Zahra Khanjani
ALDAS: Audio-Linguistic Data Augmentation for Spoofed Audio Detection
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Spoofed audio, i.e. audio that is manipulated or AI-generated deepfake audio, is difficult to detect when only using acoustic features. Some recent innovative work involving AI-spoofed audio detection models augmented with phonetic and phonological features of spoken English, manually annotated by experts, led to improved model performance. While this augmented model produced substantial improvements over traditional acoustic features based models, a scalability challenge motivates inquiry into auto labeling of features. In this paper we propose an AI framework, Audio-Linguistic Data Augmentation for Spoofed audio detection (ALDAS), for auto labeling linguistic features. ALDAS is trained on linguistic features selected and extracted by sociolinguistics experts; these auto labeled features are used to evaluate the quality of ALDAS predictions. Findings indicate that while the detection enhancement is not as substantial as when involving the pure ground truth linguistic features, there is improvement in performance while achieving auto labeling. Labels generated by ALDAS are also validated by the sociolinguistics experts.
Investigating Causal Cues: Strengthening Spoofed Audio Detection with Human-Discernible Linguistic Features
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:Several types of spoofed audio, such as mimicry, replay attacks, and deepfakes, have created societal challenges to information integrity. Recently, researchers have worked with sociolinguistics experts to label spoofed audio samples with Expert Defined Linguistic Features (EDLFs) that can be discerned by the human ear: pitch, pause, word-initial and word-final release bursts of consonant stops, audible intake or outtake of breath, and overall audio quality. It is established that there is an improvement in several deepfake detection algorithms when they augmented the traditional and common features of audio data with these EDLFs. In this paper, using a hybrid dataset comprised of multiple types of spoofed audio augmented with sociolinguistic annotations, we investigate causal discovery and inferences between the discernible linguistic features and the label in the audio clips, comparing the findings of the causal models with the expert ground truth validation labeling process. Our findings suggest that the causal models indicate the utility of incorporating linguistic features to help discern spoofed audio, as well as the overall need and opportunity to incorporate human knowledge into models and techniques for strengthening AI models. The causal discovery and inference can be used as a foundation of training humans to discern spoofed audio as well as automating EDLFs labeling for the purpose of performance improvement of the common AI-based spoofed audio detectors.
Audio Deepfake Perceptions in College Going Populations
Dec 06, 2021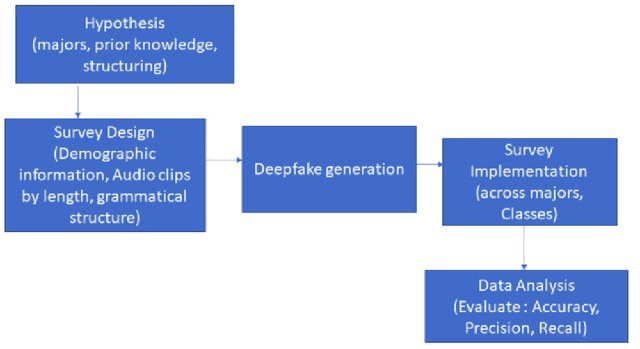
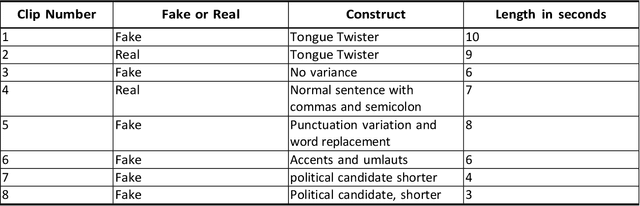

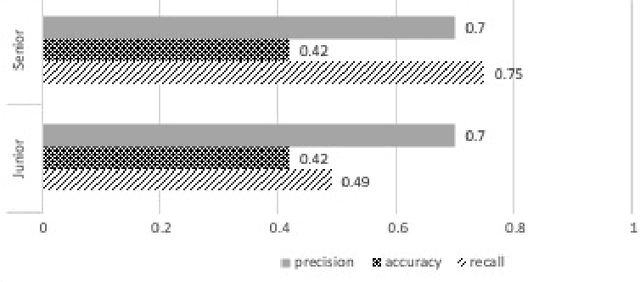
Abstract:Deepfake is content or material that is generated or manipulated using AI methods, to pass off as real. There are four different deepfake types: audio, video, image and text. In this research we focus on audio deepfakes and how people perceive it. There are several audio deepfake generation frameworks, but we chose MelGAN which is a non-autoregressive and fast audio deepfake generating framework, requiring fewer parameters. This study tries to assess audio deepfake perceptions among college students from different majors. This study also answers the question of how their background and major can affect their perception towards AI generated deepfakes. We also analyzed the results based on different aspects of: grade level, complexity of the grammar used in the audio clips, length of the audio clips, those who knew the term deepfakes and those who did not, as well as the political angle. It is interesting that the results show when an audio clip has a political connotation, it can affect what people think about whether it is real or fake, even if the content is fairly similar. This study also explores the question of how background and major can affect perception towards deepfakes.
How Deep Are the Fakes? Focusing on Audio Deepfake: A Survey
Nov 28, 2021
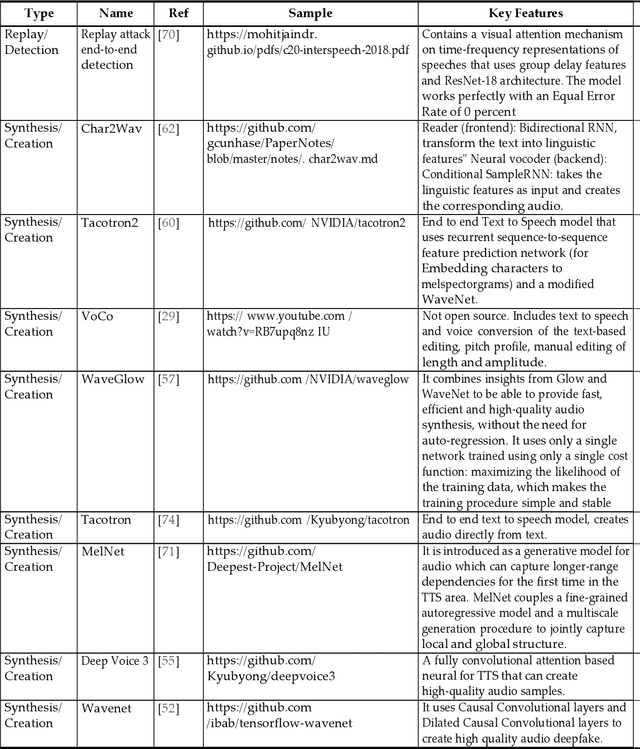
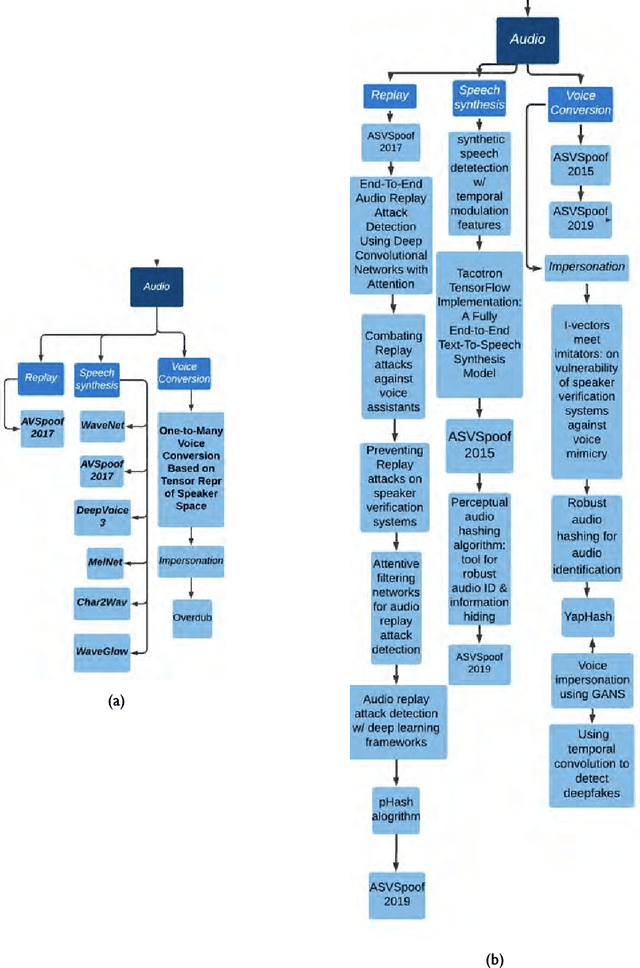
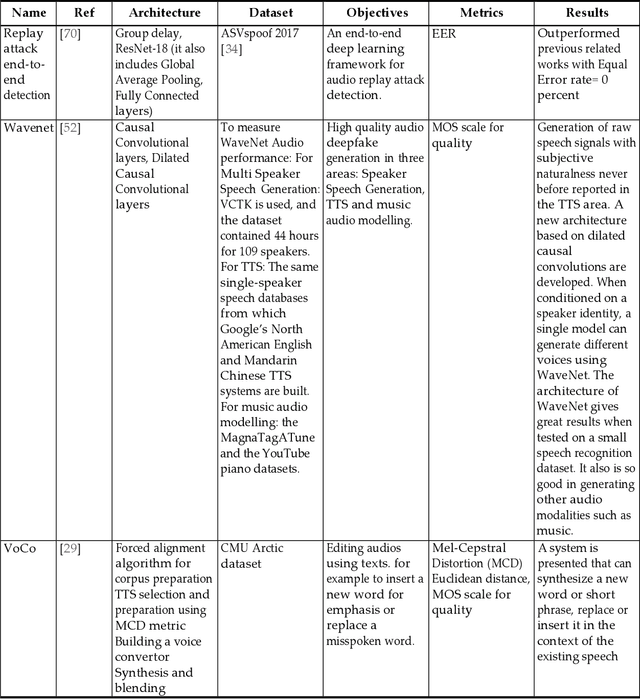
Abstract:Deepfake is content or material that is synthetically generated or manipulated using artificial intelligence (AI) methods, to be passed off as real and can include audio, video, image, and text synthesis. This survey has been conducted with a different perspective compared to existing survey papers, that mostly focus on just video and image deepfakes. This survey not only evaluates generation and detection methods in the different deepfake categories, but mainly focuses on audio deepfakes that are overlooked in most of the existing surveys. This paper critically analyzes and provides a unique source of audio deepfake research, mostly ranging from 2016 to 2020. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first survey focusing on audio deepfakes in English. This survey provides readers with a summary of 1) different deepfake categories 2) how they could be created and detected 3) the most recent trends in this domain and shortcomings in detection methods 4) audio deepfakes, how they are created and detected in more detail which is the main focus of this paper. We found that Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), and Deep Neural Networks (DNN) are common ways of creating and detecting deepfakes. In our evaluation of over 140 methods we found that the majority of the focus is on video deepfakes and in particular in the generation of video deepfakes. We found that for text deepfakes there are more generation methods but very few robust methods for detection, including fake news detection, which has become a controversial area of research because of the potential of heavy overlaps with human generation of fake content. This paper is an abbreviated version of the full survey and reveals a clear need to research audio deepfakes and particularly detection of audio deepfakes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge