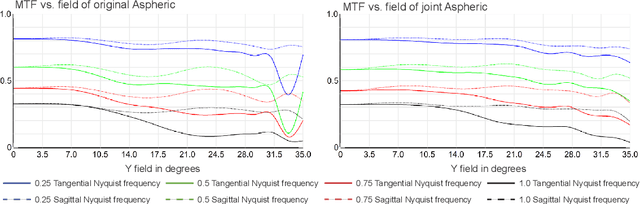
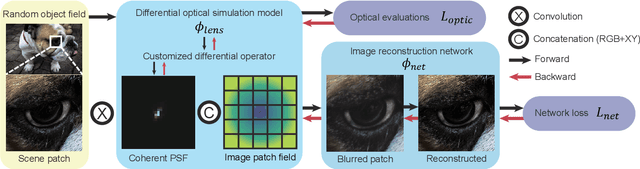
Abstract:Recently, the joint design of optical systems and downstream algorithms is showing significant potential. However, existing rays-described methods are limited to optimizing geometric degradation, making it difficult to fully represent the optical characteristics of complex, miniaturized lenses constrained by wavefront aberration or diffraction effects. In this work, we introduce a precise optical simulation model, and every operation in pipeline is differentiable. This model employs a novel initial value strategy to enhance the reliability of intersection calculation on high aspherics. Moreover, it utilizes a differential operator to reduce memory consumption during coherent point spread function calculations. To efficiently address various degradation, we design a joint optimization procedure that leverages field information. Guided by a general restoration network, the proposed method not only enhances the image quality, but also successively improves the optical performance across multiple lenses that are already in professional level. This joint optimization pipeline offers innovative insights into the practical design of sophisticated optical systems and post-processing algorithms. The source code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Zrr-ZJU/Successive-optimization
DSBERT:Unsupervised Dialogue Structure learning with BERT
Nov 09, 2021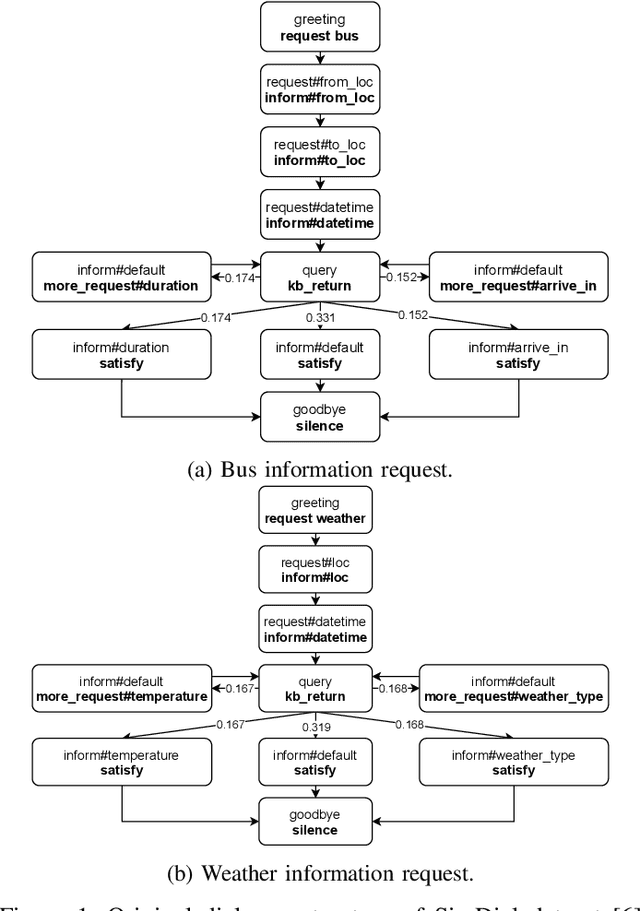

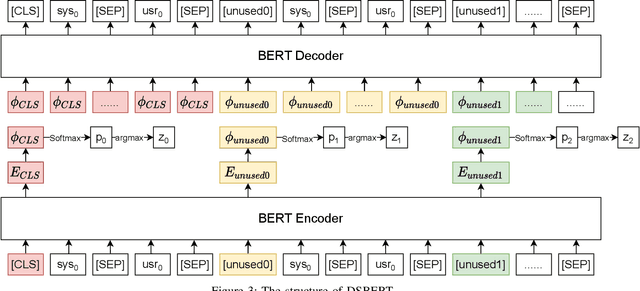

Abstract:Unsupervised dialogue structure learning is an important and meaningful task in natural language processing. The extracted dialogue structure and process can help analyze human dialogue, and play a vital role in the design and evaluation of dialogue systems. The traditional dialogue system requires experts to manually design the dialogue structure, which is very costly. But through unsupervised dialogue structure learning, dialogue structure can be automatically obtained, reducing the cost of developers constructing dialogue process. The learned dialogue structure can be used to promote the dialogue generation of the downstream task system, and improve the logic and consistency of the dialogue robot's reply.In this paper, we propose a Bert-based unsupervised dialogue structure learning algorithm DSBERT (Dialogue Structure BERT). Different from the previous SOTA models VRNN and SVRNN, we combine BERT and AutoEncoder, which can effectively combine context information. In order to better prevent the model from falling into the local optimal solution and make the dialogue state distribution more uniform and reasonable, we also propose three balanced loss functions that can be used for dialogue structure learning. Experimental results show that DSBERT can generate a dialogue structure closer to the real structure, can distinguish sentences with different semantics and map them to different hidden states.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge