Yu-Shan Tai
Andy
MPTQ-ViT: Mixed-Precision Post-Training Quantization for Vision Transformer
Feb 01, 2024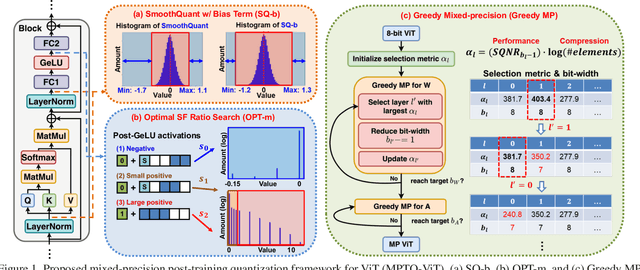
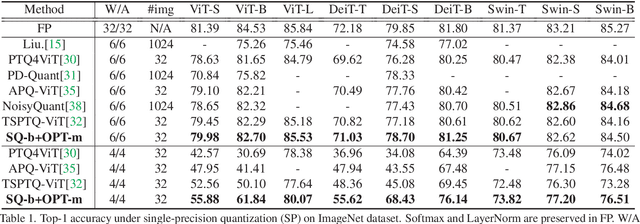
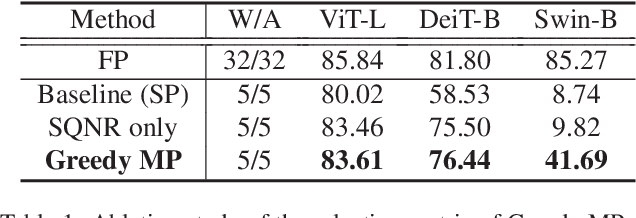
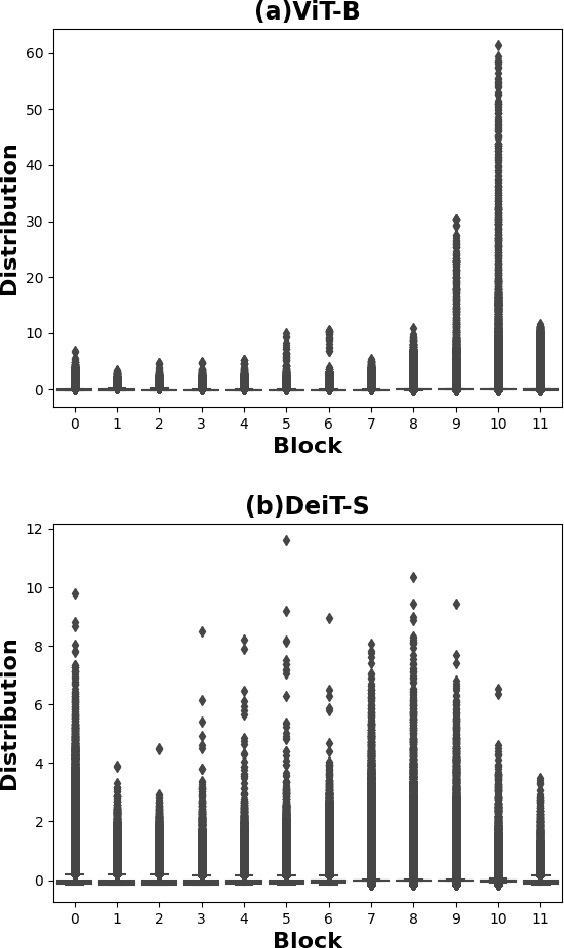
Abstract:While vision transformers (ViTs) have shown great potential in computer vision tasks, their intense computation and memory requirements pose challenges for practical applications. Existing post-training quantization methods leverage value redistribution or specialized quantizers to address the non-normal distribution in ViTs. However, without considering the asymmetry in activations and relying on hand-crafted settings, these methods often struggle to maintain performance under low-bit quantization. To overcome these challenges, we introduce SmoothQuant with bias term (SQ-b) to alleviate the asymmetry issue and reduce the clamping loss. We also introduce optimal scaling factor ratio search (OPT-m) to determine quantization parameters by a data-dependent mechanism automatically. To further enhance the compressibility, we incorporate the above-mentioned techniques and propose a mixed-precision post-training quantization framework for vision transformers (MPTQ-ViT). We develop greedy mixed-precision quantization (Greedy MP) to allocate layer-wise bit-width considering both model performance and compressibility. Our experiments on ViT, DeiT, and Swin demonstrate significant accuracy improvements compared with SOTA on the ImageNet dataset. Specifically, our proposed methods achieve accuracy improvements ranging from 0.90% to 23.35% on 4-bit ViTs with single-precision and from 3.82% to 78.14% on 5-bit fully quantized ViTs with mixed-precision.
TSPTQ-ViT: Two-scaled post-training quantization for vision transformer
May 22, 2023



Abstract:Vision transformers (ViTs) have achieved remarkable performance in various computer vision tasks. However, intensive memory and computation requirements impede ViTs from running on resource-constrained edge devices. Due to the non-normally distributed values after Softmax and GeLU, post-training quantization on ViTs results in severe accuracy degradation. Moreover, conventional methods fail to address the high channel-wise variance in LayerNorm. To reduce the quantization loss and improve classification accuracy, we propose a two-scaled post-training quantization scheme for vision transformer (TSPTQ-ViT). We design the value-aware two-scaled scaling factors (V-2SF) specialized for post-Softmax and post-GeLU values, which leverage the bit sparsity in non-normal distribution to save bit-widths. In addition, the outlier-aware two-scaled scaling factors (O-2SF) are introduced to LayerNorm, alleviating the dominant impacts from outlier values. Our experimental results show that the proposed methods reach near-lossless accuracy drops (<0.5%) on the ImageNet classification task under 8-bit fully quantized ViTs.
Learnable Mixed-precision and Dimension Reduction Co-design for Low-storage Activation
Jul 19, 2022



Abstract:Recently, deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved many eye-catching results. However, deploying CNNs on resource-constrained edge devices is constrained by limited memory bandwidth for transmitting large intermediated data during inference, i.e., activation. Existing research utilizes mixed-precision and dimension reduction to reduce computational complexity but pays less attention to its application for activation compression. To further exploit the redundancy in activation, we propose a learnable mixed-precision and dimension reduction co-design system, which separates channels into groups and allocates specific compression policies according to their importance. In addition, the proposed dynamic searching technique enlarges search space and finds out the optimal bit-width allocation automatically. Our experimental results show that the proposed methods improve 3.54%/1.27% in accuracy and save 0.18/2.02 bits per value over existing mixed-precision methods on ResNet18 and MobileNetv2, respectively.
Compression-aware Projection with Greedy Dimension Reduction for Convolutional Neural Network Activations
Oct 17, 2021

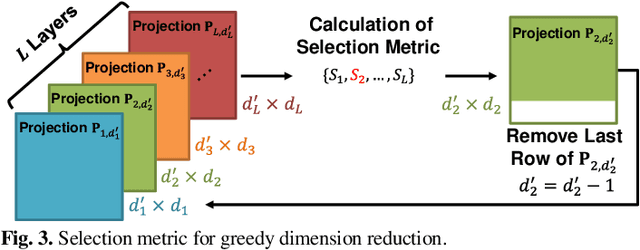
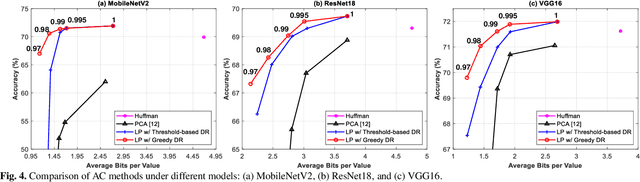
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) achieve remarkable performance in a wide range of fields. However, intensive memory access of activations introduces considerable energy consumption, impeding deployment of CNNs on resourceconstrained edge devices. Existing works in activation compression propose to transform feature maps for higher compressibility, thus enabling dimension reduction. Nevertheless, in the case of aggressive dimension reduction, these methods lead to severe accuracy drop. To improve the trade-off between classification accuracy and compression ratio, we propose a compression-aware projection system, which employs a learnable projection to compensate for the reconstruction loss. In addition, a greedy selection metric is introduced to optimize the layer-wise compression ratio allocation by considering both accuracy and #bits reduction simultaneously. Our test results show that the proposed methods effectively reduce 2.91x~5.97x memory access with negligible accuracy drop on MobileNetV2/ResNet18/VGG16.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge