Yueyang Cang
DINT Transformer
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:DIFF Transformer addresses the issue of irrelevant context interference by introducing a differential attention mechanism that enhances the robustness of local attention. However, it has two critical limitations: the lack of global context modeling, which is essential for identifying globally significant tokens, and numerical instability due to the absence of strict row normalization in the attention matrix. To overcome these challenges, we propose DINT Transformer, which extends DIFF Transformer by incorporating a differential-integral mechanism. By computing global importance scores and integrating them into the attention matrix, DINT Transformer improves its ability to capture global dependencies. Moreover, the unified parameter design enforces row-normalized attention matrices, improving numerical stability. Experimental results demonstrate that DINT Transformer excels in accuracy and robustness across various practical applications, such as long-context language modeling and key information retrieval. These results position DINT Transformer as a highly effective and promising architecture.
Shared DIFF Transformer
Jan 29, 2025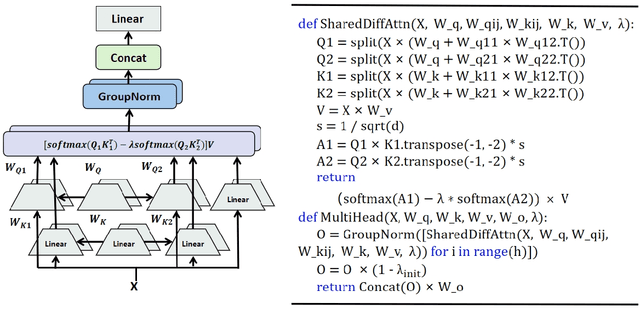
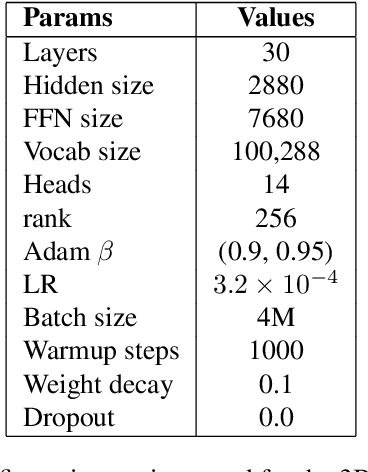
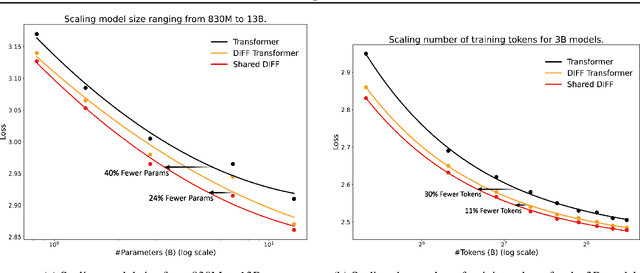
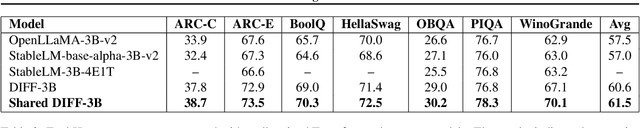
Abstract:DIFF Transformer improves attention allocation by enhancing focus on relevant context while suppressing noise. It introduces a differential attention mechanism that calculates the difference between two independently generated attention distributions, effectively reducing noise and promoting sparse attention patterns. However, the independent signal generation in DIFF Transformer results in parameter redundancy and suboptimal utilization of information. In this work, we propose Shared DIFF Transformer, which draws on the idea of a differential amplifier by introducing a shared base matrix to model global patterns and incorporating low-rank updates to enhance task-specific flexibility. This design significantly reduces parameter redundancy, improves efficiency, and retains strong noise suppression capabilities. Experimental results show that, compared to DIFF Transformer, our method achieves better performance in tasks such as long-sequence modeling, key information retrieval, and in-context learning. Our work provides a novel and efficient approach to optimizing differential attention mechanisms and advancing robust Transformer architectures.
Can KAN Work? Exploring the Potential of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks in Computer Vision
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks(KANs), as a theoretically efficient neural network architecture, have garnered attention for their potential in capturing complex patterns. However, their application in computer vision remains relatively unexplored. This study first analyzes the potential of KAN in computer vision tasks, evaluating the performance of KAN and its convolutional variants in image classification and semantic segmentation. The focus is placed on examining their characteristics across varying data scales and noise levels. Results indicate that while KAN exhibits stronger fitting capabilities, it is highly sensitive to noise, limiting its robustness. To address this challenge, we propose a smoothness regularization method and introduce a Segment Deactivation technique. Both approaches enhance KAN's stability and generalization, demonstrating its potential in handling complex visual data tasks.
RetCompletion:High-Speed Inference Image Completion with Retentive Network
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:Time cost is a major challenge in achieving high-quality pluralistic image completion. Recently, the Retentive Network (RetNet) in natural language processing offers a novel approach to this problem with its low-cost inference capabilities. Inspired by this, we apply RetNet to the pluralistic image completion task in computer vision. We present RetCompletion, a two-stage framework. In the first stage, we introduce Bi-RetNet, a bidirectional sequence information fusion model that integrates contextual information from images. During inference, we employ a unidirectional pixel-wise update strategy to restore consistent image structures, achieving both high reconstruction quality and fast inference speed. In the second stage, we use a CNN for low-resolution upsampling to enhance texture details. Experiments on ImageNet and CelebA-HQ demonstrate that our inference speed is 10$\times$ faster than ICT and 15$\times$ faster than RePaint. The proposed RetCompletion significantly improves inference speed and delivers strong performance, especially when masks cover large areas of the image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge