Youssef Achari Berrada
Let Quantum Neural Networks Choose Their Own Frequencies
Sep 06, 2023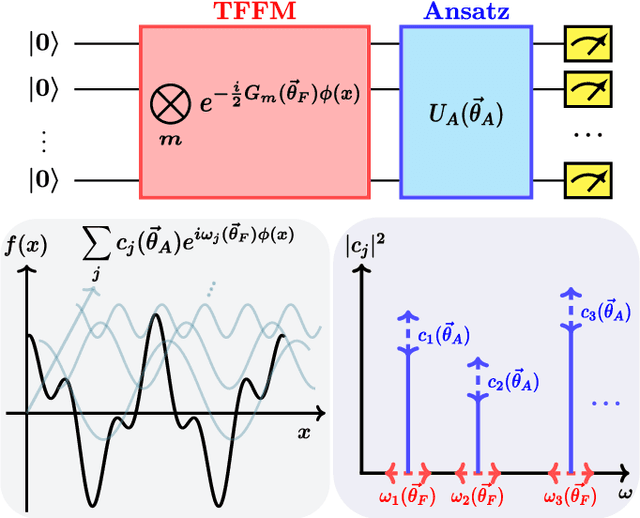
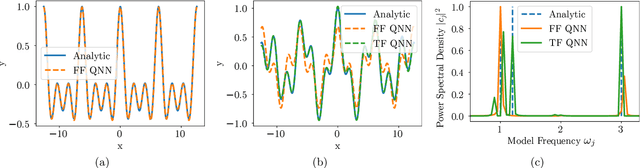
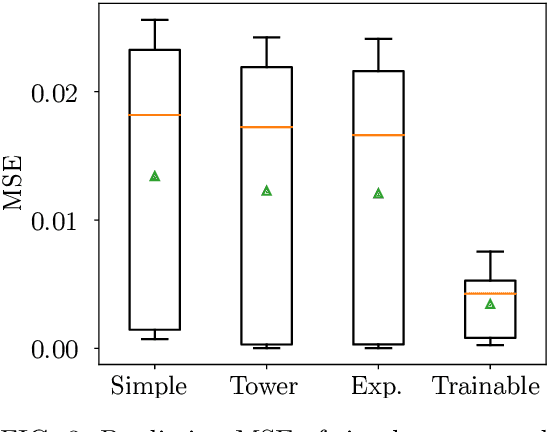
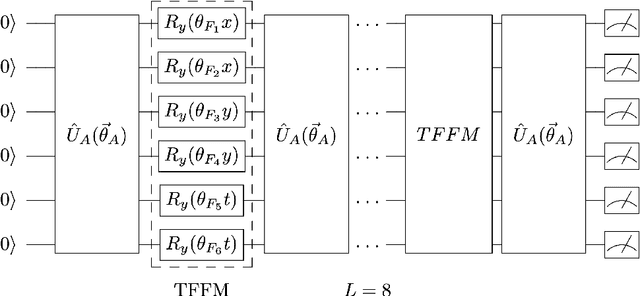
Abstract:Parameterized quantum circuits as machine learning models are typically well described by their representation as a partial Fourier series of the input features, with frequencies uniquely determined by the feature map's generator Hamiltonians. Ordinarily, these data-encoding generators are chosen in advance, fixing the space of functions that can be represented. In this work we consider a generalization of quantum models to include a set of trainable parameters in the generator, leading to a trainable frequency (TF) quantum model. We numerically demonstrate how TF models can learn generators with desirable properties for solving the task at hand, including non-regularly spaced frequencies in their spectra and flexible spectral richness. Finally, we showcase the real-world effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating an improved accuracy in solving the Navier-Stokes equations using a TF model with only a single parameter added to each encoding operation. Since TF models encompass conventional fixed frequency models, they may offer a sensible default choice for variational quantum machine learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge