Yuta Tokuoka
Frequency-Calibrated Membership Inference Attacks on Medical Image Diffusion Models
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The increasing use of diffusion models for image generation, especially in sensitive areas like medical imaging, has raised significant privacy concerns. Membership Inference Attack (MIA) has emerged as a potential approach to determine if a specific image was used to train a diffusion model, thus quantifying privacy risks. Existing MIA methods often rely on diffusion reconstruction errors, where member images are expected to have lower reconstruction errors than non-member images. However, applying these methods directly to medical images faces challenges. Reconstruction error is influenced by inherent image difficulty, and diffusion models struggle with high-frequency detail reconstruction. To address these issues, we propose a Frequency-Calibrated Reconstruction Error (FCRE) method for MIAs on medical image diffusion models. By focusing on reconstruction errors within a specific mid-frequency range and excluding both high-frequency (difficult to reconstruct) and low-frequency (less informative) regions, our frequency-selective approach mitigates the confounding factor of inherent image difficulty. Specifically, we analyze the reverse diffusion process, obtain the mid-frequency reconstruction error, and compute the structural similarity index score between the reconstructed and original images. Membership is determined by comparing this score to a threshold. Experiments on several medical image datasets demonstrate that our FCRE method outperforms existing MIA methods.
Symbolic integration by integrating learning models with different strengths and weaknesses
Mar 09, 2021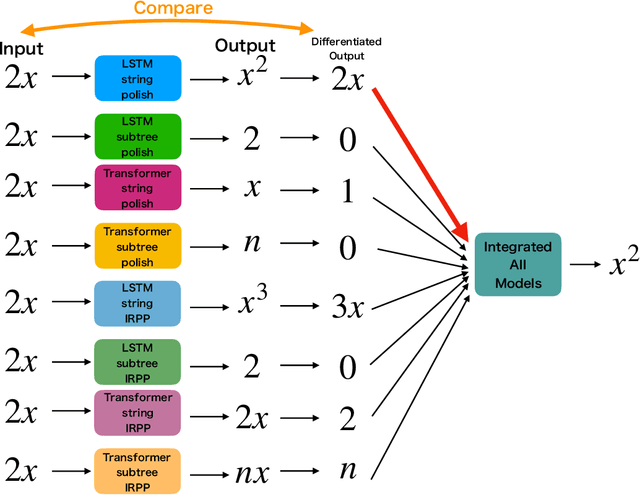
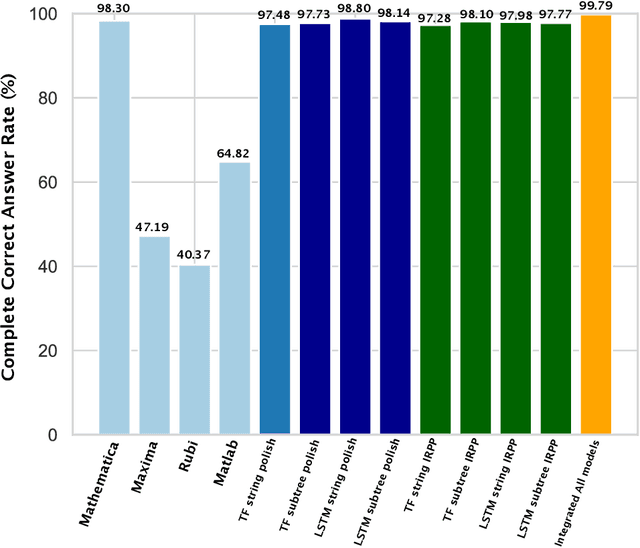
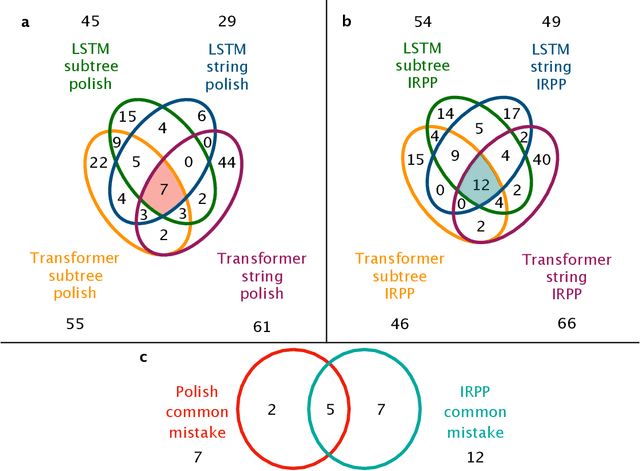
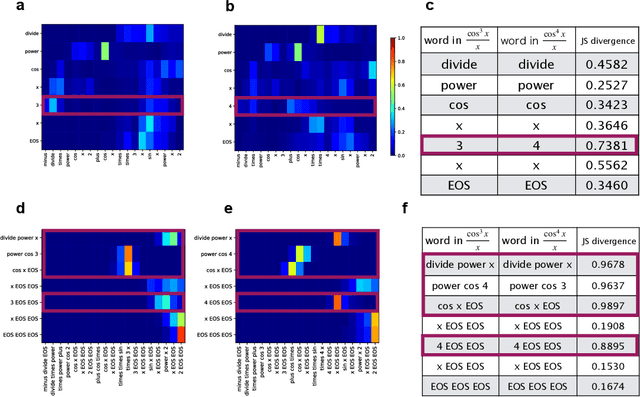
Abstract:Integration is indispensable, not only in mathematics, but also in a wide range of other fields. A deep learning method has recently been developed and shown to be capable of integrating mathematical functions that could not previously be integrated on a computer. However, that method treats integration as equivalent to natural language translation and does not reflect mathematical information. In this study, we adjusted the learning model to take mathematical information into account and developed a wide range of learning models that learn the order of numerical operations more robustly. In this way, we achieved a 98.80% correct answer rate with symbolic integration, a higher rate than that of any existing method. We judged the correctness of the integration based on whether the derivative of the primitive function was consistent with the integrand. By building an integrated model based on this strategy, we achieved a 99.79% rate of correct answers with symbolic integration.
An Inductive Transfer Learning Approach using Cycle-consistent Adversarial Domain Adaptation with Application to Brain Tumor Segmentation
May 11, 2020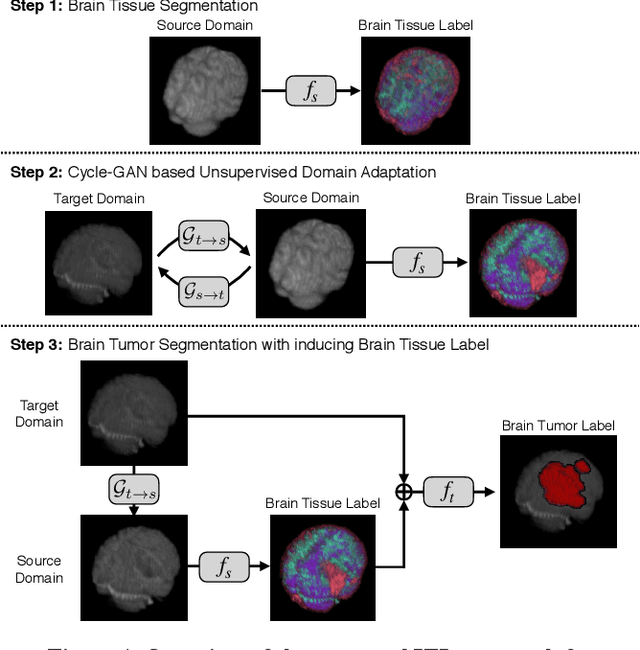
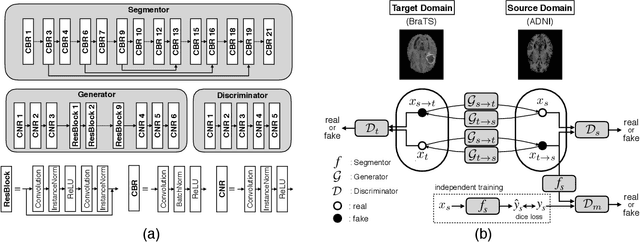
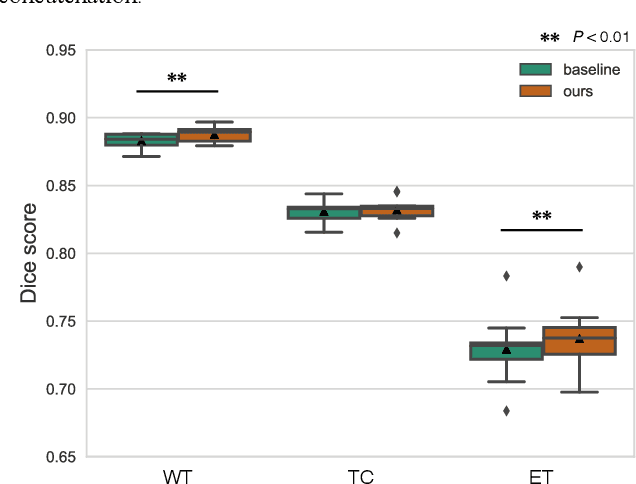
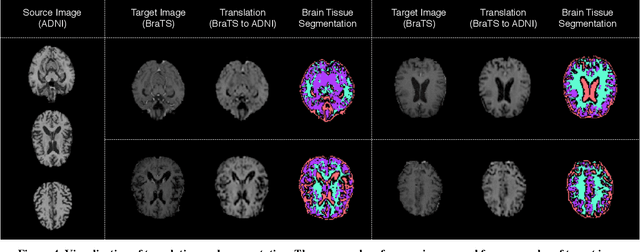
Abstract:With recent advances in supervised machine learning for medical image analysis applications, the annotated medical image datasets of various domains are being shared extensively. Given that the annotation labelling requires medical expertise, such labels should be applied to as many learning tasks as possible. However, the multi-modal nature of each annotated image renders it difficult to share the annotation label among diverse tasks. In this work, we provide an inductive transfer learning (ITL) approach to adopt the annotation label of the source domain datasets to tasks of the target domain datasets using Cycle-GAN based unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA). To evaluate the applicability of the ITL approach, we adopted the brain tissue annotation label on the source domain dataset of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images to the task of brain tumor segmentation on the target domain dataset of MRI. The results confirm that the segmentation accuracy of brain tumor segmentation improved significantly. The proposed ITL approach can make significant contribution to the field of medical image analysis, as we develop a fundamental tool to improve and promote various tasks using medical images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge