Yoshiaki Kisaka
Optical Link Tomography: First Field Trial and 4D Extension
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Optical link tomography (OLT) is a rapidly evolving field that allows the multi-span, end-to-end visualization of optical power along fiber links in multiple dimensions from network endpoints, solely by processing signals received at coherent receivers. This paper has two objectives: (1) to report the first field trial of OLT, using a commercial transponder under standard DWDM transmission, and (2) to extend its capability to visualize across 4D (distance, time, frequency, and polarization), allowing for locating and measuring multiple QoT degradation causes, including time-varying power anomalies, spectral anomalies, and excessive polarization dependent loss. We also address a critical aspect of OLT, i.e., its need for high fiber launch power, by improving power profile signal-to-noise ratio through averaging across all available dimensions. Consequently, multiple loss anomalies in a field-deployed link are observed even at launch power lower than the system-optimal level. The applications and use cases of OLT from network commissioning to provisioning and operation for current and near-term network scenarios are also discussed.
* 12 pages, 7 figures, accepted version for Journal of Lightwave Technology
Linear Least Squares Estimation of Fiber-Longitudinal Optical Power Profile
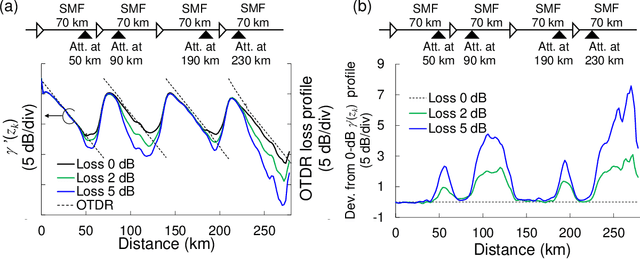
Oct 07, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a linear least squares method for fiber-longitudinal power profile estimation (PPE), which estimates an optical signal power distribution throughout a fiber-optic link at a coherent receiver. The method finds the global optimum in least square estimation of longitudinal power profiles, thus closely matching true optical power profiles and locating loss anomalies in a link with high spatial resolution. Experimental results show that the method achieves accurate PPE with an RMS error from OTDR of 0.18 dB. Consequently, it successfully identifies a loss anomaly as small as 0.77 dB, demonstrating the potential of a coherent receiver in locating even splice and connector losses. The method is also evaluated under a WDM condition with optimal system fiber launch power, highlighting its feasibility for use in operations. Furthermore, a fundamental limit for stable estimation and spatial resolution of least-squares-based PPE is quantitatively discussed in relation to the ill-posedness of PPE by evaluating the condition number of a nonlinear perturbation matrix.
Performance limit of Fiber-Longitudinal Power Profile Estimation Methods
Nov 15, 2022Abstract:This paper presents analytical results on power profile estimation (PPE) methods, which visualize a signal power evolution in the fiber-longitudinal direction at a coherent receiver. Two types of PPE methods are reviewed and analyzed, including correlation-based methods (CMs) and minimum-mean-square-error-based methods (MMSEs). The analytical expressions for their output power profiles and spatial resolution are provided, and thus the theoretical performance limits of the two PPE methods and their differences are clarified. The derived equations indicate that the estimated power profiles of CMs can be understood as the convolution of a true power profile and a smoothing function. Thus, the spatial resolution and measurement accuracy of CMs are limited, even under noiseless and distortionless conditions. Based on this fact, closed-form formulas for the spatial resolution of CMs are presented. On the other hand, in MMSEs, such a convolution effect is canceled out and thus the estimated power profiles approach a true power profile under a fine spatial step size.
A Transponder Aggregator with Efficient Use of Filtering Function for Transponder Noise Suppression
Oct 03, 2022



Abstract:Colorless, directionless, and contentionless reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexing (CDC-ROADM) provides highly flexible physical layer network configuration. Such CDC-ROADM must operate in multiple wavelength bands which are being increasingly implemented in optical transmission systems. The operation in C+L bands requires switch devices used in CDC-ROADM to also be capable of multiband operation. Recent studies on wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) systems have pointed out the impact of amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) noise generated by signals of different wavelengths, which causes OSNR degradation. Therefore, it is desirable to filter out the ASE noise from different transponders when multiplexing multiple wavelengths at the transmitter side, especially in a system with non-wavelength selective combiners such as directional couplers and multicast switches. The use of transponder aggregators with filtering functions, such as the M x N wavelength selective switch (WSS), is preferable for this filtering. However, the downside of these devices is that it is difficult to provide economical multiband support. Therefore, we propose an economical transponder aggregator configuration by allowing a certain amount of ASE superposition and reducing the number of filtering functions. In this paper, we fabricated a prototype of the proposed transponder aggregator by combining silica-based planar lightwave circuit technology and C+L band WSS, both commercially available, and verified its feasibility through transmission experiments. The novel transponder aggregator is a practical solution for a multiband CDC-ROADM system with improved OSNR performance.
First demonstration of C + L band CDCROADM with simple node configuration using multiband switching devices
Jun 04, 2021



Abstract:While ultrahigh-baud-rate optical signals are effective for extending the transmission distance of large capacity signals, they also reduce the number of wavelengths that can be arranged in a band because of their wider bandwidth. This reduces the flexibility of optical path configuration in reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexing (ROADM) networks. In colorless, directionless and contentionless (CDC)-ROADM in particular, the effect reduces the add/drop ratio at a node. Multiband ROADM systems are an effective countermeasure for overcoming this issue, but they make the node configuration more complicated and its operation more difficult. In this paper, we analyze the challenges of C + L band CDC-ROADM and show that optical switch devices that operate over multiple bands are effective in meeting them. For this purpose, we built a C + L band CDC-ROADM node based on C + L band wavelength selective switches (WSSs) and multicast switches (MCSs) and confirmed its effectiveness experimentally. In particular, to simplify the node configuration, we propose a reduction in the number of optical amplifiers used for node loss compensation and experimentally verify its feasibility.
Physics-oriented learning of nonlinear Schrödinger equation: optical fiber loss and dispersion profile identification
Apr 13, 2021


Abstract:In optical fiber communication, system identification (SI) for the nonlinear Schr\"odinger equation (NLSE) has long been studied mainly for fiber nonlinearity compensation (NLC). One recent line of inquiry to combine a behavioral-model approach like digital backpropagation (DBP) and a data-driven approach like neural network (NN). These works are aimed for more NLC gain; however, by directing our attention to the learned parameters in such a SI process, system status information, i.e., optical fiber parameters, will possibly be extracted. Here, we show that the model-based optimization and interpretable nature of the learned parameters in NN-based DBP enable transmission line monitoring, fully extracting the actual in-line NLSE parameter distributions. Specifically, we demonstrate that longitudinal loss and dispersion profiles along a multi-span link can be obtained at once, directly from data-carrying signals without any dedicated analog devices such as optical time-domain reflectometry. We apply the method to a long-haul (~2,080 km) link and various link conditions are tested, including excess loss inserted, different fiber input power, and non-uniform level diagram. The measurement performance is also investigated in terms of measurement range, accuracy, and fiber launch power. These results provide a path toward simplified and automated network management as another application of DBP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge