Yukiko Osawa
AIST
Material Classification Using Active Temperature Controllable Robotic Gripper
Nov 30, 2021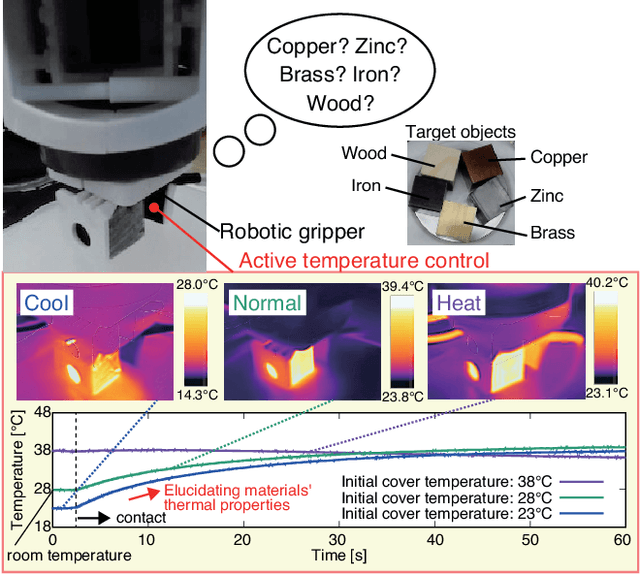
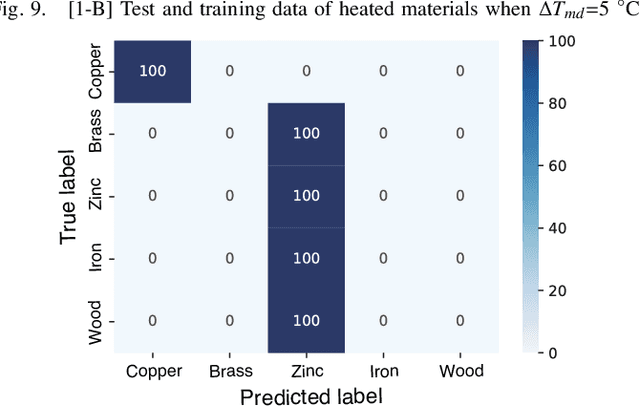
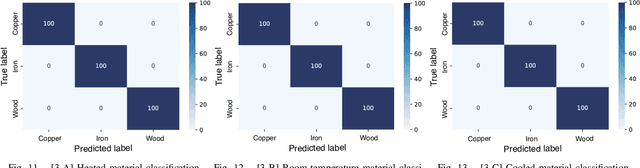
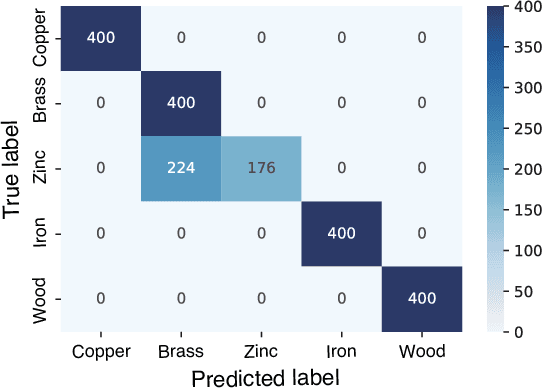
Abstract:Recognition techniques allow robots to make proper planning and control strategies to manipulate various objects. Object recognition is more reliable when made by combining several percepts, e.g., vision and haptics. One of the distinguishing features of each object's material is its heat properties, and classification can exploit heat transfer, similarly to human thermal sensation. Thermal-based recognition has the advantage of obtaining contact surface information in realtime by simply capturing temperature change using a tiny and cheap sensor. However, heat transfer between a robot surface and a contact object is strongly affected by the initial temperature and environmental conditions. A given object's material cannot be recognized when its temperature is the same as the robotic grippertip. We present a material classification system using active temperature controllable robotic gripper to induce heat flow. Subsequently, our system can recognize materials independently from their ambient temperature. The robotic gripper surface can be regulated to any temperature that differentiates it from the touched object's surface. We conducted some experiments by integrating the temperature control system with the Academic SCARA Robot, classifying them based on a long short-term memory (LSTM) using temperature data obtained from grasping target objects.
Detection of Human Contact by Thermal Exchange Observer of Robot Skin
May 05, 2020



Abstract:Physical human-robot interaction (pHRI) enables to achieve various assistive tasks for people by robots such as collaborative robotics or motion assistance. It pertains both planning-control and hardware considerations. We propose a new soft robot skin that can detect human contact through thermal features. An electrically conductive pipe is interposed between graphite sheet that has high heat conductivity and soft material for cover compliance. Then the temperature of the water pipe is controlled by a heat source and a small water pump. Besides, an observer for estimating heat flow is implemented; it can detect human interaction by measuring the temperature change of the water pipe. Hence, there is no need to attach sensors to the robot skin's surface, which can be kept soft and eventually textured with a desired pattern. We assessed the validity of the prototype in experiments of contact detection by human fingers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge