Yuejin Sun
Brightness Perceiving for Recursive Low-Light Image Enhancement
Apr 03, 2025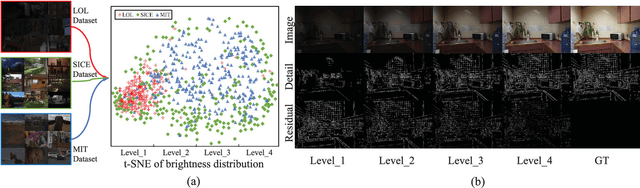



Abstract:Due to the wide dynamic range in real low-light scenes, there will be large differences in the degree of contrast degradation and detail blurring of captured images, making it difficult for existing end-to-end methods to enhance low-light images to normal exposure. To address the above issue, we decompose low-light image enhancement into a recursive enhancement task and propose a brightness-perceiving-based recursive enhancement framework for high dynamic range low-light image enhancement. Specifically, our recursive enhancement framework consists of two parallel sub-networks: Adaptive Contrast and Texture enhancement network (ACT-Net) and Brightness Perception network (BP-Net). The ACT-Net is proposed to adaptively enhance image contrast and details under the guidance of the brightness adjustment branch and gradient adjustment branch, which are proposed to perceive the degradation degree of contrast and details in low-light images. To adaptively enhance images captured under different brightness levels, BP-Net is proposed to control the recursive enhancement times of ACT-Net by exploring the image brightness distribution properties. Finally, in order to coordinate ACT-Net and BP-Net, we design a novel unsupervised training strategy to facilitate the training procedure. To further validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we construct a new dataset with a broader brightness distribution by mixing three low-light datasets. Compared with eleven existing representative methods, the proposed method achieves new SOTA performance on six reference and no reference metrics. Specifically, the proposed method improves the PSNR by 0.9 dB compared to the existing SOTA method.
Lightweight Adaptive Feature De-drifting for Compressed Image Classification
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:JPEG is a widely used compression scheme to efficiently reduce the volume of transmitted images. The artifacts appear among blocks due to the information loss, which not only affects the quality of images but also harms the subsequent high-level tasks in terms of feature drifting. High-level vision models trained on high-quality images will suffer performance degradation when dealing with compressed images, especially on mobile devices. Numerous learning-based JPEG artifact removal methods have been proposed to handle visual artifacts. However, it is not an ideal choice to use these JPEG artifact removal methods as a pre-processing for compressed image classification for the following reasons: 1. These methods are designed for human vision rather than high-level vision models; 2. These methods are not efficient enough to serve as pre-processing on resource-constrained devices. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel lightweight AFD module to boost the performance of pre-trained image classification models when facing compressed images. First, a FDE-Net is devised to generate the spatial-wise FDM in the DCT domain. Next, the estimated FDM is transmitted to the FE-Net to generate the mapping relationship between degraded features and corresponding high-quality features. A simple but effective RepConv block equipped with structural re-parameterization is utilized in FE-Net, which enriches feature representation in the training phase while maintaining efficiency in the deployment phase. After training on limited compressed images, the AFD-Module can serve as a "plug-and-play" model for pre-trained classification models to improve their performance on compressed images. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed AFD module can comprehensively improve the accuracy of the pre-trained classification models and significantly outperform the existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge