Zdeněk Hanzálek
Czech Institute of Informatics, Robotics and Cybernetics, Czech Technical University in Prague
Resource-constrained Project Scheduling with Time-of-Use Energy Tariffs and Machine States: A Logic-based Benders Decomposition Approach
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP) with time-of-use energy tariffs (TOU) and machine states, a variant of RCPSP for production scheduling where energy price is part of the criteria and one machine is highly energy-demanding and can be in one of the following three states: proc, idle, or off. The problem involves scheduling all tasks, respecting precedence constraints and resource limitations, while minimizing the combination of the overall makespan and the total energy cost (TEC), which varies according to the TOU pricing, which can take negative values. We propose two novel approaches to solve it: a monolithic Constraint Programming (CP) approach and a Logic-Based Benders Decomposition (LBBD) approach. The latter combines a master problem dealing with energy cost solved using Integer Linear Programming (ILP) with a subproblem handling the RCPSP resolved using CP. Both approaches surpass the monolithic compact ILP approach, but the LBBD significantly outperforms the CP when the ratio of energy-intensive tasks over the overall tasks is moderate, allowing for solving instances with up to 1600 tasks in sparse instances. Finally, we put forth a way of generalizing our LBBD approach to other problems sharing similar characteristics, and we applied it to a problem based on an RCPSP problem with blocking times & total weighted tardiness criterion and a flexible job shop.
Reinforcement Learning for Search Tree Size Minimization in Constraint Programming: New Results on Scheduling Benchmarks
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Failure-Directed Search (FDS) is a significant complete generic search algorithm used in Constraint Programming (CP) to efficiently explore the search space, proven particularly effective on scheduling problems. This paper analyzes FDS's properties, showing that minimizing the size of its search tree guided by ranked branching decisions is closely related to the Multi-armed bandit (MAB) problem. Building on this insight, MAB reinforcement learning algorithms are applied to FDS, extended with problem-specific refinements and parameter tuning, and evaluated on the two most fundamental scheduling problems, the Job Shop Scheduling Problem (JSSP) and Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP). The resulting enhanced FDS, using the best extended MAB algorithm and configuration, performs 1.7 times faster on the JSSP and 2.1 times faster on the RCPSP benchmarks compared to the original implementation in a new solver called OptalCP, while also being 3.5 times faster on the JSSP and 2.1 times faster on the RCPSP benchmarks than the current state-of-the-art FDS algorithm in IBM CP Optimizer 22.1. Furthermore, using only a 900-second time limit per instance, the enhanced FDS improved the existing state-of-the-art lower bounds of 78 of 84 JSSP and 226 of 393 RCPSP standard open benchmark instances while also completely closing a few of them.
POMDP-Based Trajectory Planning for On-Ramp Highway Merging
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses the trajectory planning problem for automated vehicle on-ramp highway merging. To tackle this challenge, we extend our previous work on trajectory planning at unsignalized intersections using Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDPs). The method utilizes the Adaptive Belief Tree (ABT) algorithm, an approximate sampling-based approach to solve POMDPs efficiently. We outline the POMDP formulation process, beginning with discretizing the highway topology to reduce problem complexity. Additionally, we describe the dynamics and measurement models used to predict future states and establish the relationship between available noisy measurements and predictions. Building on our previous work, the dynamics model is expanded to account for lateral movements necessary for lane changes during the merging process. We also define the reward function, which serves as the primary mechanism for specifying the desired behavior of the automated vehicle, combining multiple goals such as avoiding collisions or maintaining appropriate velocity. Our simulation results, conducted on three scenarios based on real-life traffic data from German highways, demonstrate the method's ability to generate safe, collision-free, and efficient merging trajectories. This work shows the versatility of this POMDP-based approach in tackling various automated driving problems.
Low Fidelity Digital Twin for Automated Driving Systems: Use Cases and Automatic Generation
May 22, 2024


Abstract:Automated driving systems are an integral part of the automotive industry. Tools such as Robot Operating System and simulators support their development. However, in the end, the developers must test their algorithms on a real vehicle. To better observe the difference between reality and simulation--the reality gap--digital twin technology offers real-time communication between the real vehicle and its model. We present low fidelity digital twin generator and describe situations where automatic generation is preferable to high fidelity simulation. We validated our approach of generating a virtual environment with a vehicle model by replaying the data recorded from the real vehicle.
Deep learning-driven scheduling algorithm for a single machine problem minimizing the total tardiness
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the use of the deep learning method for solving a well-known NP-hard single machine scheduling problem with the objective of minimizing the total tardiness. We propose a deep neural network that acts as a polynomial-time estimator of the criterion value used in a single-pass scheduling algorithm based on Lawler's decomposition and symmetric decomposition proposed by Della Croce et al. Essentially, the neural network guides the algorithm by estimating the best splitting of the problem into subproblems. The paper also describes a new method for generating the training data set, which speeds up the training dataset generation and reduces the average optimality gap of solutions. The experimental results show that our machine learning-driven approach can efficiently generalize information from the training phase to significantly larger instances. Even though the instances used in the training phase have from 75 to 100 jobs, the average optimality gap on instances with up to 800 jobs is 0.26%, which is almost five times less than the gap of the state-of-the-art heuristic.
Improving RRT for Automated Parking in Real-world Scenarios
Oct 31, 2023



Abstract:Automated parking is a self-driving feature that has been in cars for several years. Parking assistants in currently sold cars fail to park in more complex real-world scenarios and require the driver to move the car to an expected starting position before the assistant is activated. We overcome these limitations by proposing a planning algorithm consisting of two stages: (1) a geometric planner for maneuvering inside the parking slot and (2) a Rapidly-exploring Random Trees (RRT)-based planner that finds a collision-free path from the initial position to the slot entry. Evaluation of computational experiments demonstrates that improvements over commonly used RRT extensions reduce the parking path cost by 21 % and reduce the computation time by 79.5 %. The suitability of the algorithm for real-world parking scenarios was verified in physical experiments with Porsche Cayenne.
Parallel Parking: Optimal Entry and Minimum Slot Dimensions
May 05, 2022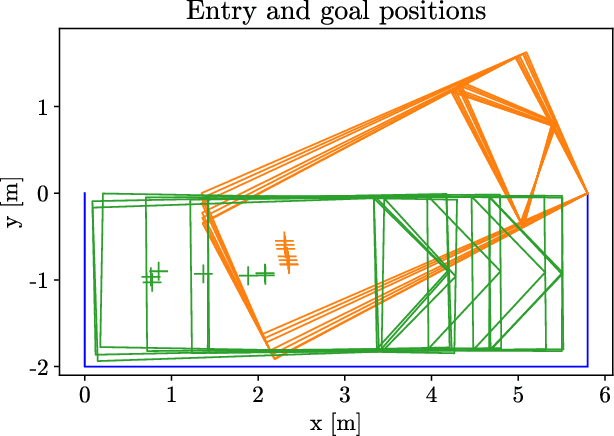
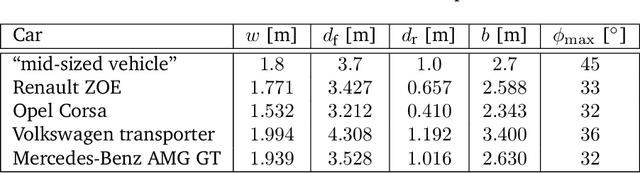
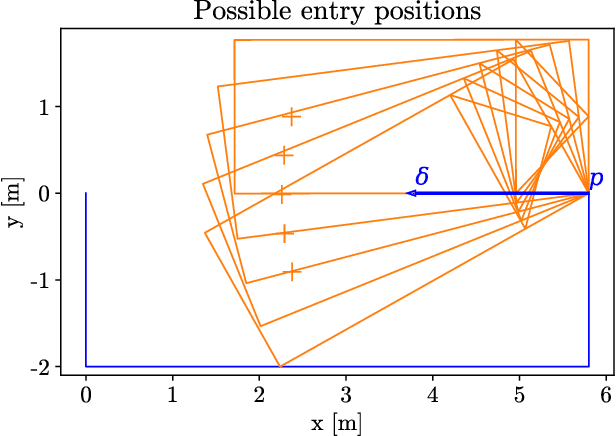
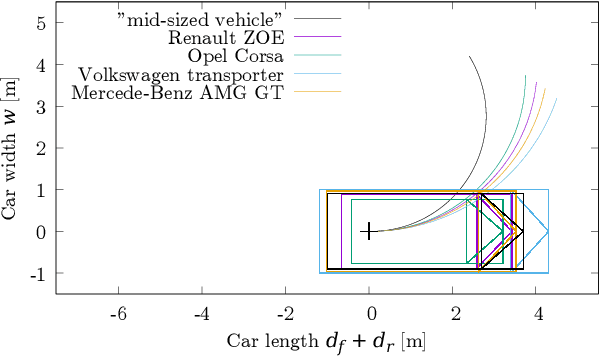
Abstract:The problem of path planning for automated parking is usually presented as finding a collision-free path from initial to goal positions, where three out of four parking slot edges represent obstacles. We rethink the path planning problem for parallel parking by decomposing it into two independent parts. The topic of this paper is finding optimal parking slot entry positions. Path planning from initial to entry position is out of scope here. We show the relation between entry positions, parking slot dimensions, and the number of backward-forward direction changes. This information can be used as an input to optimize other parts of the automated parking process.
* 14 pages (title + 9 of paper + 4 of appendix), 11 (paper) + 4 (appendix) figures, sent to VEHITS 2022 conference
Data-driven Algorithm for Scheduling with Total Tardiness
May 12, 2020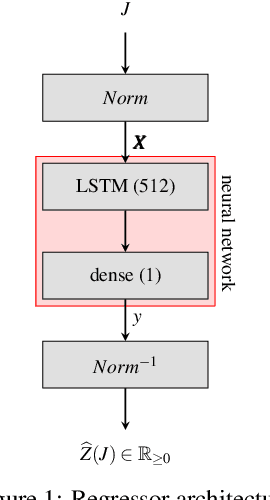
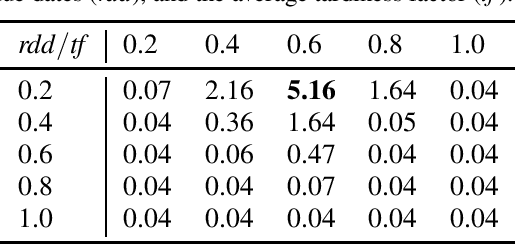
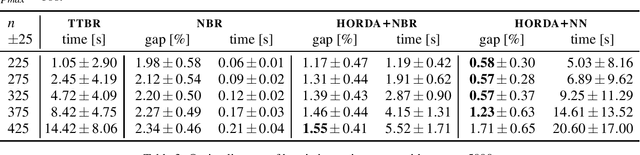
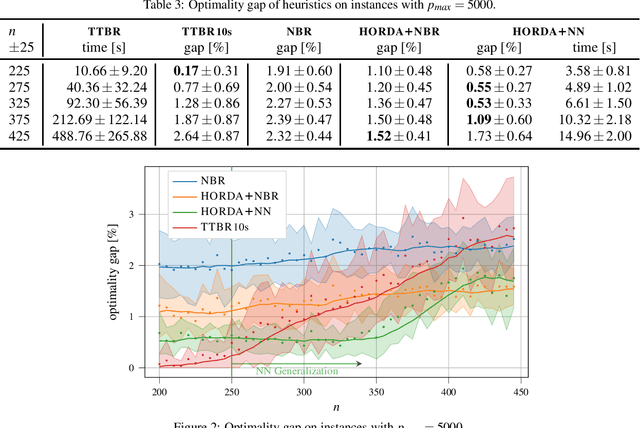
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the use of deep learning for solving a classical NP-Hard single machine scheduling problem where the criterion is to minimize the total tardiness. Instead of designing an end-to-end machine learning model, we utilize well known decomposition of the problem and we enhance it with a data-driven approach. We have designed a regressor containing a deep neural network that learns and predicts the criterion of a given set of jobs. The network acts as a polynomial-time estimator of the criterion that is used in a single-pass scheduling algorithm based on Lawler's decomposition theorem. Essentially, the regressor guides the algorithm to select the best position for each job. The experimental results show that our data-driven approach can efficiently generalize information from the training phase to significantly larger instances (up to 350 jobs) where it achieves an optimality gap of about 0.5%, which is four times less than the gap of the state-of-the-art NBR heuristic.
Accelerated RRT* and its evaluation on Autonomous Parking
Feb 11, 2020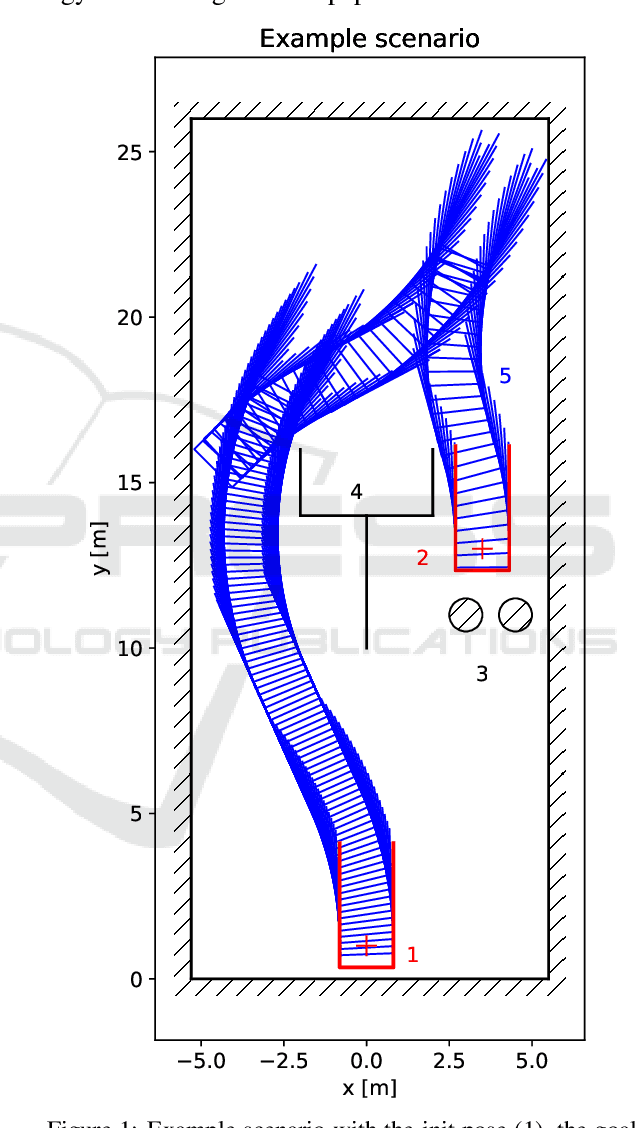
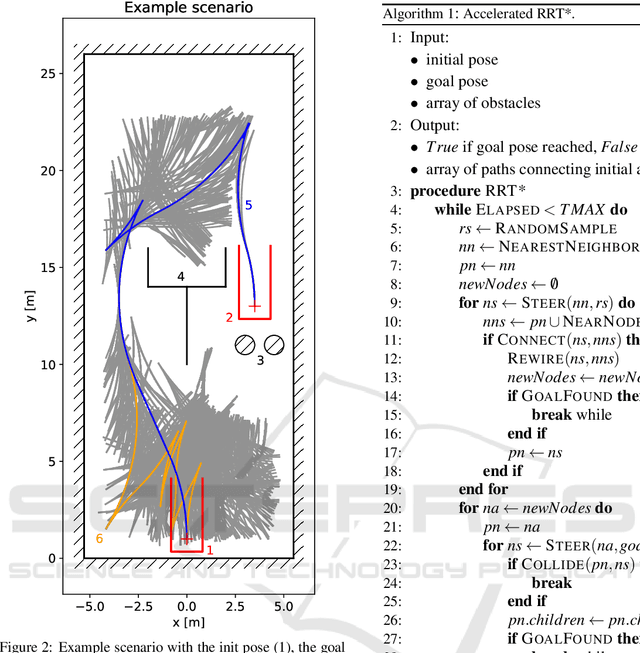
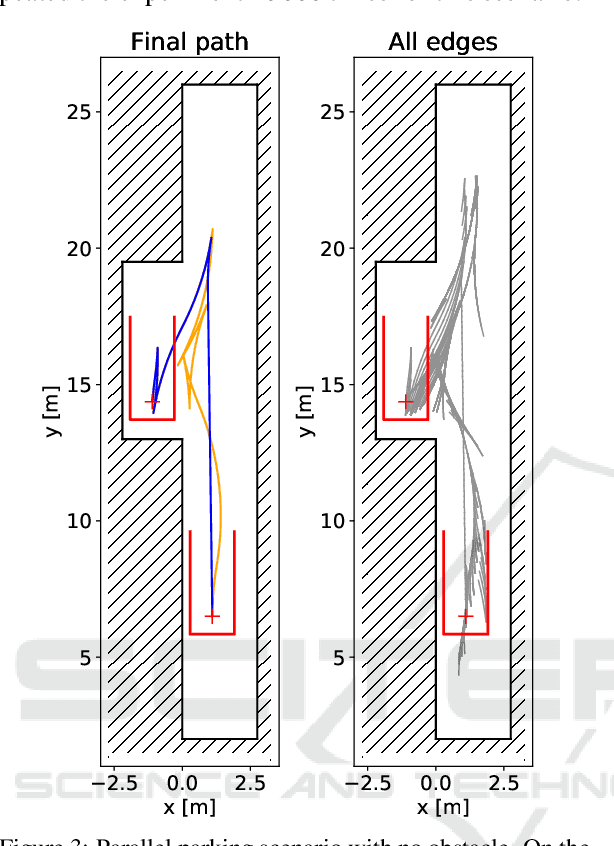
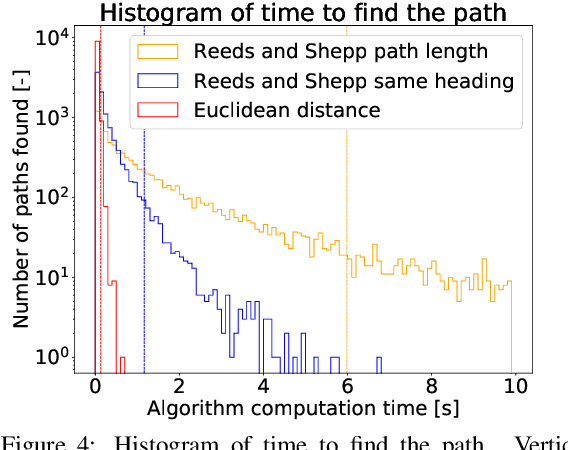
Abstract:Finding a collision-free path for autonomous parking is usually performed by computing geometric equations, but the geometric approach may become unusable under challenging situations where space is highly constrained. We propose an algorithm based on Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees Star (RRT*), which works even in highly constrained environments and improvements to RRT*-based algorithm that accelerate computational time and decrease the final path cost. Our improved RRT* algorithm found a path for parallel parking maneuver in 95 % of cases in less than 0.15 seconds.
* 12 pages, 6 figures, 3 pseudocodes, VEHITS 2019 conference proceedings
Roster Evaluation Based on Classifiers for the Nurse Rostering Problem
Apr 13, 2018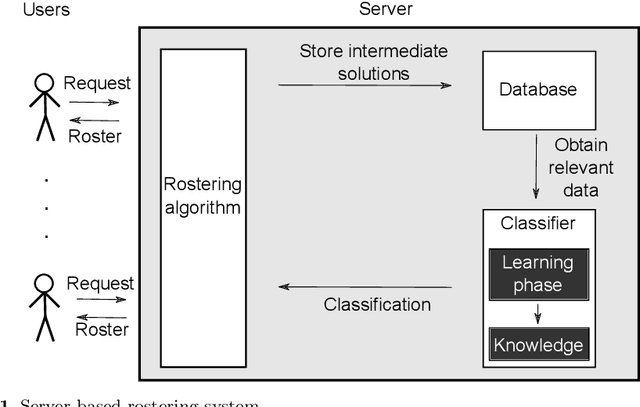
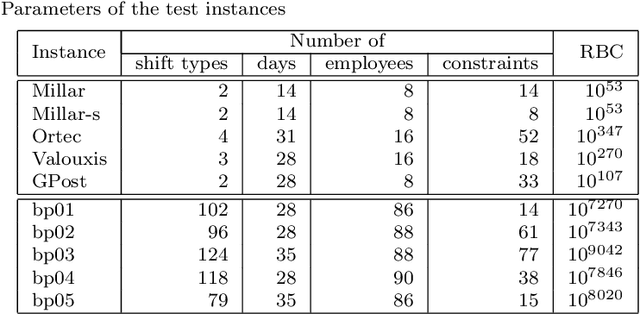
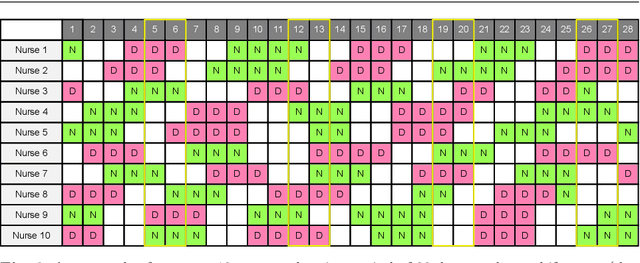
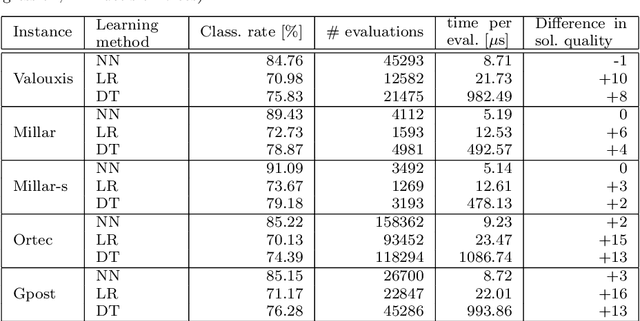
Abstract:The personnel scheduling problem is a well-known NP-hard combinatorial problem. Due to the complexity of this problem and the size of the real-world instances, it is not possible to use exact methods, and thus heuristics, meta-heuristics, or hyper-heuristics must be employed. The majority of heuristic approaches are based on iterative search, where the quality of intermediate solutions must be calculated. Unfortunately, this is computationally highly expensive because these problems have many constraints and some are very complex. In this study, we propose a machine learning technique as a tool to accelerate the evaluation phase in heuristic approaches. The solution is based on a simple classifier, which is able to determine whether the changed solution (more precisely, the changed part of the solution) is better than the original or not. This decision is made much faster than a standard cost-oriented evaluation process. However, the classification process cannot guarantee 100% correctness. Therefore, our approach, which is illustrated using a tabu search algorithm in this study, includes a filtering mechanism, where the classifier rejects the majority of the potentially bad solutions and the remaining solutions are then evaluated in a standard manner. We also show how the boosting algorithms can improve the quality of the final solution compared with a simple classifier. We verified our proposed approach and premises, based on standard and real-world benchmark instances, to demonstrate the significant speedup obtained with comparable solution quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge