Yunze Chen
Face-NMS: A Core-set Selection Approach for Efficient Face Recognition
Sep 10, 2021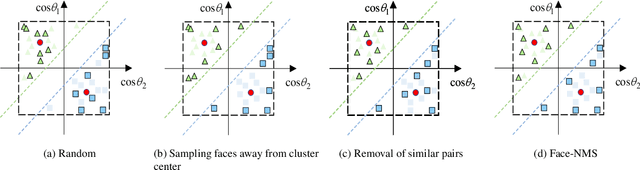
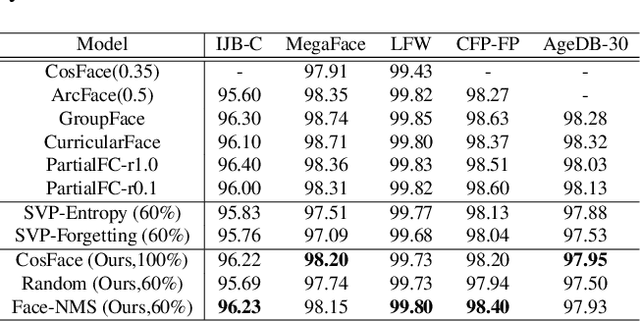
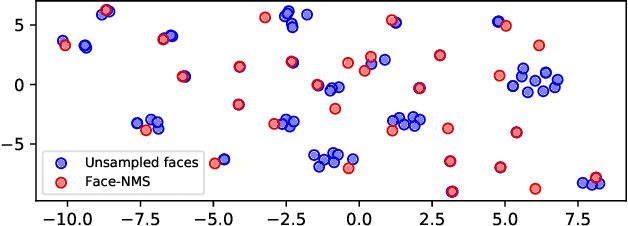
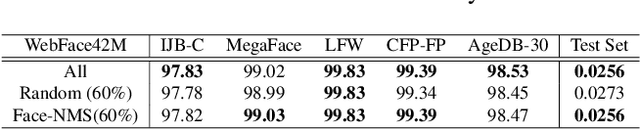
Abstract:Recently, face recognition in the wild has achieved remarkable success and one key engine is the increasing size of training data. For example, the largest face dataset, WebFace42M contains about 2 million identities and 42 million faces. However, a massive number of faces raise the constraints in training time, computing resources, and memory cost. The current research on this problem mainly focuses on designing an efficient Fully-connected layer (FC) to reduce GPU memory consumption caused by a large number of identities. In this work, we relax these constraints by resolving the redundancy problem of the up-to-date face datasets caused by the greedily collecting operation (i.e. the core-set selection perspective). As the first attempt in this perspective on the face recognition problem, we find that existing methods are limited in both performance and efficiency. For superior cost-efficiency, we contribute a novel filtering strategy dubbed Face-NMS. Face-NMS works on feature space and simultaneously considers the local and global sparsity in generating core sets. In practice, Face-NMS is analogous to Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) in the object detection community. It ranks the faces by their potential contribution to the overall sparsity and filters out the superfluous face in the pairs with high similarity for local sparsity. With respect to the efficiency aspect, Face-NMS accelerates the whole pipeline by applying a smaller but sufficient proxy dataset in training the proxy model. As a result, with Face-NMS, we successfully scale down the WebFace42M dataset to 60% while retaining its performance on the main benchmarks, offering a 40% resource-saving and 1.64 times acceleration. The code is publicly available for reference at https://github.com/HuangJunJie2017/Face-NMS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge