Yuan-Hao Liu
Improving the Accuracy of Global Forecasting Models using Time Series Data Augmentation
Aug 06, 2020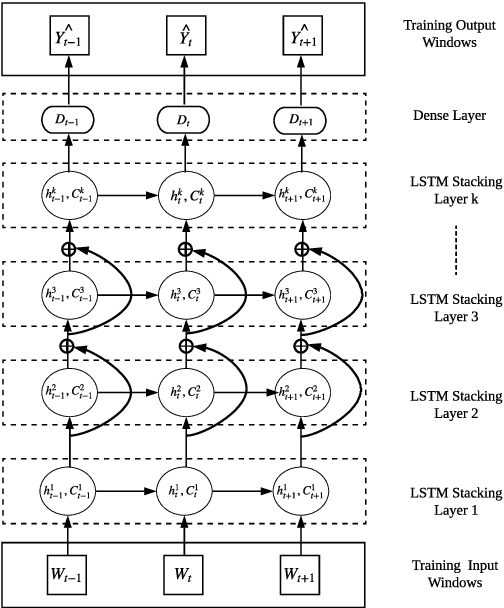
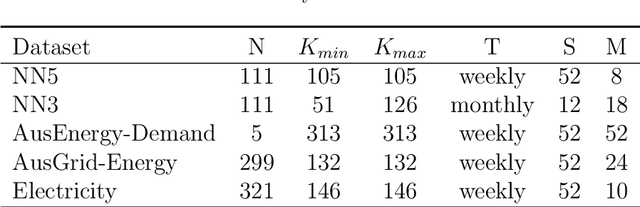
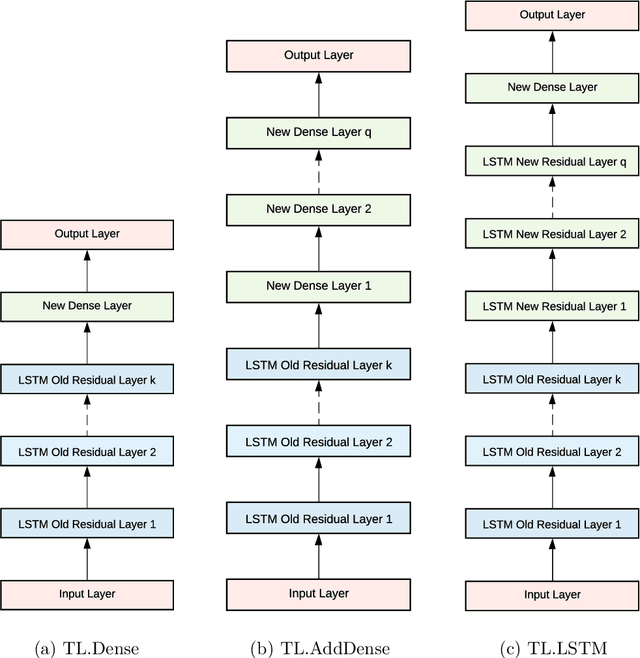

Abstract:Forecasting models that are trained across sets of many time series, known as Global Forecasting Models (GFM), have shown recently promising results in forecasting competitions and real-world applications, outperforming many state-of-the-art univariate forecasting techniques. In most cases, GFMs are implemented using deep neural networks, and in particular Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), which require a sufficient amount of time series to estimate their numerous model parameters. However, many time series databases have only a limited number of time series. In this study, we propose a novel, data augmentation based forecasting framework that is capable of improving the baseline accuracy of the GFM models in less data-abundant settings. We use three time series augmentation techniques: GRATIS, moving block bootstrap (MBB), and dynamic time warping barycentric averaging (DBA) to synthetically generate a collection of time series. The knowledge acquired from these augmented time series is then transferred to the original dataset using two different approaches: the pooled approach and the transfer learning approach. When building GFMs, in the pooled approach, we train a model on the augmented time series alongside the original time series dataset, whereas in the transfer learning approach, we adapt a pre-trained model to the new dataset. In our evaluation on competition and real-world time series datasets, our proposed variants can significantly improve the baseline accuracy of GFM models and outperform state-of-the-art univariate forecasting methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge