Yoshiharu Ikutani
Towards Generation of Visual Attention Map for Source Code
Aug 13, 2019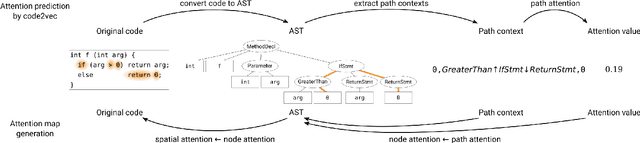


Abstract:Program comprehension is a dominant process in software development and maintenance. Experts are considered to comprehend the source code efficiently by directing their gaze, or attention, to important components in it. However, reflecting the importance of components is still a remaining issue in gaze behavior analysis for source code comprehension. Here we show a conceptual framework to compare the quantified importance of source code components with the gaze behavior of programmers. We use "attention" in attention models (e.g., code2vec) as the importance indices for source code components and evaluate programmers' gaze locations based on the quantified importance. In this report, we introduce the idea of our gaze behavior analysis using the attention map, and the results of a preliminary experiment.
Toward Imitating Visual Attention of Experts in Software Development Tasks
Mar 15, 2019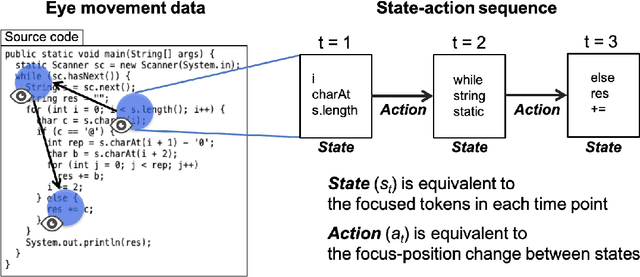
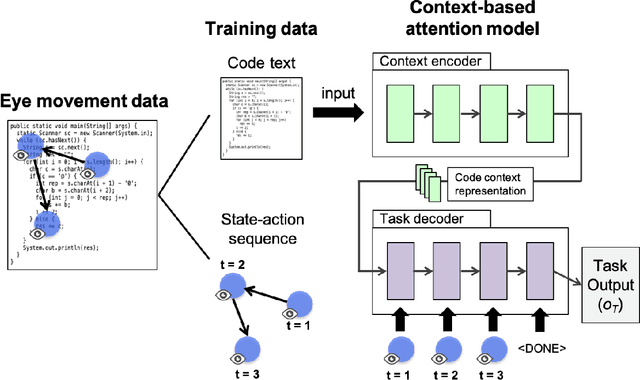
Abstract:Expert programmers' eye-movements during source code reading are valuable sources that are considered to be associated with their domain expertise. We advocate a vision of new intelligent systems incorporating expertise of experts for software development tasks, such as issue localization, comment generation, and code generation. We present a conceptual framework of neural autonomous agents based on imitation learning (IL), which enables agents to mimic the visual attention of an expert via his/her eye movement. In this framework, an autonomous agent is constructed as a context-based attention model that consists of encoder/decoder network and trained with state-action sequences generated by an experts' demonstration. Challenges to implement an IL-based autonomous agent specialized for software development task are discussed in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge