Yuna Hwang
Understanding Generative AI in Robot Logic Parametrization
Nov 06, 2024
Abstract:Leveraging generative AI (for example, Large Language Models) for language understanding within robotics opens up possibilities for LLM-driven robot end-user development (EUD). Despite the numerous design opportunities it provides, little is understood about how this technology can be utilized when constructing robot program logic. In this paper, we outline the background in capturing natural language end-user intent and summarize previous use cases of LLMs within EUD. Taking the context of filmmaking as an example, we explore how a cinematography practitioner's intent to film a certain scene can be articulated using natural language, captured by an LLM, and further parametrized as low-level robot arm movement. We explore the capabilities of an LLM interpreting end-user intent and mapping natural language to predefined, cross-modal data in the process of iterative program development. We conclude by suggesting future opportunities for domain exploration beyond cinematography to support language-driven robotic camera navigation.
Understanding On-the-Fly End-User Robot Programming
Jun 02, 2024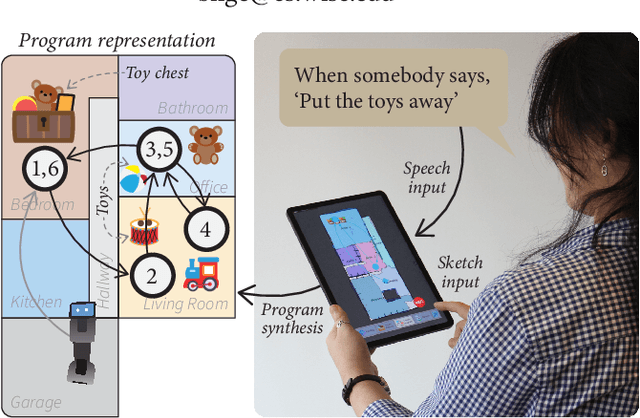

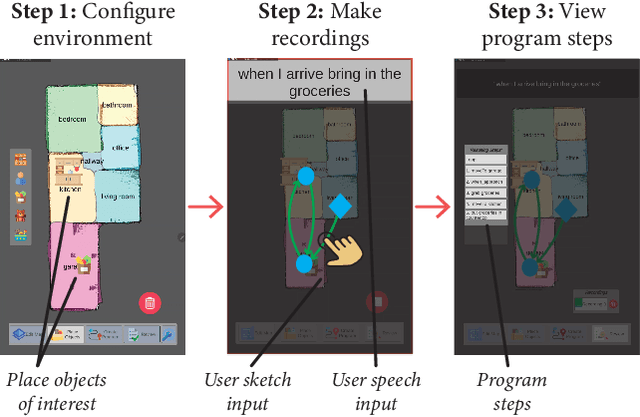
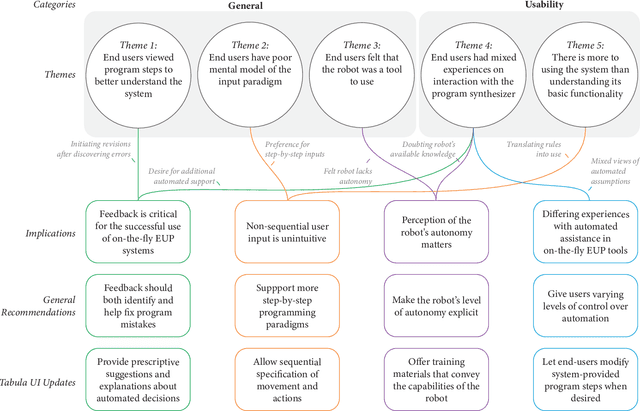
Abstract:Novel end-user programming (EUP) tools enable on-the-fly (i.e., spontaneous, easy, and rapid) creation of interactions with robotic systems. These tools are expected to empower users in determining system behavior, although very little is understood about how end users perceive, experience, and use these systems. In this paper, we seek to address this gap by investigating end-user experience with on-the-fly robot EUP. We trained 21 end users to use an existing on-the-fly EUP tool, asked them to create robot interactions for four scenarios, and assessed their overall experience. Our findings provide insight into how these systems should be designed to better support end-user experience with on-the-fly EUP, focusing on user interaction with an automatic program synthesizer that resolves imprecise user input, the use of multimodal inputs to express user intent, and the general process of programming a robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge