Zahid Ullah
Korea National University of Transportation
VL-OrdinalFormer: Vision Language Guided Ordinal Transformers for Interpretable Knee Osteoarthritis Grading
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a leading cause of disability worldwide, and accurate severity assessment using the Kellgren Lawrence (KL) grading system is critical for clinical decision making. However, radiographic distinctions between early disease stages, particularly KL1 and KL2, are subtle and frequently lead to inter-observer variability among radiologists. To address these challenges, we propose VLOrdinalFormer, a vision language guided ordinal learning framework for fully automated KOA grading from knee radiographs. The proposed method combines a ViT L16 backbone with CORAL based ordinal regression and a Contrastive Language Image Pretraining (CLIP) driven semantic alignment module, allowing the model to incorporate clinically meaningful textual concepts related to joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, and subchondral sclerosis. To improve robustness and mitigate overfitting, we employ stratified five fold cross validation, class aware re weighting to emphasize challenging intermediate grades, and test time augmentation with global threshold optimization. Experiments conducted on the publicly available OAI kneeKL224 dataset demonstrate that VLOrdinalFormer achieves state of the art performance, outperforming CNN and ViT baselines in terms of macro F1 score and overall accuracy. Notably, the proposed framework yields substantial performance gains for KL1 and KL2 without compromising classification accuracy for mild or severe cases. In addition, interpretability analyses using Grad CAM and CLIP similarity maps confirm that the model consistently attends to clinically relevant anatomical regions. These results highlight the potential of vision language aligned ordinal transformers as reliable and interpretable tools for KOA grading and disease progression assessment in routine radiological practice.
Unified Review and Benchmark of Deep Segmentation Architectures for Cardiac Ultrasound on CAMUS
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Several review papers summarize cardiac imaging and DL advances, few works connect this overview to a unified and reproducible experimental benchmark. In this study, we combine a focused review of cardiac ultrasound segmentation literature with a controlled comparison of three influential architectures, U-Net, Attention U-Net, and TransUNet, on the Cardiac Acquisitions for Multi-Structure Ultrasound Segmentation (CAMUS) echocardiography dataset. Our benchmark spans multiple preprocessing routes, including native NIfTI volumes, 16-bit PNG exports, GPT-assisted polygon-based pseudo-labels, and self-supervised pretraining (SSL) on thousands of unlabeled cine frames. Using identical training splits, losses, and evaluation criteria, a plain U-Net achieved a 94% mean Dice when trained directly on NIfTI data (preserving native dynamic range), while the PNG-16-bit workflow reached 91% under similar conditions. Attention U-Net provided modest improvements on small or low-contrast regions, reducing boundary leakage, whereas TransUNet demonstrated the strongest generalization on challenging frames due to its ability to model global spatial context, particularly when initialized with SSL. Pseudo-labeling expanded the training set and improved robustness after confidence filtering. Overall, our contributions are threefold: a harmonized, apples-to-apples benchmark of U-Net, Attention U-Net, and TransUNet under standardized CAMUS preprocessing and evaluation; practical guidance on maintaining intensity fidelity, resolution consistency, and alignment when preparing ultrasound data; and an outlook on scalable self-supervision and emerging multimodal GPT-based annotation pipelines for rapid labeling, quality assurance, and targeted dataset curation.
Hybrid Ensemble Approaches: Optimal Deep Feature Fusion and Hyperparameter-Tuned Classifier Ensembling for Enhanced Brain Tumor Classification
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is widely recognized as the most reliable tool for detecting tumors due to its capability to produce detailed images that reveal their presence. However, the accuracy of diagnosis can be compromised when human specialists evaluate these images. Factors such as fatigue, limited expertise, and insufficient image detail can lead to errors. For example, small tumors might go unnoticed, or overlap with healthy brain regions could result in misidentification. To address these challenges and enhance diagnostic precision, this study proposes a novel double ensembling framework, consisting of ensembled pre-trained deep learning (DL) models for feature extraction and ensembled fine-tuned hyperparameter machine learning (ML) models to efficiently classify brain tumors. Specifically, our method includes extensive preprocessing and augmentation, transfer learning concepts by utilizing various pre-trained deep convolutional neural networks and vision transformer networks to extract deep features from brain MRI, and fine-tune hyperparameters of ML classifiers. Our experiments utilized three different publicly available Kaggle MRI brain tumor datasets to evaluate the pre-trained DL feature extractor models, ML classifiers, and the effectiveness of an ensemble of deep features along with an ensemble of ML classifiers for brain tumor classification. Our results indicate that the proposed feature fusion and classifier fusion improve upon the state of the art, with hyperparameter fine-tuning providing a significant enhancement over the ensemble method. Additionally, we present an ablation study to illustrate how each component contributes to accurate brain tumor classification.
Hierarchical Deep Feature Fusion and Ensemble Learning for Enhanced Brain Tumor MRI Classification
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Accurate brain tumor classification is crucial in medical imaging to ensure reliable diagnosis and effective treatment planning. This study introduces a novel double ensembling framework that synergistically combines pre-trained deep learning (DL) models for feature extraction with optimized machine learning (ML) classifiers for robust classification. The framework incorporates comprehensive preprocessing and data augmentation of brain magnetic resonance images (MRI), followed by deep feature extraction using transfer learning with pre-trained Vision Transformer (ViT) networks. The novelty lies in the dual-level ensembling strategy: feature-level ensembling, which integrates deep features from the top-performing ViT models, and classifier-level ensembling, which aggregates predictions from hyperparameter-optimized ML classifiers. Experiments on two public Kaggle MRI brain tumor datasets demonstrate that this approach significantly surpasses state-of-the-art methods, underscoring the importance of feature and classifier fusion. The proposed methodology also highlights the critical roles of hyperparameter optimization (HPO) and advanced preprocessing techniques in improving diagnostic accuracy and reliability, advancing the integration of DL and ML for clinically relevant medical image analysis.
DAM-Seg: Anatomically accurate cardiac segmentation using Dense Associative Networks
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Deep learning-based cardiac segmentation has seen significant advancements over the years. Many studies have tackled the challenge of anatomically incorrect segmentation predictions by introducing auxiliary modules. These modules either post-process segmentation outputs or enforce consistency between specific points to ensure anatomical correctness. However, such approaches often increase network complexity, require separate training for these modules, and may lack robustness in scenarios with poor visibility. To address these limitations, we propose a novel transformer-based architecture that leverages dense associative networks to learn and retain specific patterns inherent to cardiac inputs. Unlike traditional methods, our approach restricts the network to memorize a limited set of patterns. During forward propagation, a weighted sum of these patterns is used to enforce anatomical correctness in the output. Since these patterns are input-independent, the model demonstrates enhanced robustness, even in cases with poor visibility. The proposed pipeline was evaluated on two publicly available datasets, CAMUS and CardiacNet. Experimental results indicate that our model consistently outperforms baseline approaches across all metrics, highlighting its effectiveness and reliability for cardiac segmentation tasks.
Ensemble CNNs for Breast Tumor Classification
Apr 11, 2023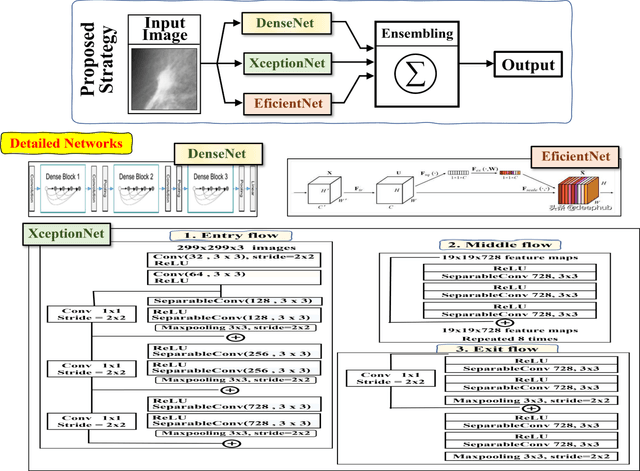
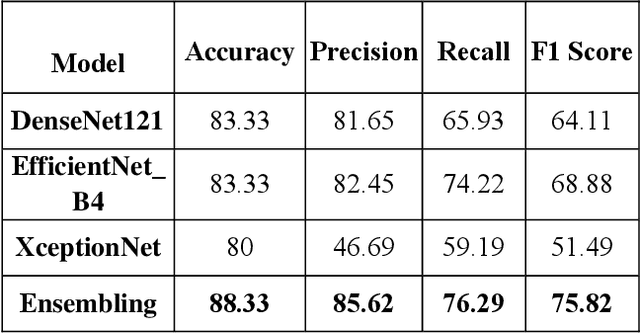
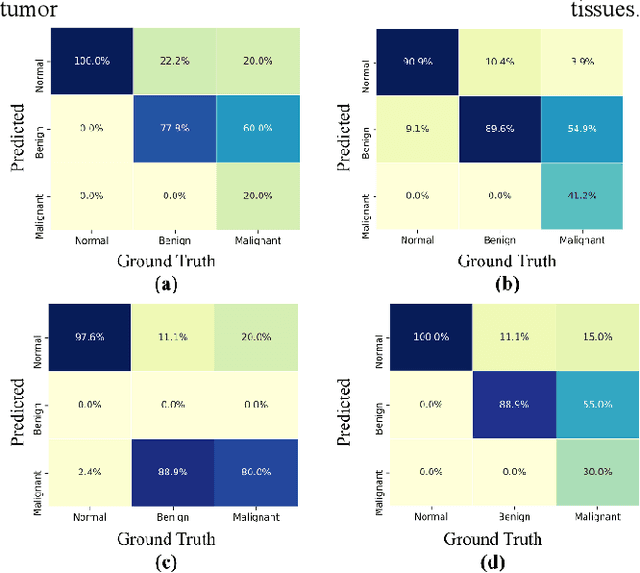
Abstract:To improve the recognition ability of computer-aided breast mass classification among mammographic images, in this work we explore the state-of-the-art classification networks to develop an ensemble mechanism. First, the regions of interest (ROIs) are obtained from the original dataset, and then three models, i.e., XceptionNet, DenseNet, and EfficientNet, are trained individually. After training, we ensemble the mechanism by summing the probabilities outputted from each network which enhances the performance up to 5%. The scheme has been validated on a public dataset and we achieved accuracy, precision, and recall 88%, 85%, and 76% respectively.
Higher Accurate Recognition of Handwritten Pashto Letters through Zoning Feature by using K-Nearest Neighbour and Artificial Neural Network
Apr 06, 2019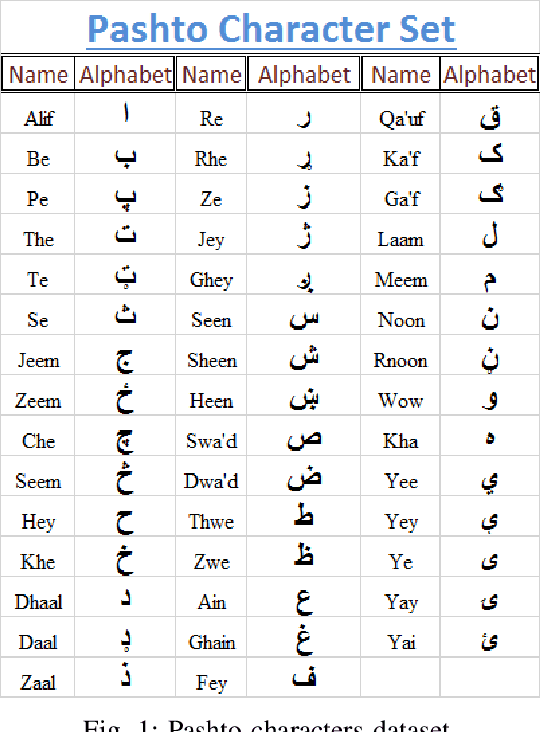
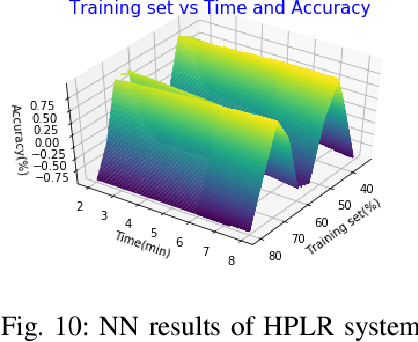
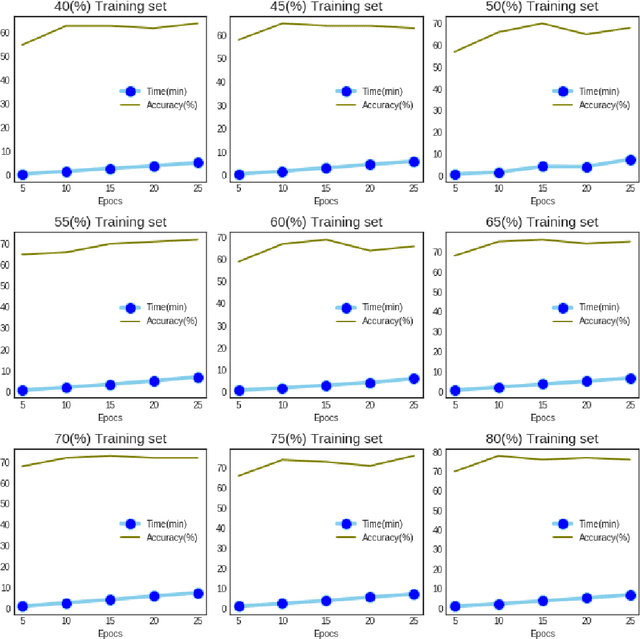
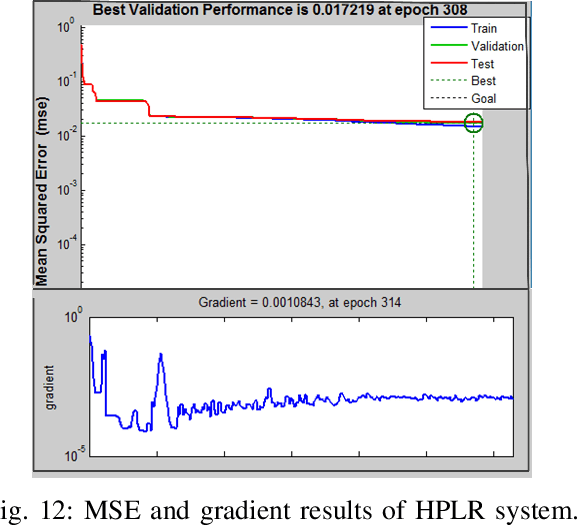
Abstract:This paper presents a recognition system for handwritten Pashto letters. However, handwritten character recognition is a challenging task. These letters not only differ in shape and style but also vary among individuals. The recognition becomes further daunting due to the lack of standard datasets for inscribed Pashto letters. In this work, we have designed a database of moderate size, which encompasses a total of 4488 images, stemming from 102 distinguishing samples for each of the 44 letters in Pashto. The recognition framework uses zoning feature extractor followed by K-Nearest Neighbour (KNN) and Neural Network (NN) classifiers for classifying individual letter. Based on the evaluation of the proposed system, an overall classification accuracy of approximately 70.05% is achieved by using KNN while 72% is achieved by using NN.
* (IJACSA) International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications,
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge