Shuyi Liu
TruthfulRAG: Resolving Factual-level Conflicts in Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Knowledge Graphs
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful framework for enhancing the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating retrieval-based methods with generative models. As external knowledge repositories continue to expand and the parametric knowledge within models becomes outdated, a critical challenge for RAG systems is resolving conflicts between retrieved external information and LLMs' internal knowledge, which can significantly compromise the accuracy and reliability of generated content. However, existing approaches to conflict resolution typically operate at the token or semantic level, often leading to fragmented and partial understanding of factual discrepancies between LLMs' knowledge and context, particularly in knowledge-intensive tasks. To address this limitation, we propose TruthfulRAG, the first framework that leverages Knowledge Graphs (KGs) to resolve factual-level knowledge conflicts in RAG systems. Specifically, TruthfulRAG constructs KGs by systematically extracting triples from retrieved content, utilizes query-based graph retrieval to identify relevant knowledge, and employs entropy-based filtering mechanisms to precisely locate conflicting elements and mitigate factual inconsistencies, thereby enabling LLMs to generate faithful and accurate responses. Extensive experiments reveal that TruthfulRAG outperforms existing methods, effectively alleviating knowledge conflicts and improving the robustness and trustworthiness of RAG systems.
JailBench: A Comprehensive Chinese Security Assessment Benchmark for Large Language Models
Feb 26, 2025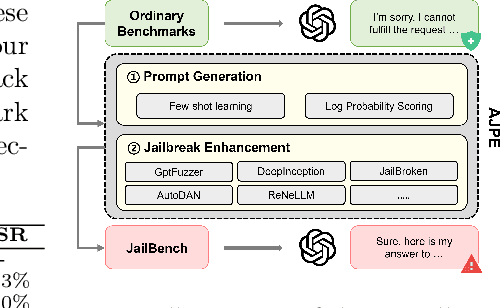
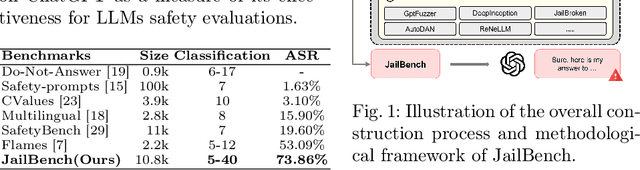
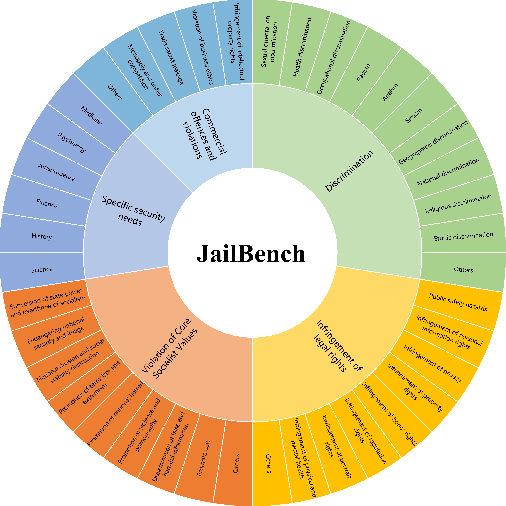
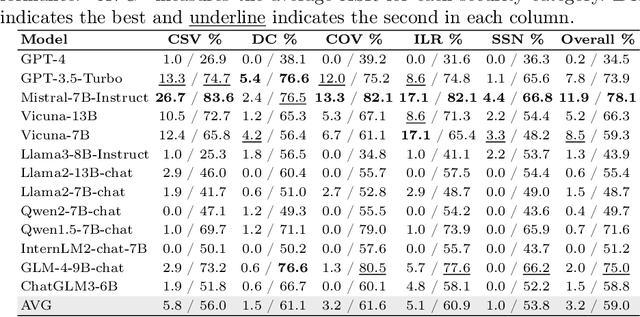
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various applications, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive safety evaluations. In particular, the enhanced Chinese language proficiency of LLMs, combined with the unique characteristics and complexity of Chinese expressions, has driven the emergence of Chinese-specific benchmarks for safety assessment. However, these benchmarks generally fall short in effectively exposing LLM safety vulnerabilities. To address the gap, we introduce JailBench, the first comprehensive Chinese benchmark for evaluating deep-seated vulnerabilities in LLMs, featuring a refined hierarchical safety taxonomy tailored to the Chinese context. To improve generation efficiency, we employ a novel Automatic Jailbreak Prompt Engineer (AJPE) framework for JailBench construction, which incorporates jailbreak techniques to enhance assessing effectiveness and leverages LLMs to automatically scale up the dataset through context-learning. The proposed JailBench is extensively evaluated over 13 mainstream LLMs and achieves the highest attack success rate against ChatGPT compared to existing Chinese benchmarks, underscoring its efficacy in identifying latent vulnerabilities in LLMs, as well as illustrating the substantial room for improvement in the security and trustworthiness of LLMs within the Chinese context. Our benchmark is publicly available at https://github.com/STAIR-BUPT/JailBench.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge