Zhankun Luo
Structural Properties, Cycloid Trajectories and Non-Asymptotic Guarantees of EM Algorithm for Mixed Linear Regression
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:This work investigates the structural properties, cycloid trajectories, and non-asymptotic convergence guarantees of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm for two-component Mixed Linear Regression (2MLR) with unknown mixing weights and regression parameters. Recent studies have established global convergence for 2MLR with known balanced weights and super-linear convergence in noiseless and high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regimes. However, the theoretical behavior of EM in the fully unknown setting remains unclear, with its trajectory and convergence order not yet fully characterized. We derive explicit EM update expressions for 2MLR with unknown mixing weights and regression parameters across all SNR regimes and analyze their structural properties and cycloid trajectories. In the noiseless case, we prove that the trajectory of the regression parameters in EM iterations traces a cycloid by establishing a recurrence relation for the sub-optimality angle, while in high SNR regimes we quantify its discrepancy from the cycloid trajectory. The trajectory-based analysis reveals the order of convergence: linear when the EM estimate is nearly orthogonal to the ground truth, and quadratic when the angle between the estimate and ground truth is small at the population level. Our analysis establishes non-asymptotic guarantees by sharpening bounds on statistical errors between finite-sample and population EM updates, relating EM's statistical accuracy to the sub-optimality angle, and proving convergence with arbitrary initialization at the finite-sample level. This work provides a novel trajectory-based framework for analyzing EM in Mixed Linear Regression.
Characterizing Evolution in Expectation-Maximization Estimates for Overspecified Mixed Linear Regression
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Mixture models have attracted significant attention due to practical effectiveness and comprehensive theoretical foundations. A persisting challenge is model misspecification, which occurs when the model to be fitted has more mixture components than those in the data distribution. In this paper, we develop a theoretical understanding of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm's behavior in the context of targeted model misspecification for overspecified two-component Mixed Linear Regression (2MLR) with unknown $d$-dimensional regression parameters and mixing weights. In Theorem 5.1 at the population level, with an unbalanced initial guess for mixing weights, we establish linear convergence of regression parameters in $O(\log(1/\epsilon))$ steps. Conversely, with a balanced initial guess for mixing weights, we observe sublinear convergence in $O(\epsilon^{-2})$ steps to achieve the $\epsilon$-accuracy at Euclidean distance. In Theorem 6.1 at the finite-sample level, for mixtures with sufficiently unbalanced fixed mixing weights, we demonstrate a statistical accuracy of $O((d/n)^{1/2})$, whereas for those with sufficiently balanced fixed mixing weights, the accuracy is $O((d/n)^{1/4})$ given $n$ data samples. Furthermore, we underscore the connection between our population level and finite-sample level results: by setting the desired final accuracy $\epsilon$ in Theorem 5.1 to match that in Theorem 6.1 at the finite-sample level, namely letting $\epsilon = O((d/n)^{1/2})$ for sufficiently unbalanced fixed mixing weights and $\epsilon = O((d/n)^{1/4})$ for sufficiently balanced fixed mixing weights, we intuitively derive iteration complexity bounds $O(\log (1/\epsilon))=O(\log (n/d))$ and $O(\epsilon^{-2})=O((n/d)^{1/2})$ at the finite-sample level for sufficiently unbalanced and balanced initial mixing weights. We further extend our analysis in overspecified setting to low SNR regime.
Unveiling the Cycloid Trajectory of EM Iterations in Mixed Linear Regression
May 28, 2024Abstract:We study the trajectory of iterations and the convergence rates of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm for two-component Mixed Linear Regression (2MLR). The fundamental goal of MLR is to learn the regression models from unlabeled observations. The EM algorithm finds extensive applications in solving the mixture of linear regressions. Recent results have established the super-linear convergence of EM for 2MLR in the noiseless and high SNR settings under some assumptions and its global convergence rate with random initialization has been affirmed. However, the exponent of convergence has not been theoretically estimated and the geometric properties of the trajectory of EM iterations are not well-understood. In this paper, first, using Bessel functions we provide explicit closed-form expressions for the EM updates under all SNR regimes. Then, in the noiseless setting, we completely characterize the behavior of EM iterations by deriving a recurrence relation at the population level and notably show that all the iterations lie on a certain cycloid. Based on this new trajectory-based analysis, we exhibit the theoretical estimate for the exponent of super-linear convergence and further improve the statistical error bound at the finite-sample level. Our analysis provides a new framework for studying the behavior of EM for Mixed Linear Regression.
High-Resolution UAV Image Generation for Sorghum Panicle Detection
May 08, 2022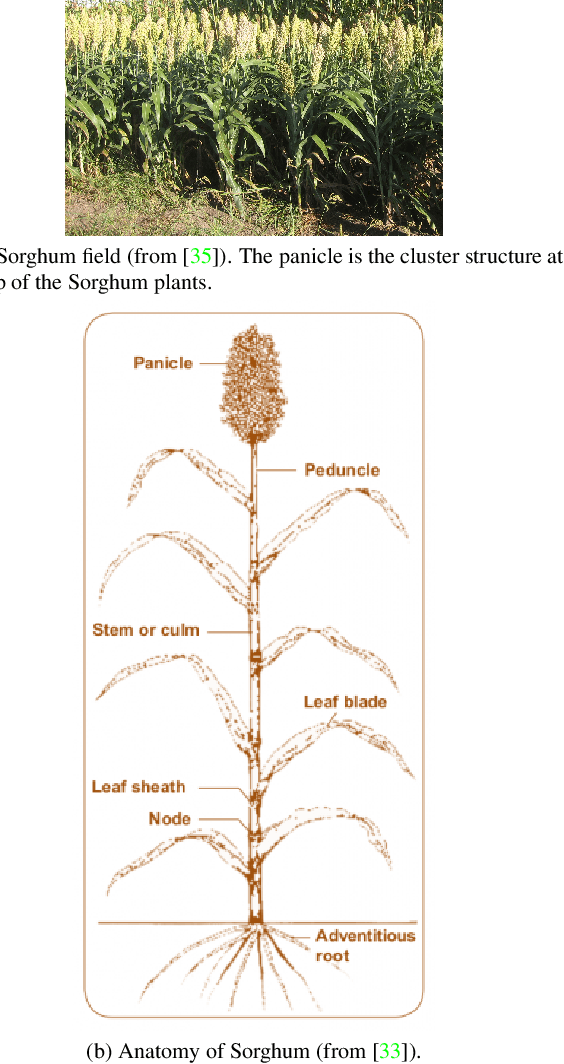
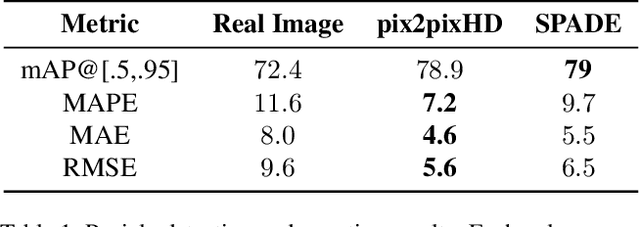

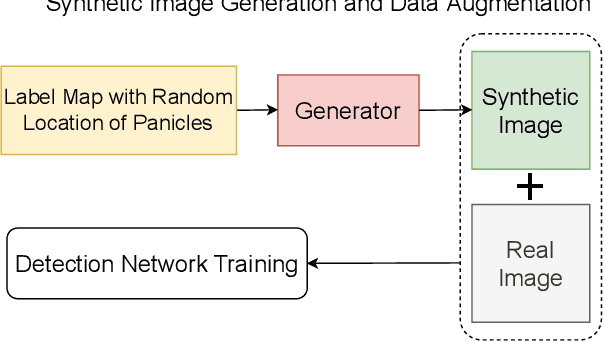
Abstract:The number of panicles (or heads) of Sorghum plants is an important phenotypic trait for plant development and grain yield estimation. The use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) enables the capability of collecting and analyzing Sorghum images on a large scale. Deep learning can provide methods for estimating phenotypic traits from UAV images but requires a large amount of labeled data. The lack of training data due to the labor-intensive ground truthing of UAV images causes a major bottleneck in developing methods for Sorghum panicle detection and counting. In this paper, we present an approach that uses synthetic training images from generative adversarial networks (GANs) for data augmentation to enhance the performance of Sorghum panicle detection and counting. Our method can generate synthetic high-resolution UAV RGB images with panicle labels by using image-to-image translation GANs with a limited ground truth dataset of real UAV RGB images. The results show the improvements in panicle detection and counting using our data augmentation approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge