Yunting Yin
Interpretable Depression Detection from Social Media Text Using LLM-Derived Embeddings
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Accurate and interpretable detection of depressive language in social media is useful for early interventions of mental health conditions, and has important implications for both clinical practice and broader public health efforts. In this paper, we investigate the performance of large language models (LLMs) and traditional machine learning classifiers across three classification tasks involving social media data: binary depression classification, depression severity classification, and differential diagnosis classification among depression, PTSD, and anxiety. Our study compares zero-shot LLMs with supervised classifiers trained on both conventional text embeddings and LLM-generated summary embeddings. Our experiments reveal that while zero-shot LLMs demonstrate strong generalization capabilities in binary classification, they struggle with fine-grained ordinal classifications. In contrast, classifiers trained on summary embeddings generated by LLMs demonstrate competitive, and in some cases superior, performance on the classification tasks, particularly when compared to models using traditional text embeddings. Our findings demonstrate the strengths of LLMs in mental health prediction, and suggest promising directions for better utilization of their zero-shot capabilities and context-aware summarization techniques.
Debate-Driven Multi-Agent LLMs for Phishing Email Detection
Mar 27, 2025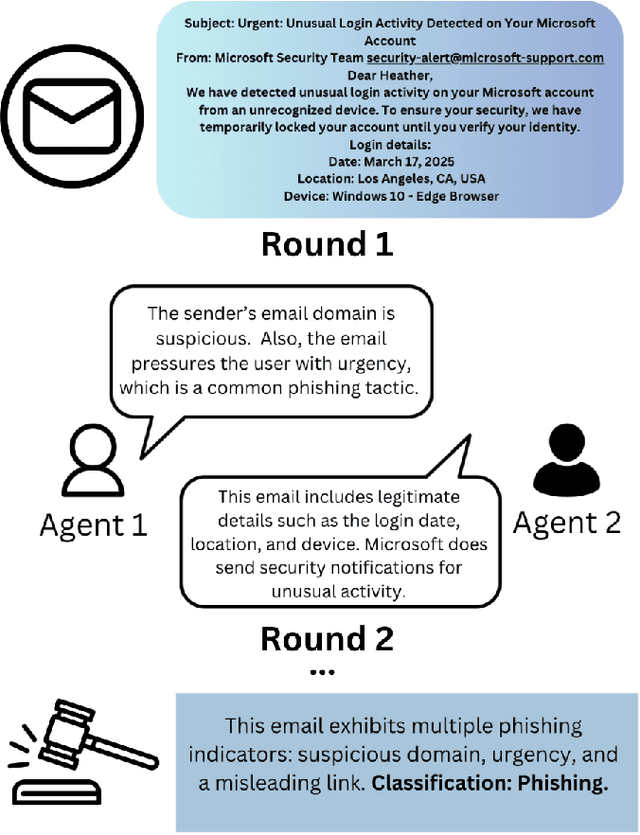
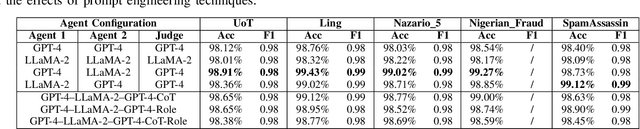
Abstract:Phishing attacks remain a critical cybersecurity threat. Attackers constantly refine their methods, making phishing emails harder to detect. Traditional detection methods, including rule-based systems and supervised machine learning models, either rely on predefined patterns like blacklists, which can be bypassed with slight modifications, or require large datasets for training and still can generate false positives and false negatives. In this work, we propose a multi-agent large language model (LLM) prompting technique that simulates debates among agents to detect whether the content presented on an email is phishing. Our approach uses two LLM agents to present arguments for or against the classification task, with a judge agent adjudicating the final verdict based on the quality of reasoning provided. This debate mechanism enables the models to critically analyze contextual cue and deceptive patterns in text, which leads to improved classification accuracy. The proposed framework is evaluated on multiple phishing email datasets and demonstrate that mixed-agent configurations consistently outperform homogeneous configurations. Results also show that the debate structure itself is sufficient to yield accurate decisions without extra prompting strategies.
Enhancing Image-Text Matching with Adaptive Feature Aggregation
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Image-text matching aims to find matched cross-modal pairs accurately. While current methods often rely on projecting cross-modal features into a common embedding space, they frequently suffer from imbalanced feature representations across different modalities, leading to unreliable retrieval results. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel Feature Enhancement Module that adaptively aggregates single-modal features for more balanced and robust image-text retrieval. Additionally, we propose a new loss function that overcomes the shortcomings of original triplet ranking loss, thereby significantly improving retrieval performance. The proposed model has been evaluated on two public datasets and achieves competitive retrieval performance when compared with several state-of-the-art models. Implementation codes can be found here.
Word Definitions from Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2023
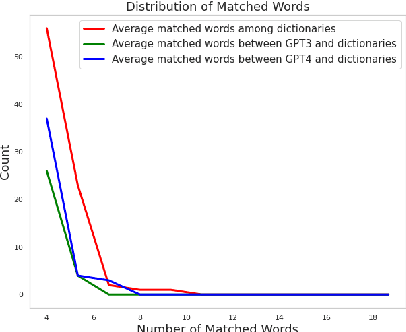


Abstract:Dictionary definitions are historically the arbitrator of what words mean, but this primacy has come under threat by recent progress in NLP, including word embeddings and generative models like ChatGPT. We present an exploratory study of the degree of alignment between word definitions from classical dictionaries and these newer computational artifacts. Specifically, we compare definitions from three published dictionaries to those generated from variants of ChatGPT. We show that (i) definitions from different traditional dictionaries exhibit more surface form similarity than do model-generated definitions, (ii) that the ChatGPT definitions are highly accurate, comparable to traditional dictionaries, and (iii) ChatGPT-based embedding definitions retain their accuracy even on low frequency words, much better than GloVE and FastText word embeddings.
Prosody Analysis of Audiobooks
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-speech have made it possible to generate natural-sounding audio from text. However, audiobook narrations involve dramatic vocalizations and intonations by the reader, with greater reliance on emotions, dialogues, and descriptions in the narrative. Using our dataset of 93 aligned book-audiobook pairs, we present improved models for prosody prediction properties (pitch, volume, and rate of speech) from narrative text using language modeling. Our predicted prosody attributes correlate much better with human audiobook readings than results from a state-of-the-art commercial TTS system: our predicted pitch shows a higher correlation with human reading for 22 out of the 24 books, while our predicted volume attribute proves more similar to human reading for 23 out of the 24 books. Finally, we present a human evaluation study to quantify the extent that people prefer prosody-enhanced audiobook readings over commercial text-to-speech systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge