Yotaro Kubo
Adaptive Dropout for Pruning Conformers
Dec 06, 2024


Abstract:This paper proposes a method to effectively perform joint training-and-pruning based on adaptive dropout layers with unit-wise retention probabilities. The proposed method is based on the estimation of a unit-wise retention probability in a dropout layer. A unit that is estimated to have a small retention probability can be considered to be prunable. The retention probability of the unit is estimated using back-propagation and the Gumbel-Softmax technique. This pruning method is applied at several application points in Conformers such that the effective number of parameters can be significantly reduced. Specifically, adaptive dropout layers are introduced in three locations in each Conformer block: (a) the hidden layer of the feed-forward-net component, (b) the query vectors and the value vectors of the self-attention component, and (c) the input vectors of the LConv component. The proposed method is evaluated by conducting a speech recognition experiment on the LibriSpeech task. It was shown that this approach could simultaneously achieve a parameter reduction and accuracy improvement. The word error rates improved by approx 1% while reducing the number of parameters by 54%.
Knowledge Transfer from Large-scale Pretrained Language Models to End-to-end Speech Recognizers
Feb 16, 2022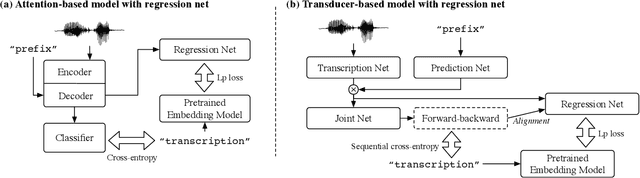
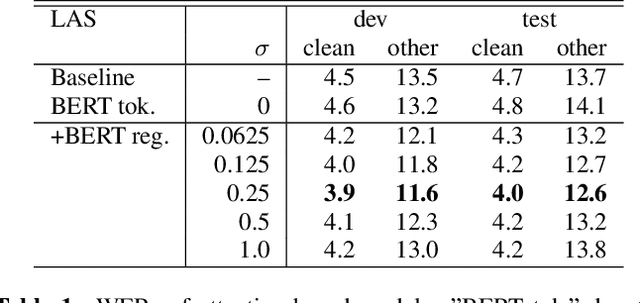
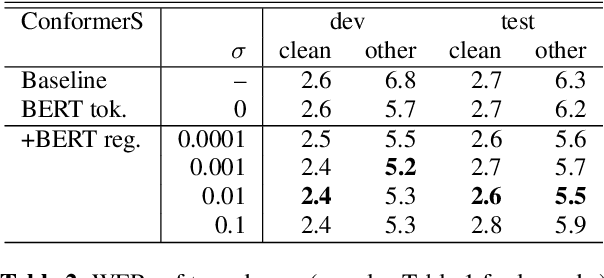
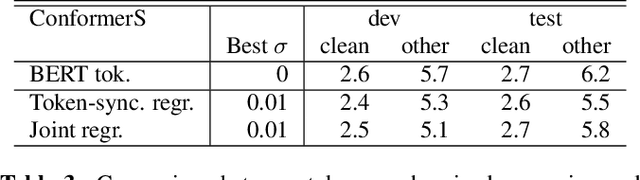
Abstract:End-to-end speech recognition is a promising technology for enabling compact automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems since it can unify the acoustic and language model into a single neural network. However, as a drawback, training of end-to-end speech recognizers always requires transcribed utterances. Since end-to-end models are also known to be severely data hungry, this constraint is crucial especially because obtaining transcribed utterances is costly and can possibly be impractical or impossible. This paper proposes a method for alleviating this issue by transferring knowledge from a language model neural network that can be pretrained with text-only data. Specifically, this paper attempts to transfer semantic knowledge acquired in embedding vectors of large-scale language models. Since embedding vectors can be assumed as implicit representations of linguistic information such as part-of-speech, intent, and so on, those are also expected to be useful modeling cues for ASR decoders. This paper extends two types of ASR decoders, attention-based decoders and neural transducers, by modifying training loss functions to include embedding prediction terms. The proposed systems were shown to be effective for error rate reduction without incurring extra computational costs in the decoding phase.
A Comparative Study on Neural Architectures and Training Methods for Japanese Speech Recognition
Jun 09, 2021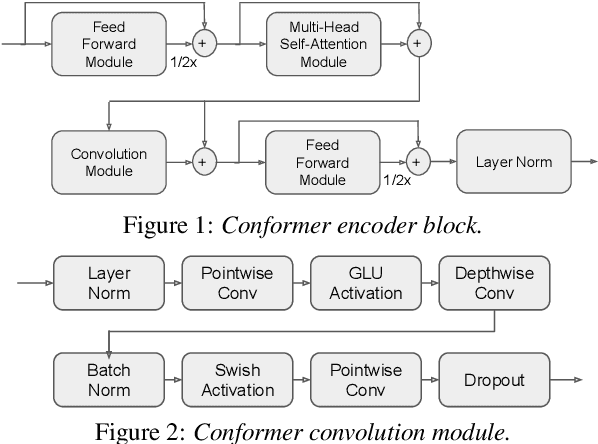
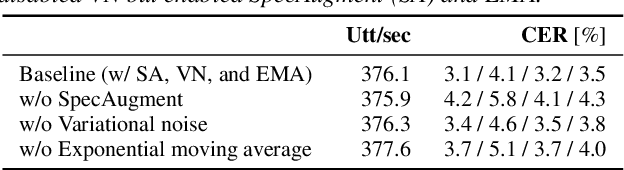
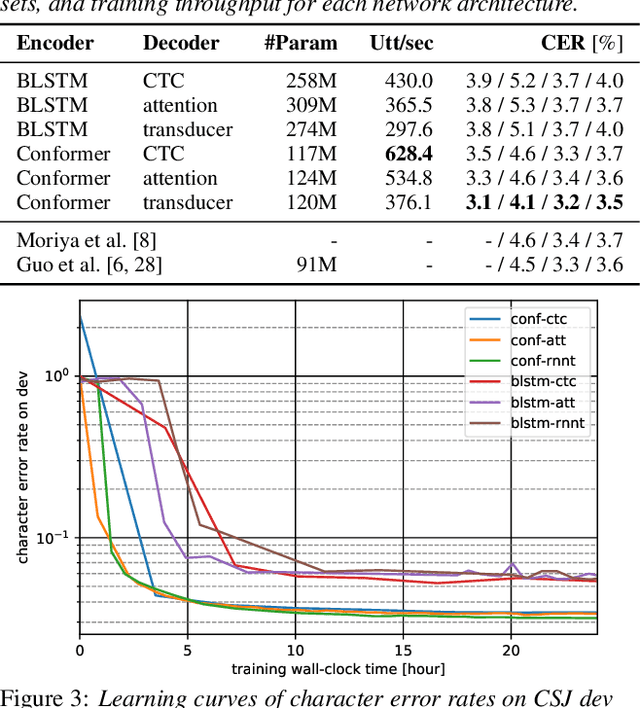
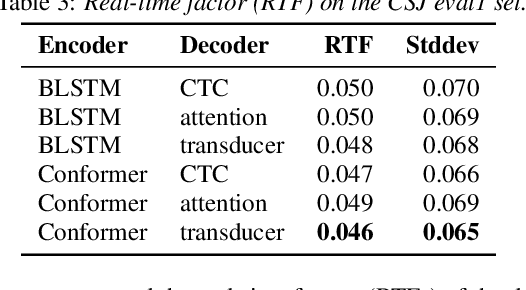
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) modeling is advantageous for automatic speech recognition (ASR) especially for Japanese since word-based tokenization of Japanese is not trivial, and E2E modeling is able to model character sequences directly. This paper focuses on the latest E2E modeling techniques, and investigates their performances on character-based Japanese ASR by conducting comparative experiments. The results are analyzed and discussed in order to understand the relative advantages of long short-term memory (LSTM), and Conformer models in combination with connectionist temporal classification, transducer, and attention-based loss functions. Furthermore, the paper investigates on effectivity of the recent training techniques such as data augmentation (SpecAugment), variational noise injection, and exponential moving average. The best configuration found in the paper achieved the state-of-the-art character error rates of 4.1%, 3.2%, and 3.5% for Corpus of Spontaneous Japanese (CSJ) eval1, eval2, and eval3 tasks, respectively. The system is also shown to be computationally efficient thanks to the efficiency of Conformer transducers.
Compacting Neural Network Classifiers via Dropout Training
May 24, 2017
Abstract:We introduce dropout compaction, a novel method for training feed-forward neural networks which realizes the performance gains of training a large model with dropout regularization, yet extracts a compact neural network for run-time efficiency. In the proposed method, we introduce a sparsity-inducing prior on the per unit dropout retention probability so that the optimizer can effectively prune hidden units during training. By changing the prior hyperparameters, we can control the size of the resulting network. We performed a systematic comparison of dropout compaction and competing methods on several real-world speech recognition tasks and found that dropout compaction achieved comparable accuracy with fewer than 50% of the hidden units, translating to a 2.5x speedup in run-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge