Zhanqiu Guo
DynaMem: Online Dynamic Spatio-Semantic Memory for Open World Mobile Manipulation
Nov 07, 2024
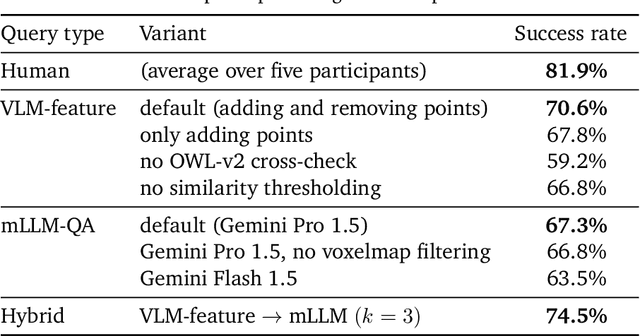
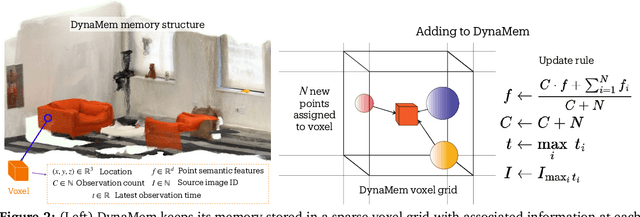
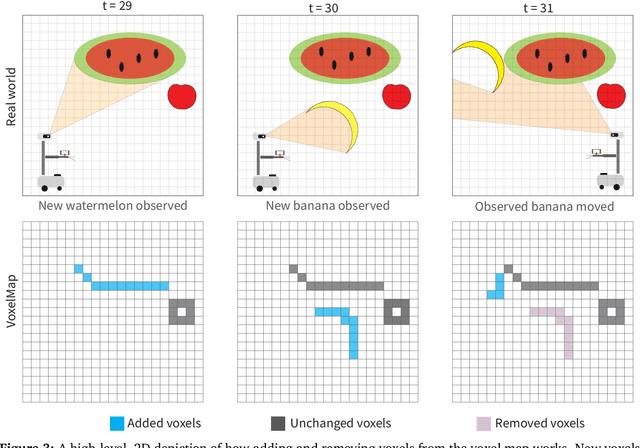
Abstract:Significant progress has been made in open-vocabulary mobile manipulation, where the goal is for a robot to perform tasks in any environment given a natural language description. However, most current systems assume a static environment, which limits the system's applicability in real-world scenarios where environments frequently change due to human intervention or the robot's own actions. In this work, we present DynaMem, a new approach to open-world mobile manipulation that uses a dynamic spatio-semantic memory to represent a robot's environment. DynaMem constructs a 3D data structure to maintain a dynamic memory of point clouds, and answers open-vocabulary object localization queries using multimodal LLMs or open-vocabulary features generated by state-of-the-art vision-language models. Powered by DynaMem, our robots can explore novel environments, search for objects not found in memory, and continuously update the memory as objects move, appear, or disappear in the scene. We run extensive experiments on the Stretch SE3 robots in three real and nine offline scenes, and achieve an average pick-and-drop success rate of 70% on non-stationary objects, which is more than a 2x improvement over state-of-the-art static systems. Our code as well as our experiment and deployment videos are open sourced and can be found on our project website: https://dynamem.github.io/
ContextWIN: Whittle Index Based Mixture-of-Experts Neural Model For Restless Bandits Via Deep RL
Oct 13, 2024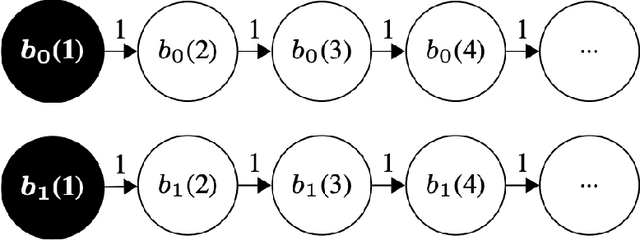
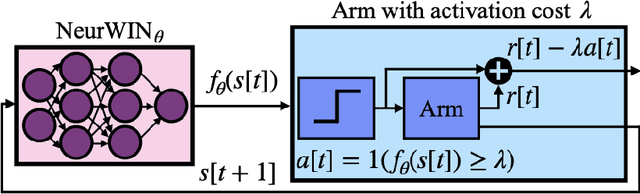
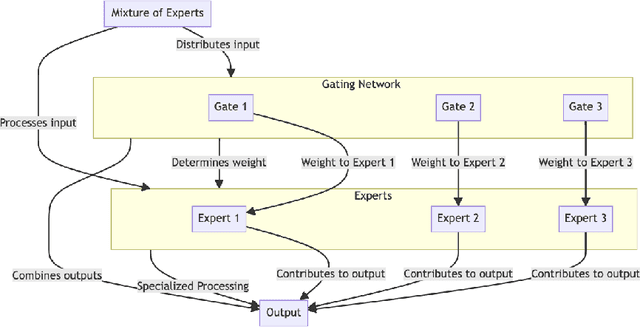

Abstract:This study introduces ContextWIN, a novel architecture that extends the Neural Whittle Index Network (NeurWIN) model to address Restless Multi-Armed Bandit (RMAB) problems with a context-aware approach. By integrating a mixture of experts within a reinforcement learning framework, ContextWIN adeptly utilizes contextual information to inform decision-making in dynamic environments, particularly in recommendation systems. A key innovation is the model's ability to assign context-specific weights to a subset of NeurWIN networks, thus enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of the Whittle index computation for each arm. The paper presents a thorough exploration of ContextWIN, from its conceptual foundation to its implementation and potential applications. We delve into the complexities of RMABs and the significance of incorporating context, highlighting how ContextWIN effectively harnesses these elements. The convergence of both the NeurWIN and ContextWIN models is rigorously proven, ensuring theoretical robustness. This work lays the groundwork for future advancements in applying contextual information to complex decision-making scenarios, recognizing the need for comprehensive dataset exploration and environment development for full potential realization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge