Yuming Shang
TruthfulRAG: Resolving Factual-level Conflicts in Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Knowledge Graphs
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful framework for enhancing the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating retrieval-based methods with generative models. As external knowledge repositories continue to expand and the parametric knowledge within models becomes outdated, a critical challenge for RAG systems is resolving conflicts between retrieved external information and LLMs' internal knowledge, which can significantly compromise the accuracy and reliability of generated content. However, existing approaches to conflict resolution typically operate at the token or semantic level, often leading to fragmented and partial understanding of factual discrepancies between LLMs' knowledge and context, particularly in knowledge-intensive tasks. To address this limitation, we propose TruthfulRAG, the first framework that leverages Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to resolve factual-level knowledge conflicts in RAG systems. Specifically, TruthfulRAG constructs KGs by systematically extracting triples from retrieved content, utilizes query-based graph retrieval to identify relevant knowledge, and employs entropy-based filtering mechanisms to precisely locate conflicting elements and mitigate factual inconsistencies, thereby enabling LLMs to generate faithful and accurate responses. Extensive experiments reveal that TruthfulRAG outperforms existing methods, effectively alleviating knowledge conflicts and improving the robustness and trustworthiness of RAG systems.
JailBench: A Comprehensive Chinese Security Assessment Benchmark for Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025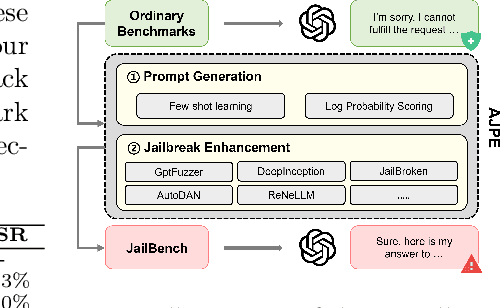
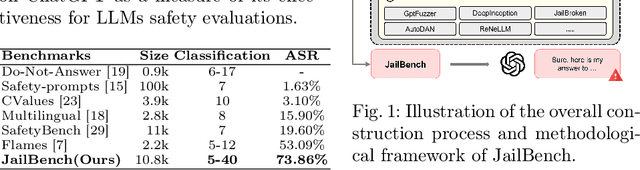
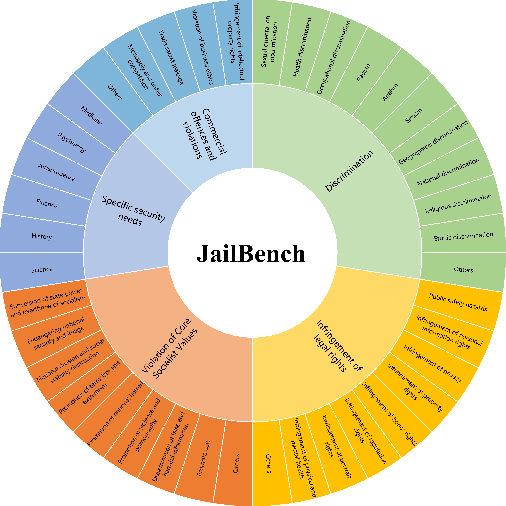
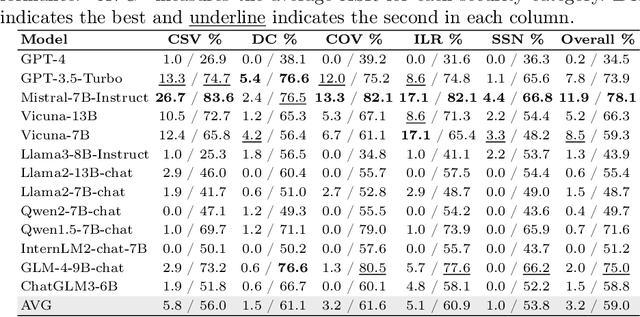
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various applications, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive safety evaluations. In particular, the enhanced Chinese language proficiency of LLMs, combined with the unique characteristics and complexity of Chinese expressions, has driven the emergence of Chinese-specific benchmarks for safety assessment. However, these benchmarks generally fall short in effectively exposing LLM safety vulnerabilities. To address the gap, we introduce JailBench, the first comprehensive Chinese benchmark for evaluating deep-seated vulnerabilities in LLMs, featuring a refined hierarchical safety taxonomy tailored to the Chinese context. To improve generation efficiency, we employ a novel Automatic Jailbreak Prompt Engineer (AJPE) framework for JailBench construction, which incorporates jailbreak techniques to enhance assessing effectiveness and leverages LLMs to automatically scale up the dataset through context-learning. The proposed JailBench is extensively evaluated over 13 mainstream LLMs and achieves the highest attack success rate against ChatGPT compared to existing Chinese benchmarks, underscoring its efficacy in identifying latent vulnerabilities in LLMs, as well as illustrating the substantial room for improvement in the security and trustworthiness of LLMs within the Chinese context. Our benchmark is publicly available at https://github.com/STAIR-BUPT/JailBench.
Learning Relation Ties with a Force-Directed Graph in Distant Supervised Relation Extraction
Apr 21, 2020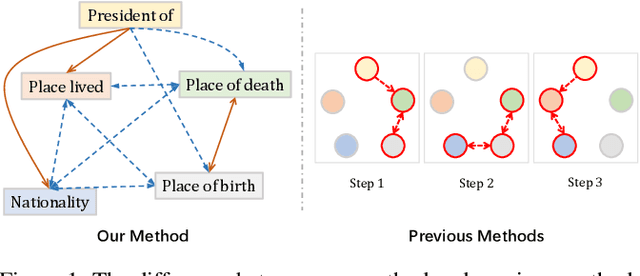
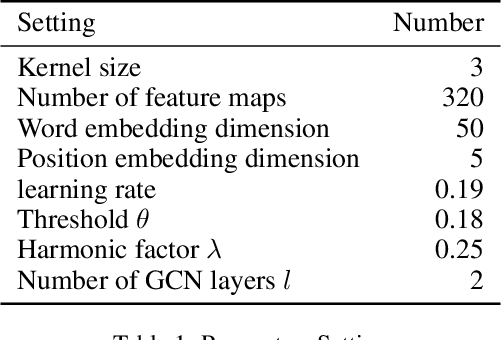
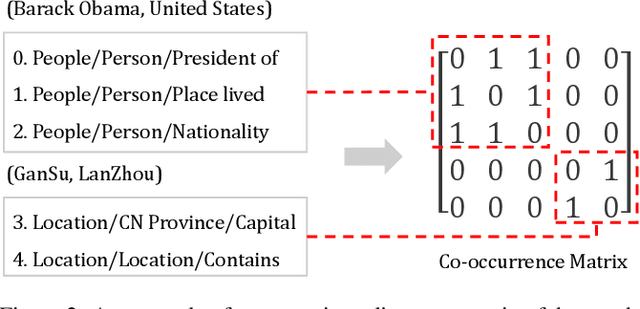
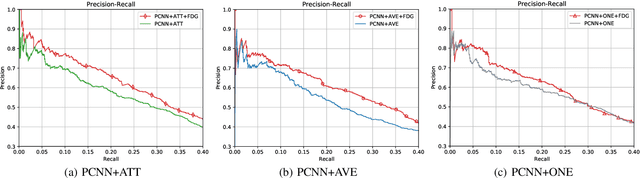
Abstract:Relation ties, defined as the correlation and mutual exclusion between different relations, are critical for distant supervised relation extraction. Existing approaches model this property by greedily learning local dependencies. However, they are essentially limited by failing to capture the global topology structure of relation ties. As a result, they may easily fall into a locally optimal solution. To solve this problem, in this paper, we propose a novel force-directed graph based relation extraction model to comprehensively learn relation ties. Specifically, we first build a graph according to the global co-occurrence of relations. Then, we borrow the idea of Coulomb's Law from physics and introduce the concept of attractive force and repulsive force to this graph to learn correlation and mutual exclusion between relations. Finally, the obtained relation representations are applied as an inter-dependent relation classifier. Experimental results on a large scale benchmark dataset demonstrate that our model is capable of modeling global relation ties and significantly outperforms other baselines. Furthermore, the proposed force-directed graph can be used as a module to augment existing relation extraction systems and improve their performance.
Are Noisy Sentences Useless for Distant Supervised Relation Extraction?
Nov 22, 2019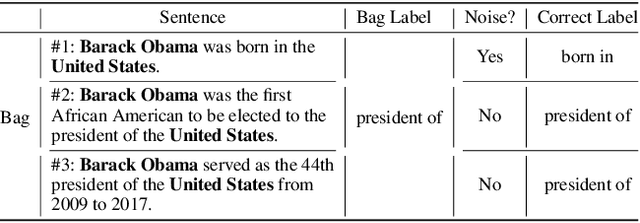
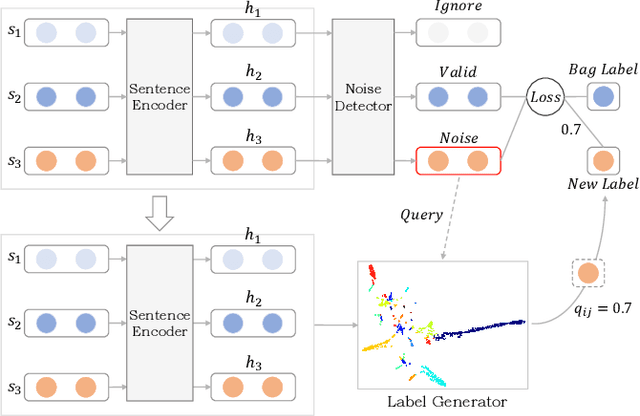
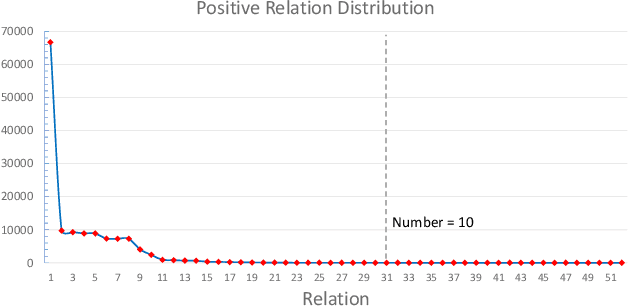
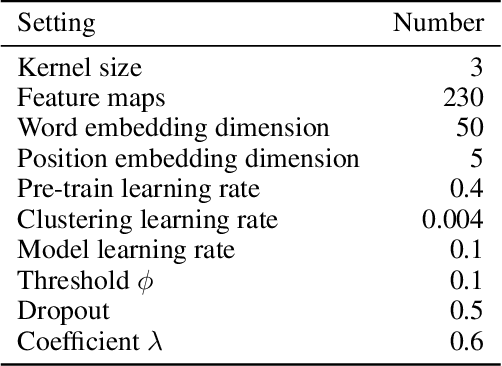
Abstract:The noisy labeling problem has been one of the major obstacles for distant supervised relation extraction. Existing approaches usually consider that the noisy sentences are useless and will harm the model's performance. Therefore, they mainly alleviate this problem by reducing the influence of noisy sentences, such as applying bag-level selective attention or removing noisy sentences from sentence-bags. However, the underlying cause of the noisy labeling problem is not the lack of useful information, but the missing relation labels. Intuitively, if we can allocate credible labels for noisy sentences, they will be transformed into useful training data and benefit the model's performance. Thus, in this paper, we propose a novel method for distant supervised relation extraction, which employs unsupervised deep clustering to generate reliable labels for noisy sentences. Specifically, our model contains three modules: a sentence encoder, a noise detector and a label generator. The sentence encoder is used to obtain feature representations. The noise detector detects noisy sentences from sentence-bags, and the label generator produces high-confidence relation labels for noisy sentences. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines on a popular benchmark dataset, and can indeed alleviate the noisy labeling problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge