Youngjin Jang
Grammar Accuracy Evaluation (GAE): Quantifiable Intrinsic Evaluation of Machine Translation Models
Jun 01, 2021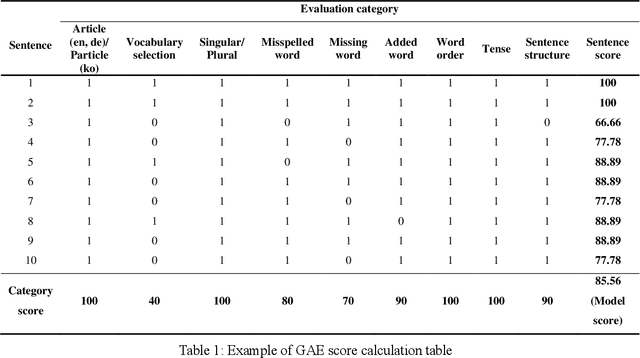
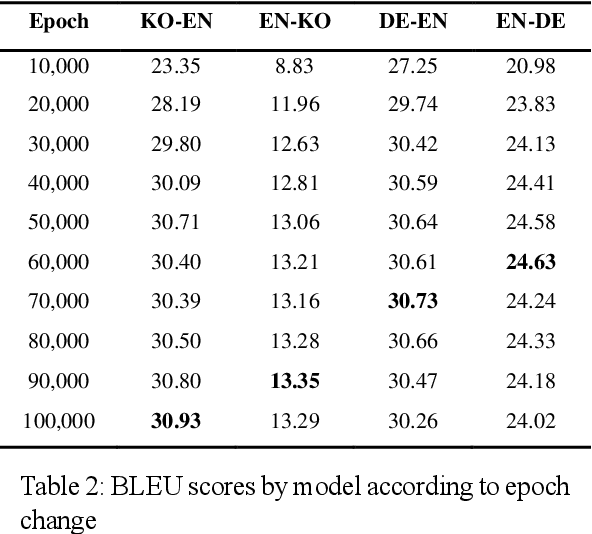
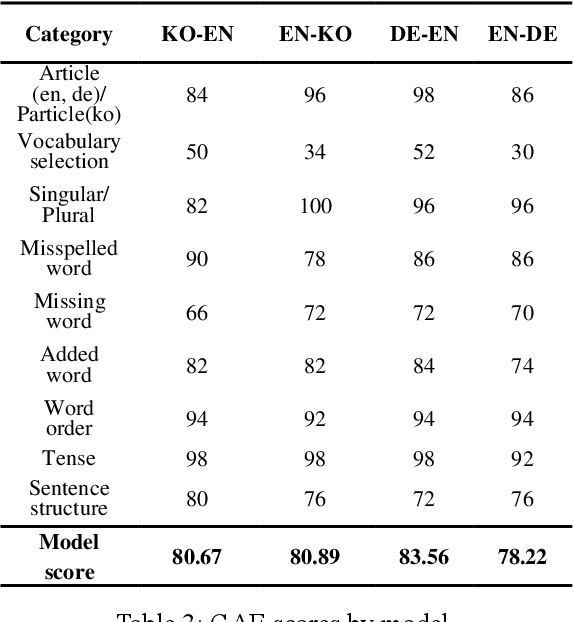

Abstract:Intrinsic evaluation by humans for the performance of natural language generation models is conducted to overcome the fact that the quality of generated sentences cannot be fully represented by only extrinsic evaluation. Nevertheless, existing intrinsic evaluations have a large score deviation according to the evaluator's criteria. In this paper, we propose Grammar Accuracy Evaluation (GAE) that can provide specific evaluating criteria. As a result of analyzing the quality of machine translation by BLEU and GAE, it was confirmed that the BLEU score does not represent the absolute performance of machine translation models and that GAE compensates for the shortcomings of BLEU with a flexible evaluation on alternative synonyms and changes in sentence structure.
Korean-English Machine Translation with Multiple Tokenization Strategy
Jun 01, 2021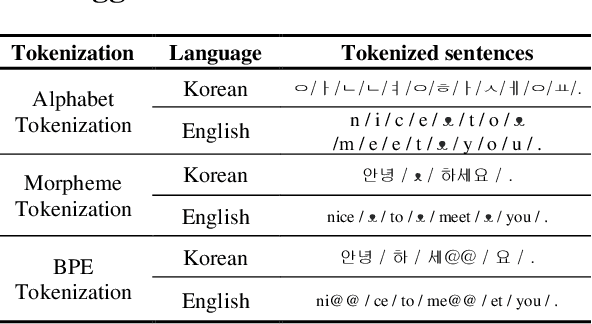
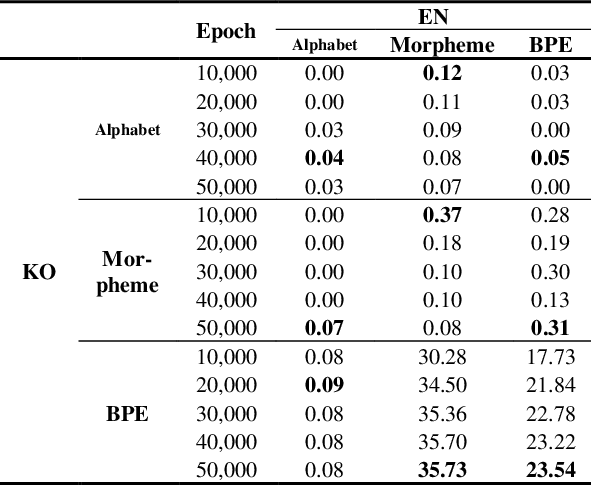
Abstract:This work was conducted to find out how tokenization methods affect the training results of machine translation models. In this work, alphabet tokenization, morpheme tokenization, and BPE tokenization were applied to Korean as the source language and English as the target language respectively, and the comparison experiment was conducted by repeating 50,000 epochs of each 9 models using the Transformer neural network. As a result of measuring the BLEU scores of the experimental models, the model that applied BPE tokenization to Korean and morpheme tokenization to English recorded 35.73, showing the best performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge