Zhaohao Wang
Helen
Comparison research on binary relations based on transitive degrees and cluster degrees
Jan 25, 2022



Abstract:Interval-valued information systems are generalized models of single-valued information systems. By rough set approach, interval-valued information systems have been extensively studied. Authors could establish many binary relations from the same interval-valued information system. In this paper, we do some researches on comparing these binary relations so as to provide numerical scales for choosing suitable relations in dealing with interval-valued information systems. Firstly, based on similarity degrees, we compare the most common three binary relations induced from the same interval-valued information system. Secondly, we propose the concepts of transitive degree and cluster degree, and investigate their properties. Finally, we provide some methods to compare binary relations by means of the transitive degree and the cluster degree. Furthermore, we use these methods to analyze the most common three relations induced from Face Recognition Dataset, and obtain that $RF_{B} ^{\lambda}$ is a good choice when we deal with an interval-valued information system by means of rough set approach.
Spintronics based Stochastic Computing for Efficient Bayesian Inference System
Nov 03, 2017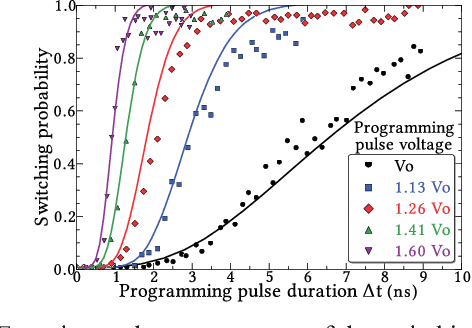
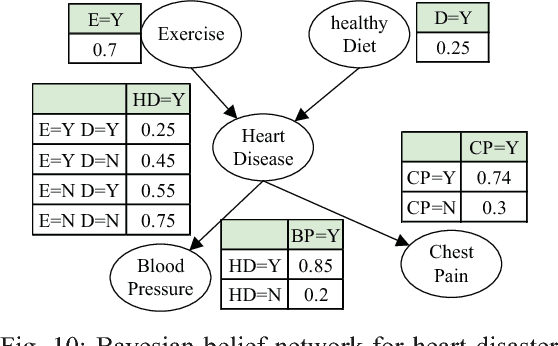
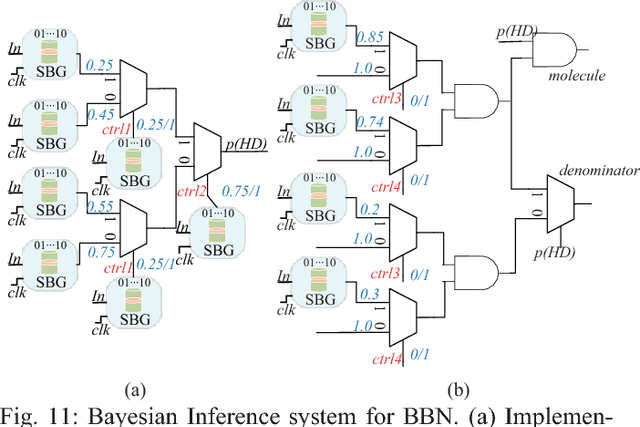
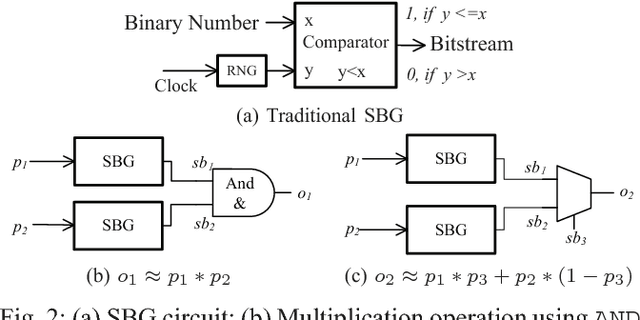
Abstract:Bayesian inference is an effective approach for solving statistical learning problems especially with uncertainty and incompleteness. However, inference efficiencies are physically limited by the bottlenecks of conventional computing platforms. In this paper, an emerging Bayesian inference system is proposed by exploiting spintronics based stochastic computing. A stochastic bitstream generator is realized as the kernel components by leveraging the inherent randomness of spintronics devices. The proposed system is evaluated by typical applications of data fusion and Bayesian belief networks. Simulation results indicate that the proposed approach could achieve significant improvement on inference efficiencies in terms of power consumption and inference speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge